About Bima Sugam:
Key Features:
Benefits:
|
Evolution of the Insurance industry:
|
An insurance is a legal agreement between an insurer (insurance company) and an insured (individual), in which an insured receives financial protection from an insurer for the losses he may suffer under specific circumstances.
News Source: The Indian Express
PM Fasal Bima Yojana
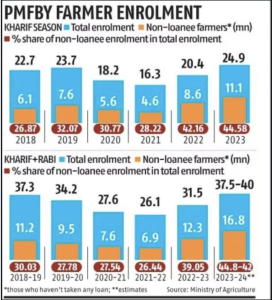
In the recently concluded Kharif season, the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) saw a surge in farmer enrollment, reaching 25 million farmers.
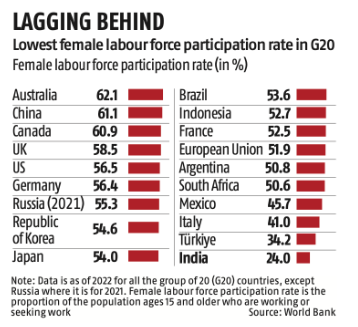
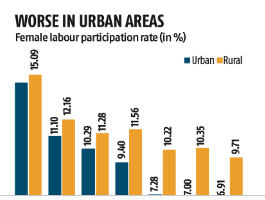
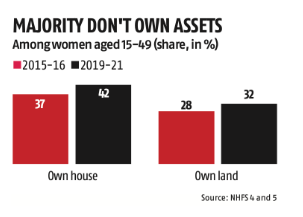
The government has introduced the Narishakti Vandan Adhiniyam to provide 33% reservation for women in the Lok Sabha and state assemblies.
| Kisan Rin Portal and WINDS Manual | Recently, the Finance Minister launched the Kisan Rin portal along with the WINDS manual.
About Weather Information Network Data Systems (WINDS) Manual:
Kisan Rin Portal:
|
| Samvidhan Sadan |
|
| WhatsApp Channel | Meta has rolled out WhatsApp Channels in India.
About:
|
Subject: GS-3 Environment
Source: The Hindu
| Khalsa is referred to as the community that practices Sikhism as a faith and a special group of initiated Sikhs. The Khalsa tradition was introduced in 1699 by Guru Gobind Singh, the 10th Guru, after his father Guru Tegh Bahadur, was beheaded in the reign of Aurangzeb. |
A brief history of Khalistan movement:
|
Separatist Groups of khalistan:
|
News Source: Indian Express
Subject: GS-3 Environment

The Addis Ababa action Agenda:
|
Subject: GS-1 – India and World Geography
Source: DTE
Subject: GS 03: S & T
| Awards | Fields |
| Vigyan Ratna | It will recognize the lifetime achievements of scientists. |
| Vigyan Shri | It will recognize distinguished contributions to a field. |
| Vigyan Yuva Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar | It will encourage young scientists who have made exceptional contributions in their field. |
| Vigyan Team | It will recognize teams of three or more. |
National Space Day:
National Technology Day:
|
Source: The Hindu
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
