Context:
The 18th G20 Summit successfully concluded in New Delhi with India handing over the Presidency to Brazil.
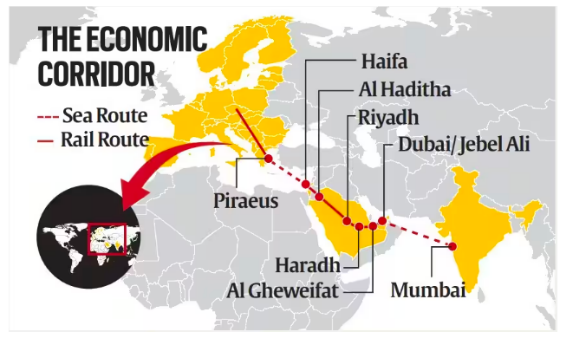
More on News:
Key Deliverables Under India’s G20 Presidency:
|
About African Union (AU):
|
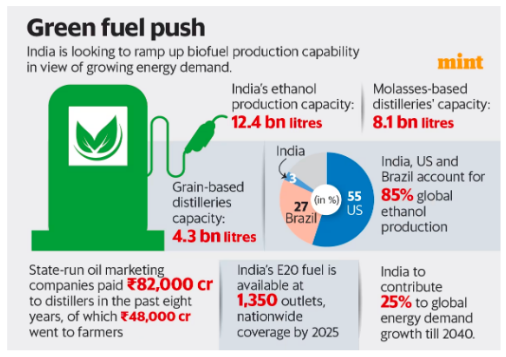 India, Singapore, Bangladesh, Italy, USA, Brazil, Argentina, Mauritius and UAE, launched the Global Biofuel Alliance.
India, Singapore, Bangladesh, Italy, USA, Brazil, Argentina, Mauritius and UAE, launched the Global Biofuel Alliance.MSME Sector in India:
|
 Gandhinagar Implementation Roadmap (GIR) & Gandhinagar Information Platform (GIP) for Priority Landscapes:
Gandhinagar Implementation Roadmap (GIR) & Gandhinagar Information Platform (GIP) for Priority Landscapes:
Conclusion:
News Source: The Indian Express
Context:
More about the news:
National Pension System (NPS) vs Old Pension System (OPS):
|
Freebies:
Welfare Measures:
Difference between freebies and welfare measures:
| Welfare Measures | Freebies |
|
|
| Example: Public distribution system, State support for education and health | Example: Distribution of laptops, two-wheelers, etc. |
Concerns associated with excessive use of freebies:
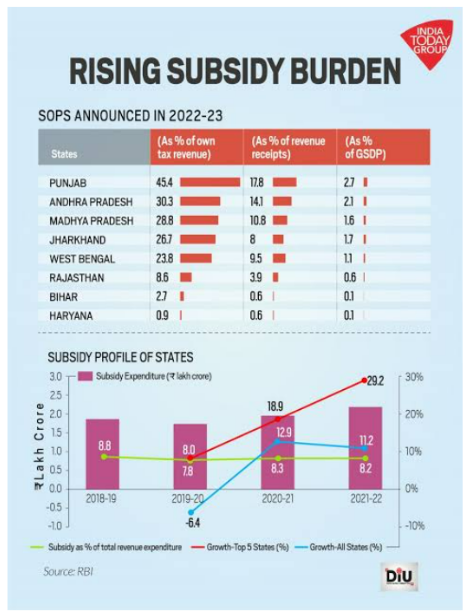 State Finance: A Risk Analysis’, a report released by the RBI in June 2022, stated that the slowdown in state revenues and increasing subsidy burden have added to the state government’s debt.
State Finance: A Risk Analysis’, a report released by the RBI in June 2022, stated that the slowdown in state revenues and increasing subsidy burden have added to the state government’s debt. Role of ECI:
|
Challenges in curtailing Freebie Culture:
Supreme Court response on Freebies:
S. Subramaniam Balaji vs Tamil Nadu judgment of 2013.
|
Way Forward:
 Model Manifesto: The ECI needs to prepare a Model Manifesto to be followed by all political parties.
Model Manifesto: The ECI needs to prepare a Model Manifesto to be followed by all political parties.
News Source: Business Standard
Context:
Recently genetic manipulation of mosquitoes is discussed which will lead to control of their populations by interfering with their reproduction.
More About News:
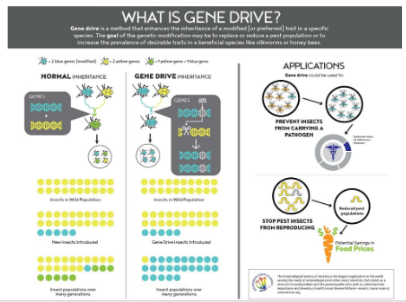
About Gene Drive Technology:
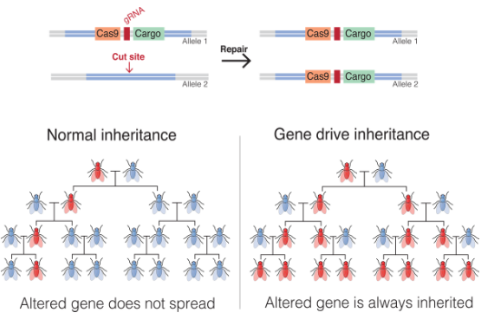
How Does It Work?
Source: The Hindu
| About Pink Bollworm(PBW):
PBW is a monophagous pest that feeds mainly on cotton. |
Context: The pink bollworm (PWB) has taken a toll on the fiber crop (cotton), even as new “mating disruption” technologies to control the pest are showing promise.
About Mating Disruptions Technology:
Distribution and Cotton Production In India:
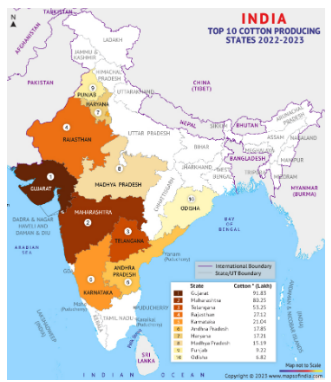
| About Bt Cotton
Genetically-modified (GM) crops. It is produced by incorporating genes isolated from a soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt). The Bt genes coded for proteins toxic to the deadly Helicoverpa armigera or American bollworm insect pest |
The Bt revolution: Between 2000-01 and 2013-14, India’s cotton production, in terms of lint, almost tripled from 140 lakh to 398 lakh bales (170 kg).
Source: The Indian Express
Context:
Crude oil prices, which have been firming up for the past few weeks on expectations of high demand and tightening supply, are at a nearly 10-month high.
More on News:
| About OPEC
OPEC is a permanent intergovernmental organization of 13 oil-exporting developing nations, founded in 1960. |
Reasons For High Oil Prices
Impact Of HIgh Oil Prices
| About OPEC+
OPEC+ is a larger group of major oil producing nations and includes members of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), along with Russia and a few other producers. OPEC+ produces around 40 percent of the world’s crude oil, with Saudi Arabia as the top producer and Russia in the second spot. |
Way Ahead: In short term, diversification from OPEC+ Countries (to Iran or Venezuela), whereas in Long term focus should be Renewable energy which enables transition to Green Economy.
Source: The Indian Express
Housewives make up over 50% of India’s female suicides
Context:
World Suicide Prevention Day (WSPD), celebrated annually on 10 September, is organized by the International Association for Suicide Prevention (IASP) and endorsed by the World Health Organization (WHO).
More on News:
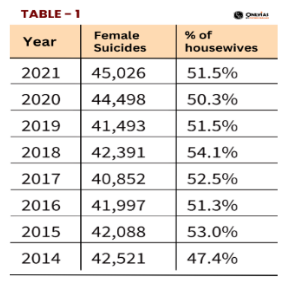
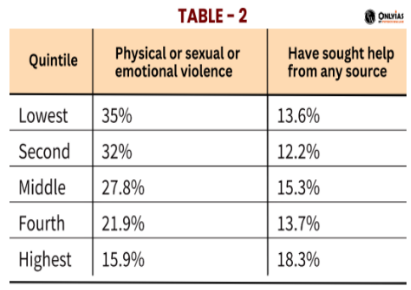
Morocco
Context:
A powerful earthquake of magnitude 6.8 struck Morocco’s High Atlas mountains leading to the death of over 2,000 people.
More on News:
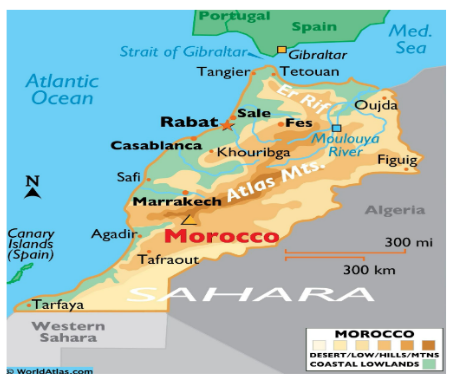
About Morocco:
| Storm-0558 |
|
| India’s External Debt |
|
| Drugs Controller General of India (DCGI) |
|
| UPI Lite X |
|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
