Context:
Recently, the Prime Minister attended the 20th ASEAN-India Summit and the 18th East Asia Summit (EAS) in Jakarta, Indonesia.
More on News:
Highlights of 20th ASEAN-India Summit:
Association of Southeast Asian Nations(ASEAN):
ASEAN operates through three main pillars:
|
Prime Minister of India presented a 12-point proposal to bolster India-ASEAN cooperation:
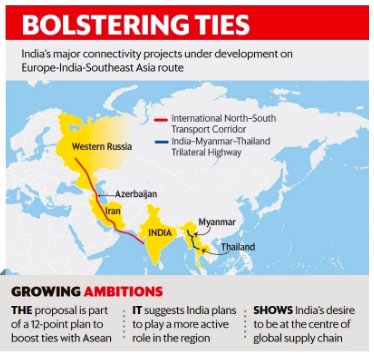 Digital Transformation: Offering to share India’s Digital Public Infrastructure Stack with ASEAN partners to facilitate digital transformation.
Digital Transformation: Offering to share India’s Digital Public Infrastructure Stack with ASEAN partners to facilitate digital transformation.Highlights of 18th East-Asia Summit:
East Asia Summit (EAS):
|
India’s Relationship with ASEAN:
 This forum provides a platform for dialogue, cooperation, and collaboration on various regional and global issues.
This forum provides a platform for dialogue, cooperation, and collaboration on various regional and global issues.Challenges in India-ASEAN Relations:
Way Forward:
News Source: The Economic Times
Context:
Highlights from the Report:
What is a heatwave?
Criterion for declaring heat wave in India:
Threats Posed by Extreme Heat:
Heat Index in India:
|
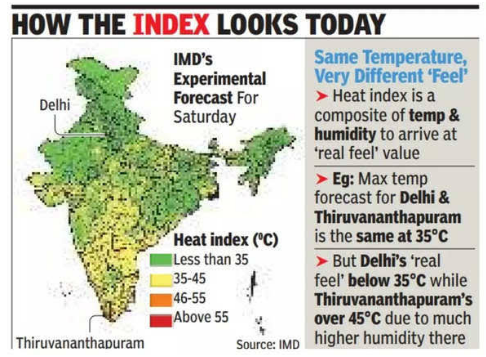
Way Forward:
 Reducing the urban heat island effect: It includes installing cool and green roofs, cool pavement, planting trees to provide shade, and cooling the air through evapotranspiration.
Reducing the urban heat island effect: It includes installing cool and green roofs, cool pavement, planting trees to provide shade, and cooling the air through evapotranspiration.News Source: DTE
Context:
RBI introduced guidelines enabling a borrower to transition from a floating interest rate-based loan to one with a fixed interest rate.
More on News:
Differences between the two exchange rates systems:
| Basis | Fixed Interest Rate | Floating (Variable) Interest Rate
|
| Meaning | Fixed Interest Rates remain constant throughout the life of the loan. | Rates can change periodically, usually in accordance with a benchmark rate, market conditions, or the lender’s discretion. |
| Initial Rates | Typically start higher than initial rates for floating rate loans since lenders charge a premium for the certainty of fixed payments. | Often start with lower initial interest rates than fixed-rate. |
| Advantages | Benefit from protection against interest rate increases regardless of fluctuations in market interest rates. | Borrowers may benefit from potential rate decreases. |
Significant Impacts of Lending Guidelines:
News Source: The Hindu
Context: In the run-up to the G20 Summit, a day-long conference on Transnational Grid Interconnections for One Sun, One World, One Grid (OSOWOG) was held in New Delhi.
More on News:
About OSOWOG or the Green Grid
News Source: PIB
Context:
Recently, the regional commissioner of Mysore was directed to clear illegal constructions in the Bandipur Eco Sensitive Zone (ESZ) as they were in violation of the law.
About Eco-Sensitive Zones
Bandipur Tiger Reserve:
News Source: The Hindu
Context: Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor has asked fintech entities to form a Self-Regulatory Organisation (SRO).
More About News:
About Self Regulatory Organisations:
Functions of an SRO:
News Source: Indian Express
| Key Agri initiatives under India’s G20 Presidency |
|
| Poila Baisakh |
|
| Siang River Barrage |
|
| Eastern Economic Forum |
|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
