About Wilful Defaults: On September 21, the RBI proposed that lenders complete the process of classifying a borrower as a ‘wilful defaulter’ within six months of the account being declared as a non-performing asset (NPA).
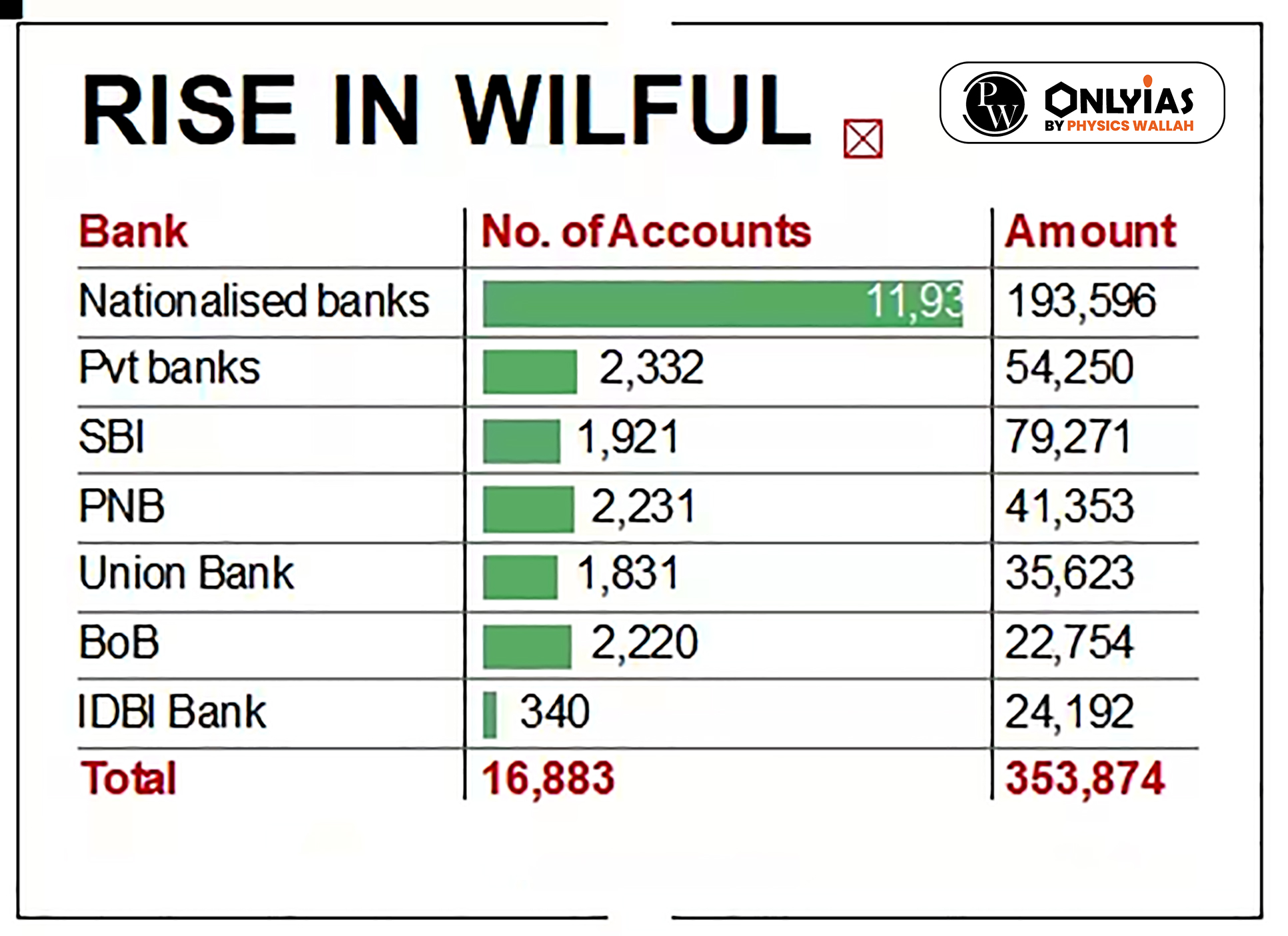
RBI’s Position:On June 8, 2023, the RBI said in a circular that banks can undertake compromise settlements or technical write-offs regarding accounts categorized as wilful defaulters or fraud without prejudice to criminal proceedings against such debtors.
| Compromise Settlement refers to a negotiated settlement where a borrower offers to pay and the bank agrees to accept in full and final settlement of its dues an amount less than the total amount due to them under the loan contract. |
|---|
Source: Indian Express
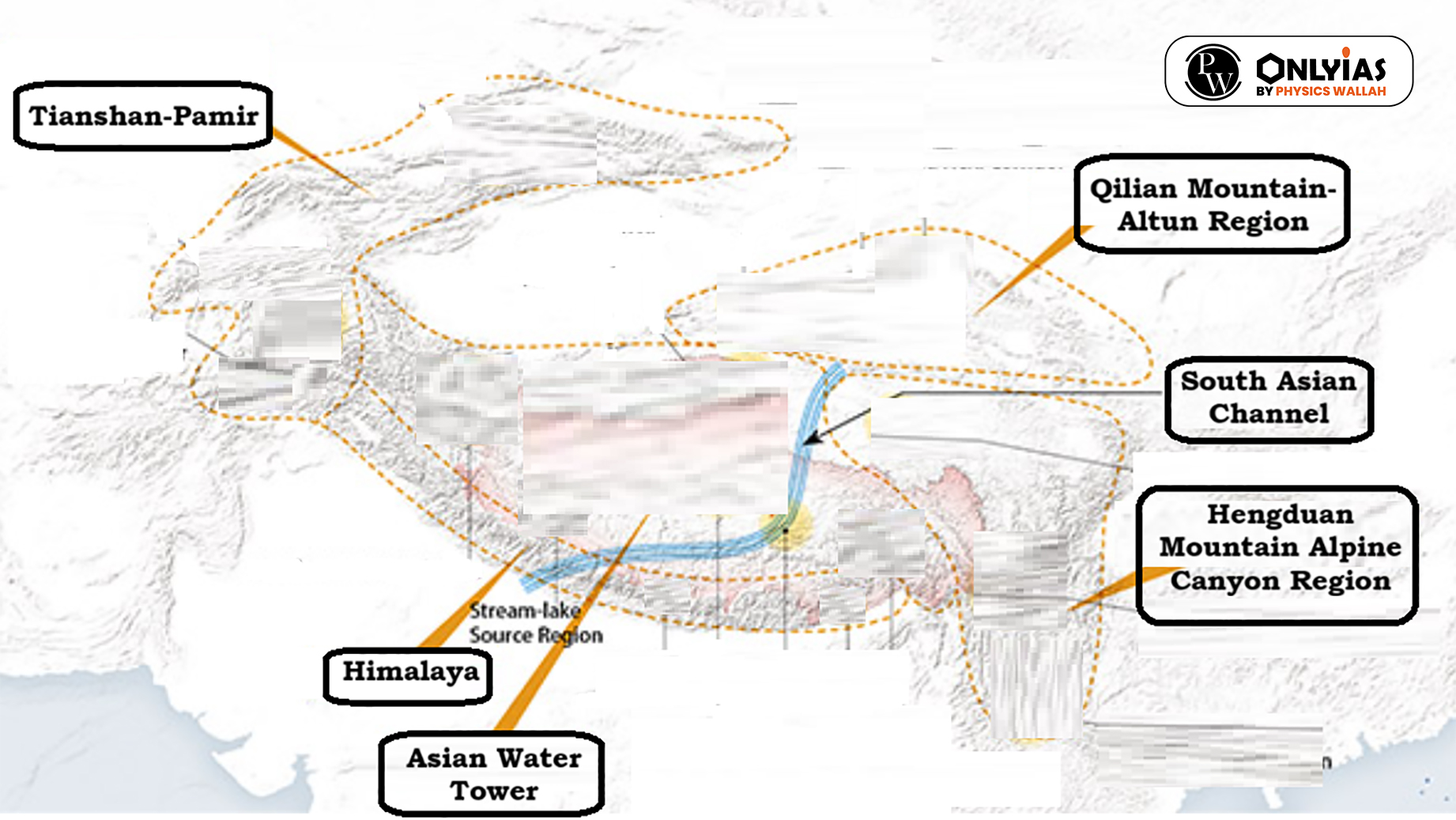
News Source: Down to Earth
| Prelims Question (2022)
Which one of the following lakes of West Africa has become dry and turned into a desert ? (a) Lake Victoria (b) Lake Faguibine (c) Lake Oguta (d) Lake Volta Ans: (b) |
|---|
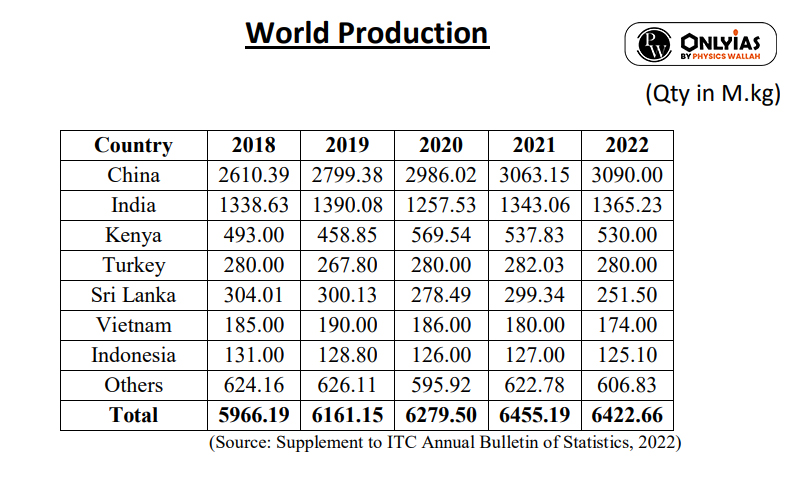
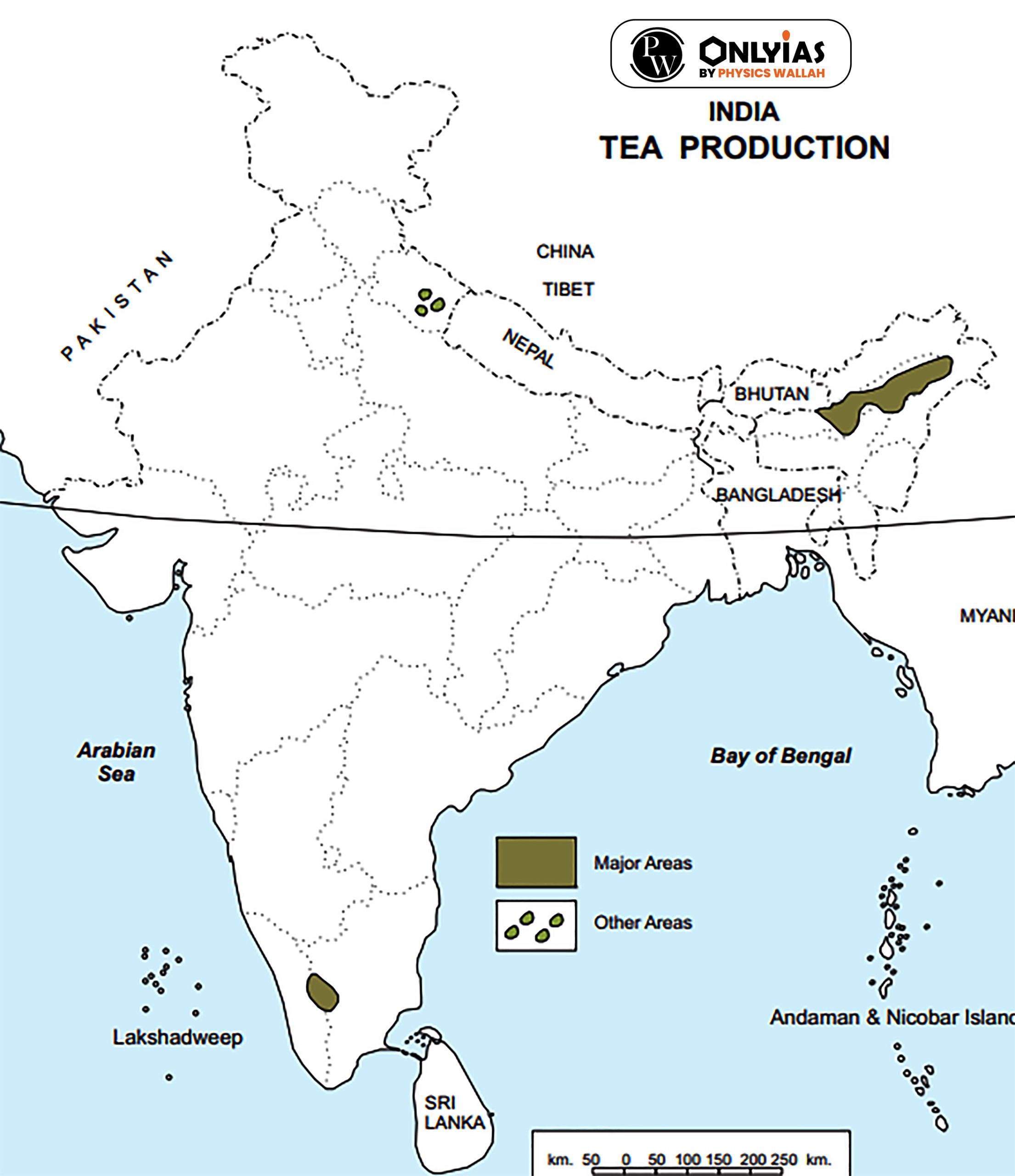
News Source: Business Standard
| Prelims Question (2022)
Consider the following States: 1. Andhra Pradesh 2. Kerala 3. Himachal Pradesh 4. Tripura How many of the above are generally known as teaproducing States? (a) Only one State (b) Only two States (c) Only three States (d) All four States Ans: (c) |
|---|
News Source: Down to Earth
| Prelims Question (2018)
How is the National Green Tribunal (NGT) different from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)? 1. The NGT has been established by an Act whereas the CPCB has been created by an executive order of the Government. 2. The NGT provides environmental justice and helps reduce the burden of litigation in the higher courts whereas the CPCB promotes cleanliness of streams and wells, and aims to improve the quality of air in the country. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (b) |
|---|
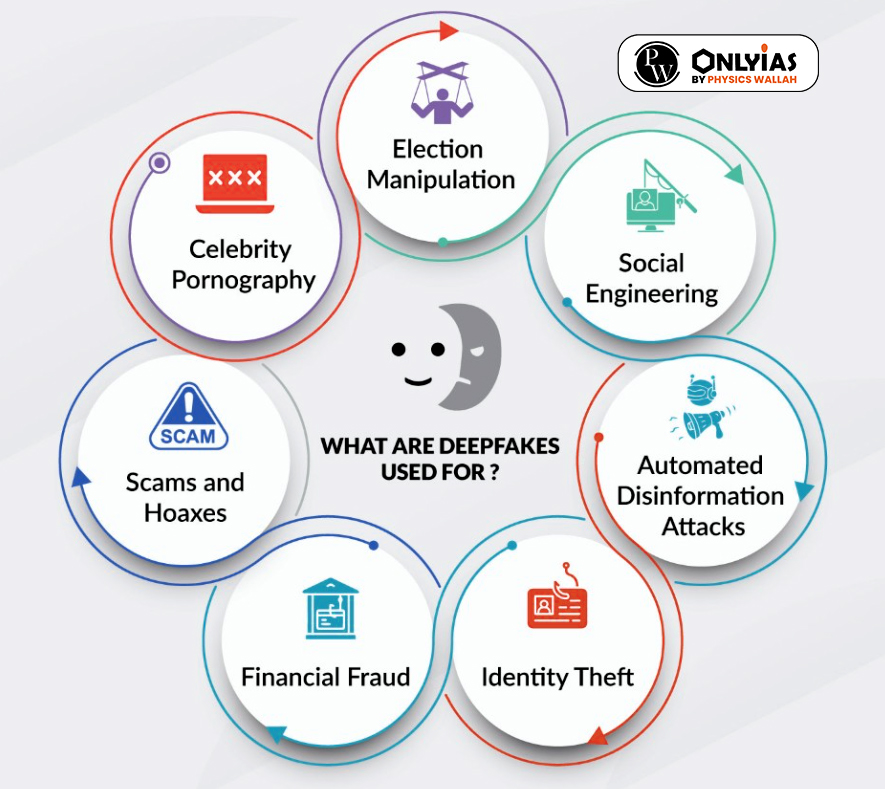
News Source: The Indian Express
| Prelims Question (2017)
In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? 1. Service providers 2. Data centres 3. Body corporate Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
|---|
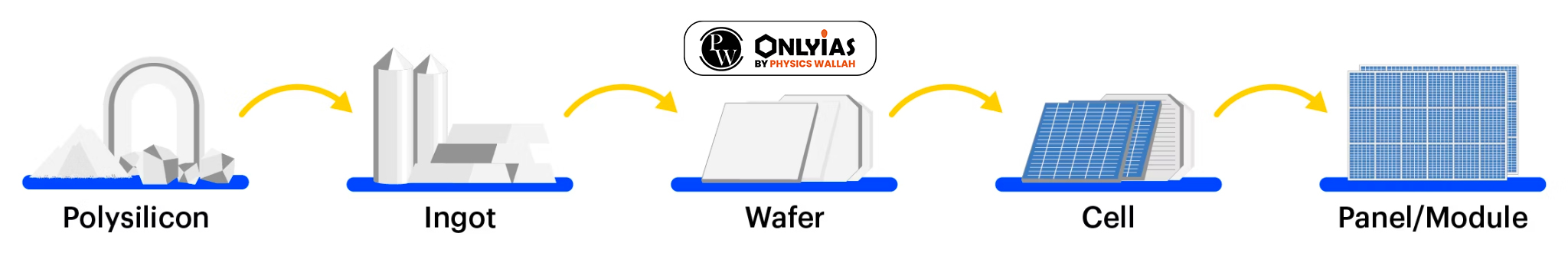
| Relevancy for Prelims: Solar Module, PLI Scheme, International Solar Alliance, PM KUSUM, National Solar Mission, and Atal Jyoti Yojana (AJAY).
Relevancy for Mains: 76% drop in solar module imports from China in the first half of 2023, India’s Solar Power Generation Potential, Challenges in India’s solar module manufacturing, and Government Initiatives. |
|---|
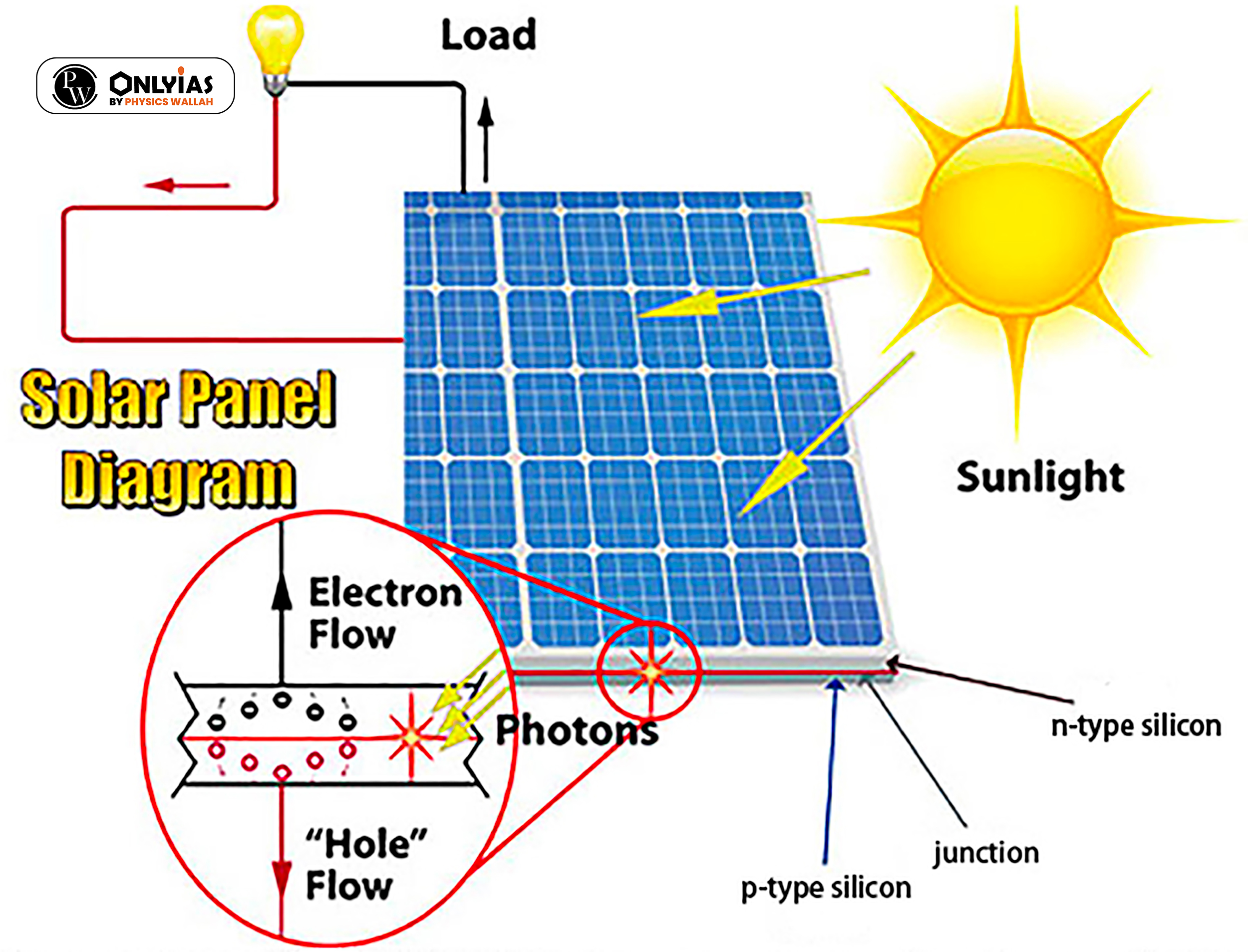
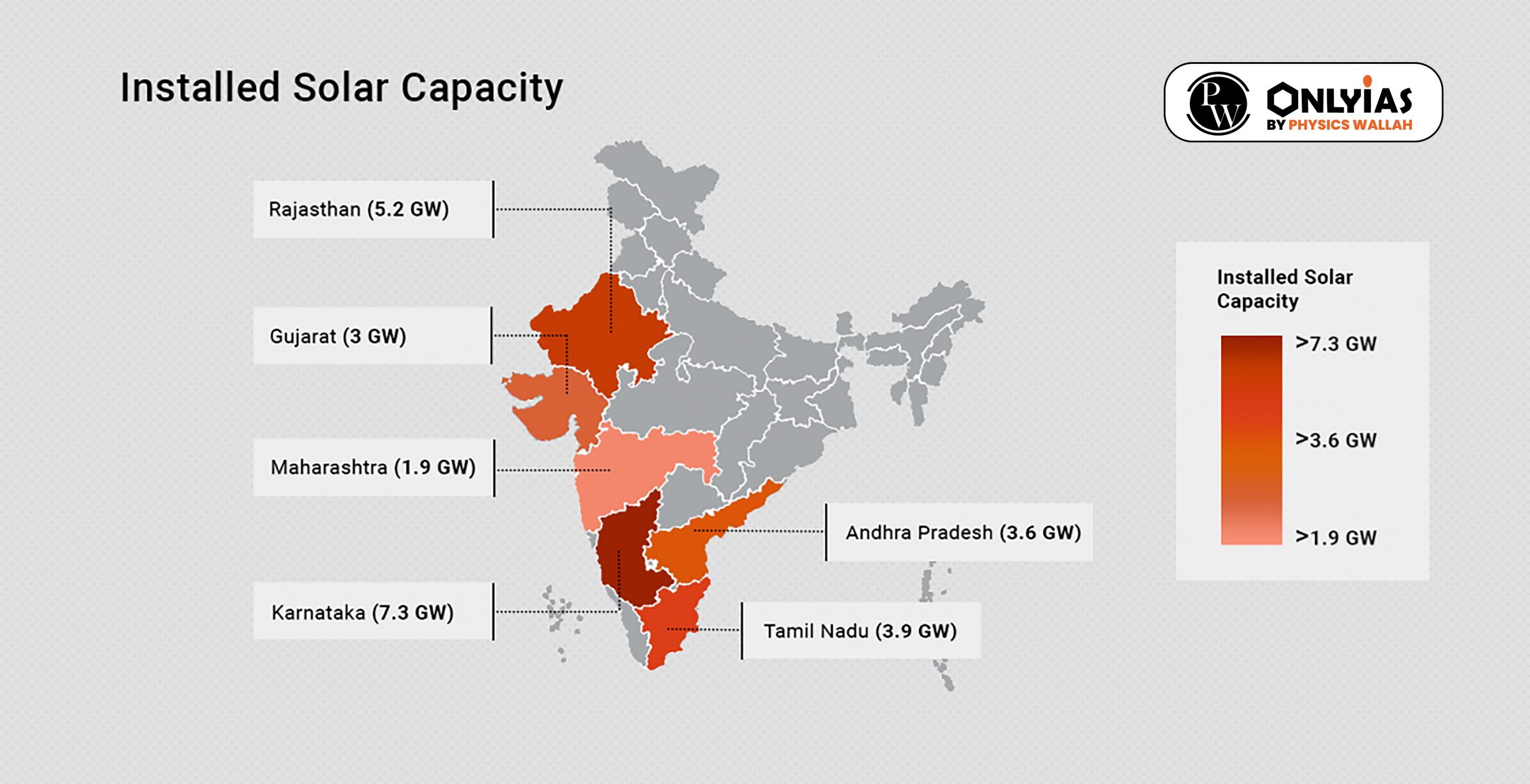
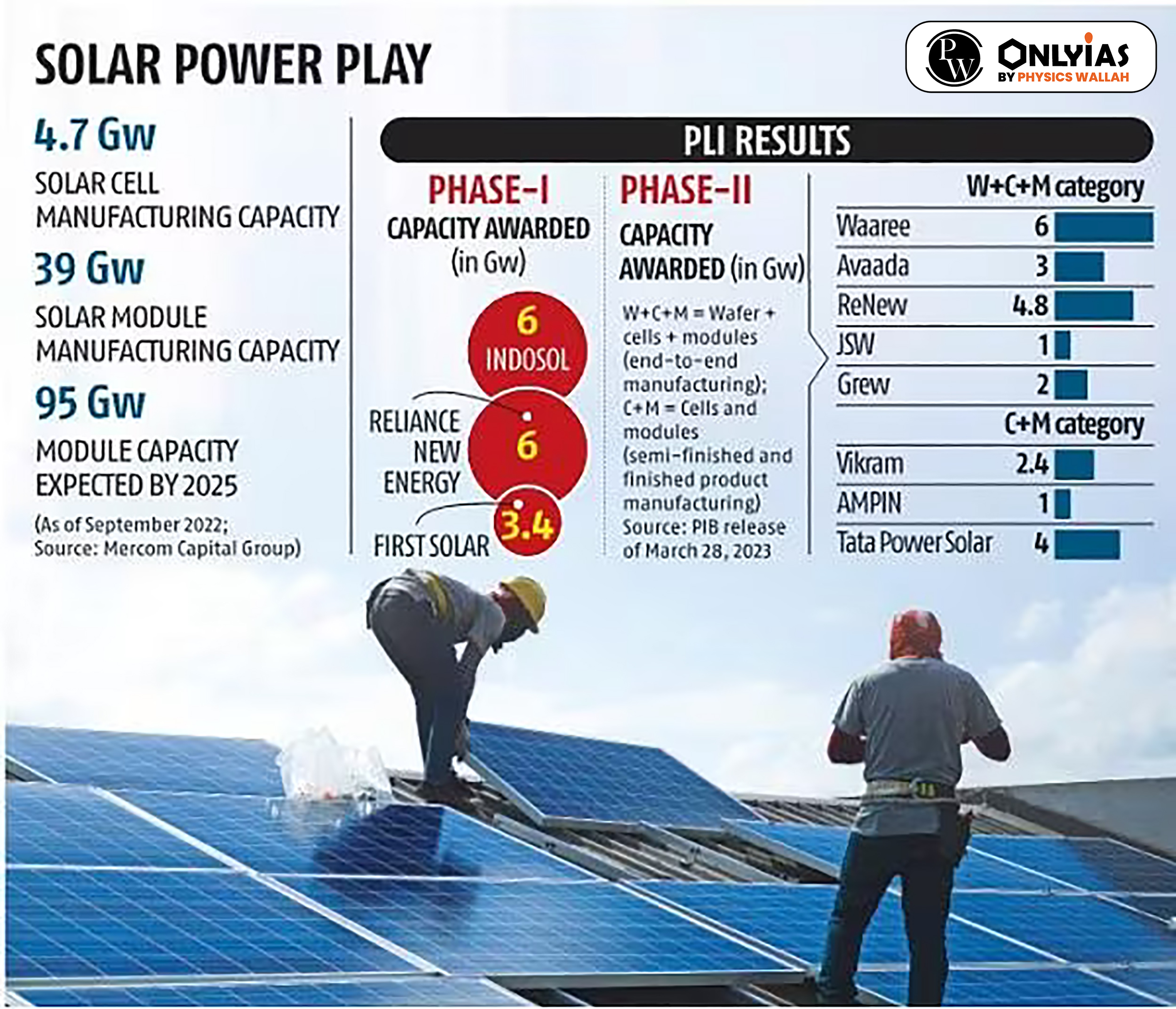
|
|---|
The International Energy Agency (IEA’s) five key policy action areas to ensure solar PV security of supply:
|
|---|
India’s remarkable 76% decline in solar module imports from China in the first half of 2023 reflects a strategic shift towards self-sufficiency, driven by government initiatives like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, signaling a positive trajectory for domestic solar module manufacturing.
| Prelims Question (2020)
With reference to solar water pumps, consider the following statements: 1. Solar power can be used for running surface pumps and not for submersible pumps. 2. Solar power can be used for running centrifugal pumps and not the ones with piston. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (d) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Describe the benefits of deriving electric energy from sunlight in contrast to conventional energy generation. What are the initiatives offered by our government for this purpose? (2020) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: World Mental Health Day 2023, Mental-Health Problems in India, WHO, National Mental-Health Survey (NMHS), National Mental-Health Policy (2014), and National Mental Health Programme (NMHP).
Relevancy for Mains: Parliamentary Committee Report on Mental Health Care, Burden of Mental-Health Issues in India, major mental-health challenges in India, and Government Initiatives. |
|---|

Mental Health Disorder
|
|---|
Also read: Spare a Thought for Psychiatric Caregivers too
What is Mental Health?
Global Initiatives
|
|---|
In light of India’s escalating mental health challenges characterized by insufficient funds, societal stigma, and limited awareness, a holistic strategy with augmented funding, community-driven programs, and stigmatisation ndeavors is essential to establish mental well-being as a universal human right for every Indian.
| Prelims Question (2020)
Consider the following statements: 1. Genetic changes can be introduced in the cells that produce eggs or sperms of a prospective parent. 2. A person’s genome can be edited before birth at the early embryonic stage. 3. Human induced pluripotent stem cells can be injected into the embryo of a pig. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 2 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
|---|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
