| India’s First Carbon Negative Garrison
|
|
| Mera Bill Mera Adhikaar Initiative by Ministry of Finance
|
|
| Yevgeny Viktorovich Prigozhin
|
|
India’s Net-Zero Transition Offers $12.7 Trillion Investment Opportunity
Context:
According to India’s New Energy Outlook report by BloombergNEF, India’s path towards a net-zero economy by 2050 presents an investment opportunity estimated at $12.7 trillion.
Changes in Energy Mix
Investment Opportunities
Context:
Commercial ships are facing delays to travel through the Panama Canal as a lengthy drought in the Central American country has led to lower the availability of water.
Reasons for Delays in Panama Canal:
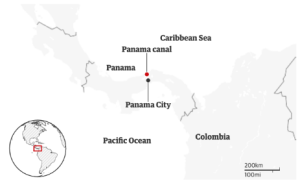 Capacity Restrictions: The Panama Canal Authority (ACP) has imposed restrictions on the number of vessels that can transit daily to and average of 32 from 36 and limited the maximum depth of ships allowed to navigate the canal.
Capacity Restrictions: The Panama Canal Authority (ACP) has imposed restrictions on the number of vessels that can transit daily to and average of 32 from 36 and limited the maximum depth of ships allowed to navigate the canal.About Panama Canal:
|
News Source: The Guardian
Context:
Recently, the Finance Minister launched HSBC India’s Green Hydrogen Partnerships.
Types of hydrogen based on extraction method:
Strategic Partnerships for Green Hydrogen Innovation:
News Source: Livemint
Context:
A study by the Indian Council of Medical Research published recently said that nearly 6.5% people hospitalized with Covid-19 died in the following year.
Key Findings of the Study on Post-Covid-19 Outcomes:
Higher Risk of Mortality Factors:
About ICMR:
|
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
Murmansk, often referred to as the capital of the Arctic region and the starting point of the Northern Sea Route (NSR), is currently experiencing a notable increase in Indian participation in cargo transportation.
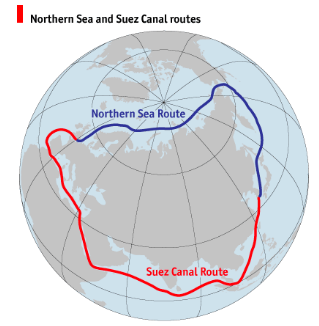
What is NSR?
NSR Development:
Factor for India’s participation in the development of the NSR:
About Arctic Region:
Significance of Arctic Region for India:
India’s Arctic Policy Six Pillars:
India’s engagement with the Arctic:
|
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
According to the National Medical Commission’s Registered Medical Practitioner (Professional Conduct) Regulations or NMC RMP Regulations 2023, doctors can now refuse treatment to the unruly and violent patients.
About The National Medical Commission Act, 2019:

Refusing treatment is a complex issue that involves various stakeholders viz. doctors and healthcare professionals, patients and their families, healthcare institutions, medical associations and regulatory bodies, legal authorities, ethics committees, public opinion and media, religious and cultural communities, etc.
Arguments in Favour of the Regulation:
Arguments against the Regulation
|
The Hippocratic Oath
|
|---|
What Should be Done?
Initiatives towards protection:
|
Conclusion
We must protect those who heal. Ethical decisions in healthcare are rarely black and white. It’s important to approach each situation with sensitivity, professionalism, and a commitment to upholding the well-being of patients, healthcare staff, and the broader community. Consulting with colleagues, supervisors, and ethics committees can provide valuable guidance in making these difficult decisions.
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Recently, during the 15th BRICS Summit, leaders decided to expand the grouping and admit six new members.
More on News
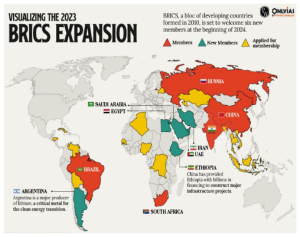 Johannesburg Declaration II: It emphasizes inclusive multilateralism, peaceful development, sustainable growth, and people-to-people exchanges, while addressing global conflicts and promoting constructive dialogue and partnership for growth.
Johannesburg Declaration II: It emphasizes inclusive multilateralism, peaceful development, sustainable growth, and people-to-people exchanges, while addressing global conflicts and promoting constructive dialogue and partnership for growth.About BRICS
Need of Expansion:
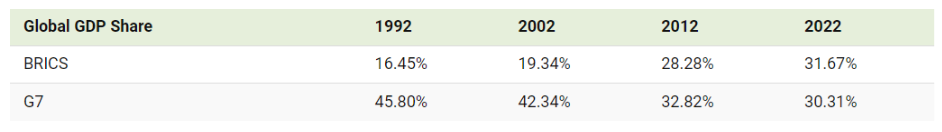
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP):
|
India’s Interest in Expansion of BRICS
Interest of Member Nation in Expansion:
Interest of New Members in Joining BRICS:
|
Possible Concerns in BRICS:
New Development Bank (NDB)
|
Other Area of Cooperation:
|
Way Forward
Conclusion
News Source: Indian Express
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
