Context: The Union Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry named Indore the best city and Madhya Pradesh the best state in the Smart Cities Mission in its India Smart Cities Awards 2022.
About Smart Cities Mission:
Smart Cities Award 2022:
News Source: The Indian Express
Global Environment Facility (GEF).
About Global Biodiversity Framework Fund (GBFF): It is created for implementation of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF)
Methodology
|
News Source: DTE
Context:The State of India’s Birds 2023, based on 30 million observations contributed by 30,000 birdwatchers across the country, was released on 25 August, 2023.
Key Findings:
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
Recently, the Indian Prime Minister presented Indian artworks and traditional items as a gift to world leaders.
| Art Form | Details |
| Bidri work pair of Surahi to South African President |
|
| Nagaland Shawl to first lady of South Africa |
|
| Gond Painting to Brazilian President |
|
| Dokra Artwork to The prime minister of Greece. |
|
| Meghalaya shawl to the spouse of the prime minister of Greece. |
|
News Source: Indian Express
| News | Details |
| BA.2.86 |
About BA.2.86
|
| China-Bhutan Boundary Talks |
Highlight
|
| Shiv Shakti Point |
|
| NMC Guideline for Generic Drugs on Hold |
For more about the News, kindly refer to the 25 August Article. |
Context: In the first Prime Ministerial visit to Greece after 40 years, India and Greece have decided to elevate bilateral ties to strategic partnership.Major Decisions:
 The discussions covered digital payments, shipping, pharma, tourism, culture, education and people to people ties.
The discussions covered digital payments, shipping, pharma, tourism, culture, education and people to people ties.News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
A 28-feet Nataraja statue meant to be placed in front of the venue of the G20 Leaders’ Summit scheduled in New Delhi.
About 28-Feet Nataraja Sculpture:

Nataraja Sculpture: Meaning of Postures and Poses
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
More about the news:
|
About Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO):
Formation:
Contribution:
|
Terms reference of the committee:
 Leveraging Expertise: The strategy incorporates leveraging the expertise of NRIs and foreign consultants, along with fostering international collaborations to drive the development of cutting-edge and disruptive defense technologies.
Leveraging Expertise: The strategy incorporates leveraging the expertise of NRIs and foreign consultants, along with fostering international collaborations to drive the development of cutting-edge and disruptive defense technologies. Challenges with the functioning of DRDO:
Other defence manufacturing organizations in India:
|
Way Forward:
 Synergy between DRDO and armed forces: The complete endorsement of DRDO by the armed forces is very crucial. They must provide clear direction and a well-defined vision regarding their requirements from DRDO.
Synergy between DRDO and armed forces: The complete endorsement of DRDO by the armed forces is very crucial. They must provide clear direction and a well-defined vision regarding their requirements from DRDO.News Source: Hindustan Times
Context:
According to a report by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Indian Council for Research on International Economic Relations (ICRIER), India’s ultra-processed food sector witnessed a compound annual growth rate of 13.37% in retail sales value from 2011 to 2021.
More on News:
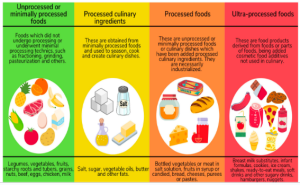
About Ultra-Processed Food Sector in India:
Key Findings of the Report:
What is Obesity?
|
Towards a Unified National Nutrition Policy: Addressing Under and Over-Nutrition
Malnutrition In India:
Child Malnutrition in India:
|
Causes of Malnutrition:
| Data related to Anaemia: The NFHS-5 survey indicates that more than 57% of women (15-49 years) and over 67% children (six-59 months) suffer from anaemia. |
Government Initiatives to address Malnutrition:
|
Way Forward:
News Source: DTE
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
