News Source: The Hindu
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
Financial Stability Board (FSB)
|
|---|
What is crypto currency and how does it work?
|
|---|
G20 Roadmap on Crypto Assets: It is an action-oriented roadmap that will help coordinate global policy as well as develop mitigating strategies and regulations on such assets.
News Source: The Indian Express
| Attempt the Prelims Question
The terms ‘WannaCry, Petya and EternalBlue’ sometimes mentioned in the news recently are related to; (2018) (a) Exoplanets (b) Cryptocurrency (c) Cyber attacks (d) Mini satellites Ans: (b) |
|---|
Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC): It is a high speed and high capacity railway corridor that is exclusively meant for the transportation of freight, or in other words, goods and commodities.
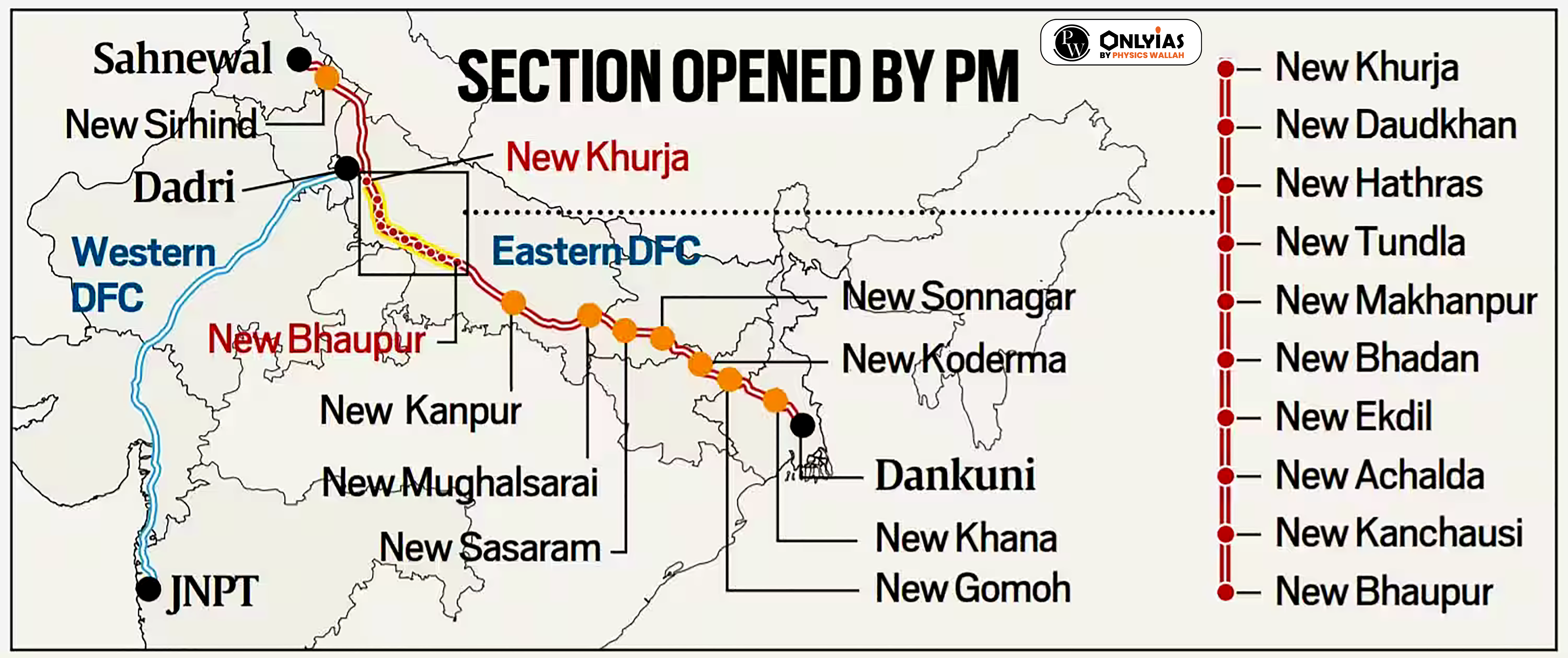

| Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Ltd. (DFCCIL): It is a Special Purpose Vehicle for construction, maintenance and operation of the dedicated freight corridor under the Ministry of Railway.. |
|---|
News Source: The Economic Times
| Attempt the Mains Question: Bring out the socio-economic effects of the introduction of railways in different countries of the world. |
|---|
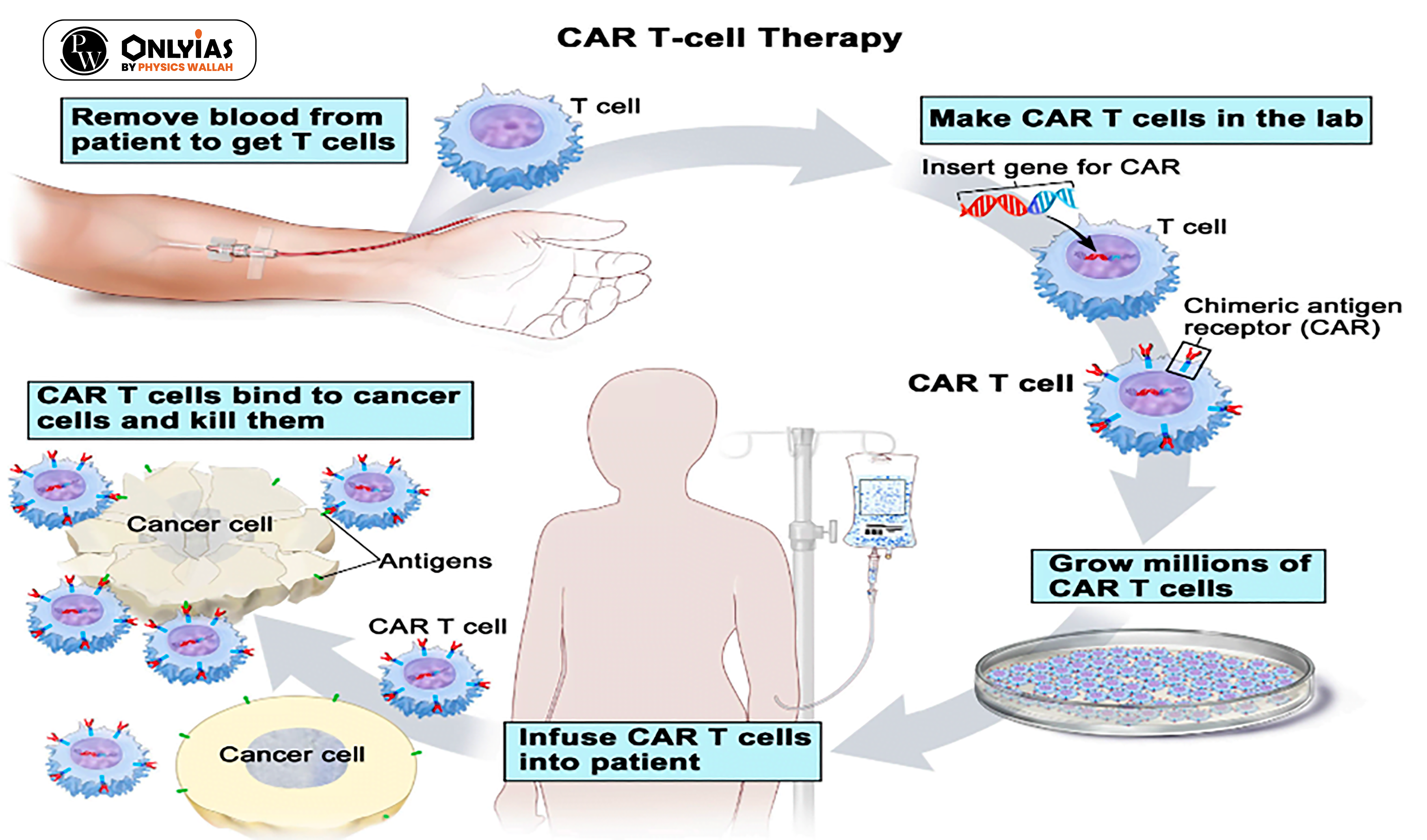
News Source: DTE
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
Consider the following statements: (2020) 1. Genetic changes can be introduced in the cells that produce eggs or sperms of a prospective parent. 2. A person’s genome can be edited before birth at the early embryonic stage. 3. Human induced pluripotent stem cells can be injected into the embryo of a pig. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 2 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
|---|
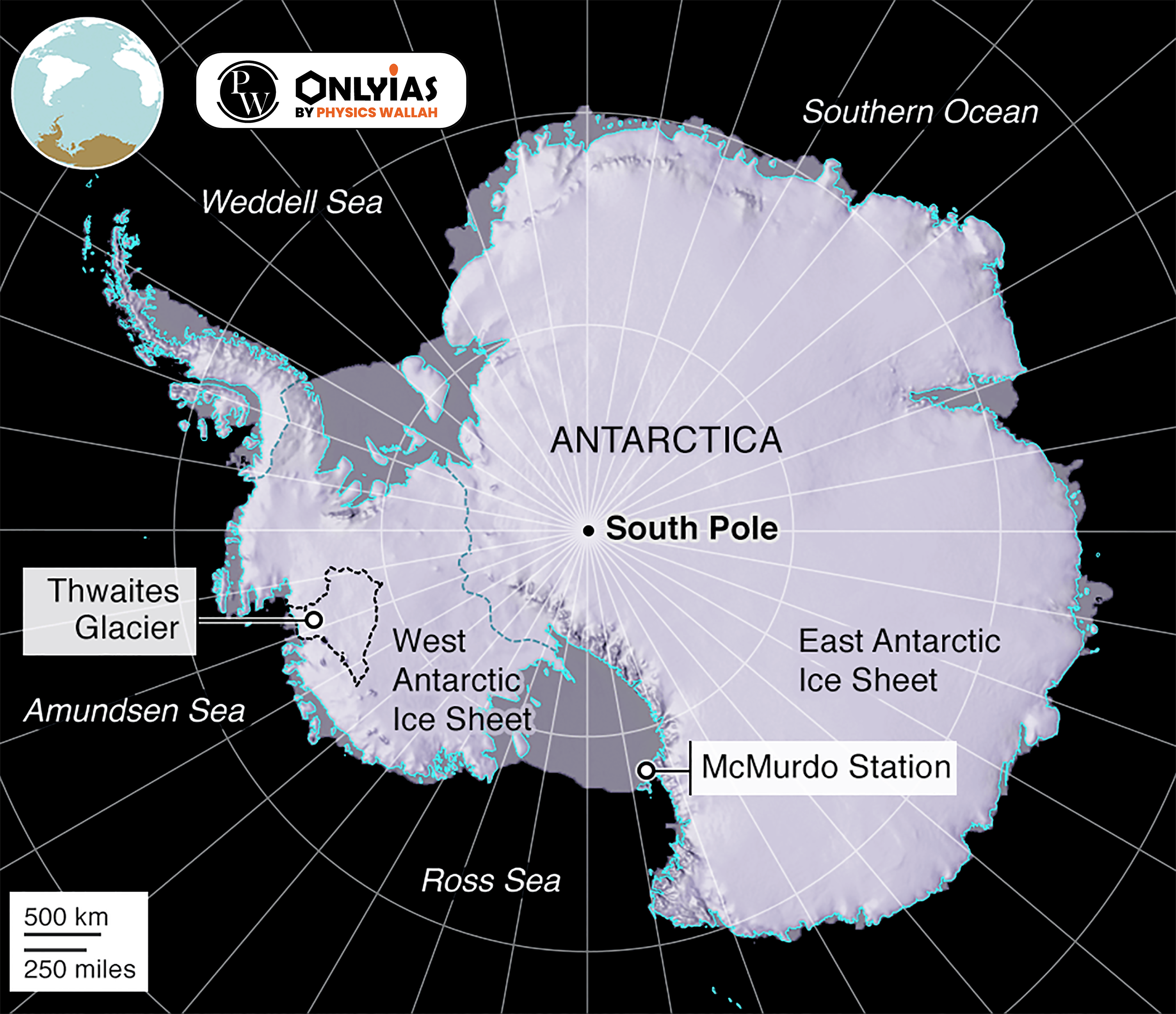
About Antarctica
|
|---|
News Source: DTE
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
In which of the following activities are Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellites used? (2015) 1. Assessment of crop productivity 2. Locating groundwater resources 3. Mineral exploration 4. Telecommunications 5. Traffic studies Select the correct answer using the code given below. (a) 1, 2 and 3 only (b) 4 and 5 only (c) 1 and 2 only (d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: Monsoon Rainfall, EL Nino, La Nina, Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), Indian GDP, and PM AASHA Scheme.
Relevancy for Mains: How dependent is India on monsoon rainfall?, and How does monsoon rainfall affect the Indian economy and agriculture? |
|---|
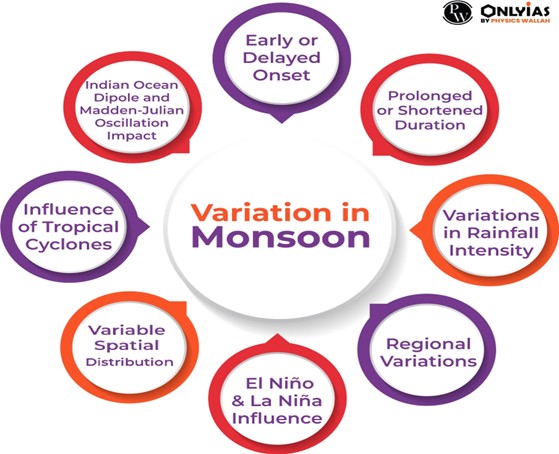
Also Read: Onset’ Of The Monsoon
What are the major phenomena influencing Monsoon Rainfall?
|
|---|
Relation between Monsoon Rainfall and Agriculture
|
|---|
Also read: Interlinking of Rivers—Advantages, Challenges, and Solutions
Monsoon rainfall is crucial for India’s economy, affecting farming, rural life, and economic growth. To address challenges, proactive steps like water conservation and advanced technologies are essential for sustainable growth.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017) 1. IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean. 2. An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon. Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (b) |
|---|
| Attempt the Mains Question: Why is the South-West Monsoon called ‘Purvaiya’ (easterly) in Bhojpur Region? How has this directional seasonal wind system influenced the cultural ethos of the region? |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: Global Terrorism Index, United Nations General Assembly (UNGA), CCIT, Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA), Financial Action Task Force (FATF), and OIC.
Relevancy for Mains: Global Terror Groups, International Conventions on Terrorism, and India’s Laws & Policies on Terrorism. |
|---|

However, consensus eludes to the adoption of the terrorism convention.
| The Organisation of Islamic Cooperation, formerly the Organisation of the Islamic Conference, is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1969, consisting of 57 member states, with 48 being Muslim-majority countries. |
|---|
| India’s Zero Tolerance Policy Towards Terrorism
Legislative Measures:
Other Measures
|
|---|
| United Nations Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy
It is a unique global instrument to enhance national, regional and international efforts to counter-terror activities. It was adopted by consensus in 2006, and all United Nations Member States agreed to a common strategic and operational approach to fighting terror groups. It is based on four pillars:
|
|---|
To counter global terrorism in all forms, countries must agree upon a definition of terrorism and rise above narrow self-interest and break the prism of good and bad terrorism.
| Attempt the PY Prelims Question
‘Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action’, often seen in the news, is (a) a strategy to tackle the regional terrorism, an outcome of a meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (b) a plan of action for sustainable economic growth in the Asia-Pacific Region, an outcome of the deliberations of the Asia-Pacific Economic Forum (c) an agenda for women’s empowerment, an outcome of a World Conference convened by the United Nations (d) a strategy to combat wildlife trafficking, a declaration of the East Asia Summit Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
