Context:
More about the news:
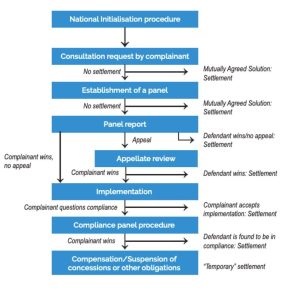
World Trade Organization (WTO):
Dispute Settlement Mechanism under WTO
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
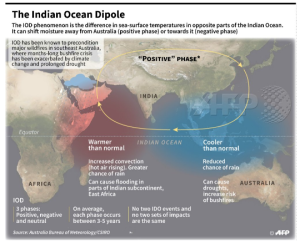
About Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD):
About IOD index:
| Positive IOD | Negative IOD |
|
|
News Source: Hindu BL
Context:
Social Welfare Spending
Context:
Social Welfare Spending
Context:
Educational Background of MPs in Lok Sabha:
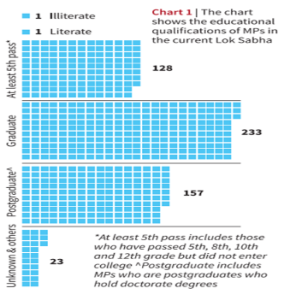 Information about the educational qualifications of 4% of the MPs is not available.
Information about the educational qualifications of 4% of the MPs is not available.17th Lok Sabha and MPs with Criminal Charges:
Context:
More about the news:
Important Highlight of NCF-SE:
Source: Indian Express
Context:
Special Provisions for the North-Eastern states in India:
| Article | Special Provision with respect to: |
| Article 371A | Nagaland (13th Amendment Act, 1962) |
| Article 371B | Assam (22nd Amendment Act, 1969) |
| Article 371C | Manipur (27th Amendment Act, 1971) |
| Article 371F | Sikkim (36th Amendment Act, 1975) |
| Article 371 G | Mizoram (53rd Amendment Act, 1986) |
| Article 371 H | Arunachal Pradesh (55th Amendment Act, 1986) |
Need of special status for North-Eastern states:
Difference between Article 370 and 371:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Government agencies and policymakers are using AI tools to analyze patterns, forecast scenarios, and offer informed recommendations. Yet, AI adoption in decision-making has potential downsides.
More on News:
| What are prompts in Generative AI?
Prompts in generative AI refer to the input or instructions provided to the AI model to generate specific output. Generative AI: Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) model that can be used to generate new text, images, video, audio, code, or synthetic data. |
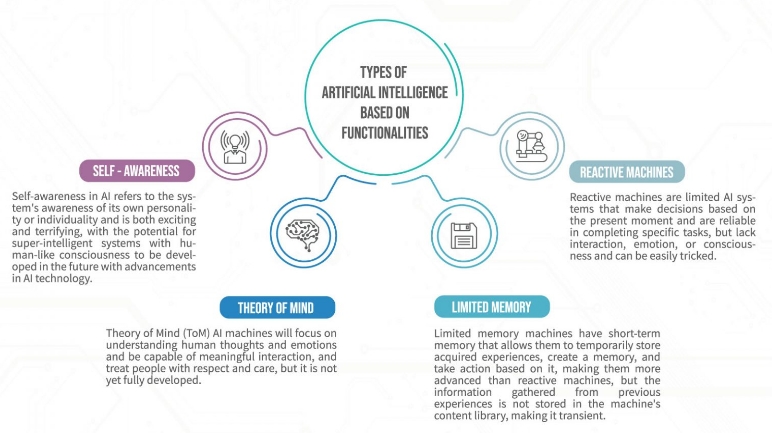
About Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Types of Artificial Intelligence
India’s Initiatives for Developing AI:
|
Benefits of AI:
Ethical Issues associated with Artificial Intelligence:
Way Forward:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Recently, ISRO’s (Indian Space Research Organisation) Chandrayaan 3 lander has successfully made a soft landing on the lunar surface.
More on News:
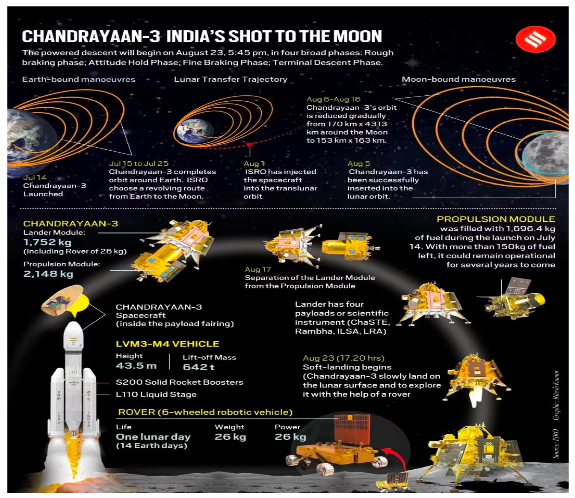
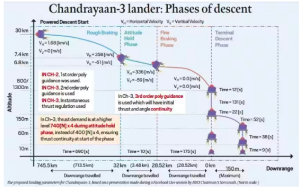
From Lunar Orbit to the Lunar Surface:
Deboosting:
Mission Experiment: Chandrayaan 3:
ISRO’s Space Journey: Satellites, Launch Vehicles, and Planetary Exploration
About ISRO
|
ISRO’s Future Mission:
Why water on the Moon is important?
|
What should be India’s Next Step Following the Success of Chandrayaan 3?
| NOTE- For more details on Chandrayaan 3, please refer to the July edition of Current Affairs Magazine. |
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
Recently, the United Nations’ International Labour Organization (ILO) released a report on the impact of Generative AI and other platforms on jobs quantity and quality.
Findings of Report:
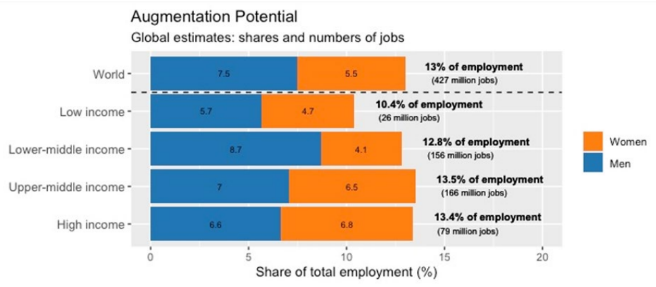
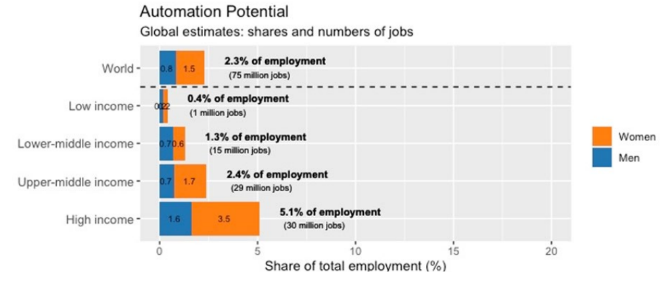
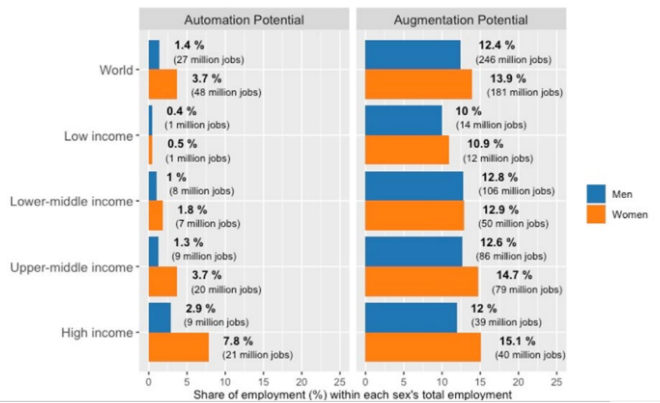
About Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI):
| Pros of Generative AI: | Cons of Generative AI: |
|
|
Report Recommendations:
International Labour Organization (ILO)
(For more information about Large language Model, kindly refer to PWONLYIAS July Current Affairs Magazine) |
News Source: Economic Times
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
