News Source: The Hindu
| Prelims Question (2022)
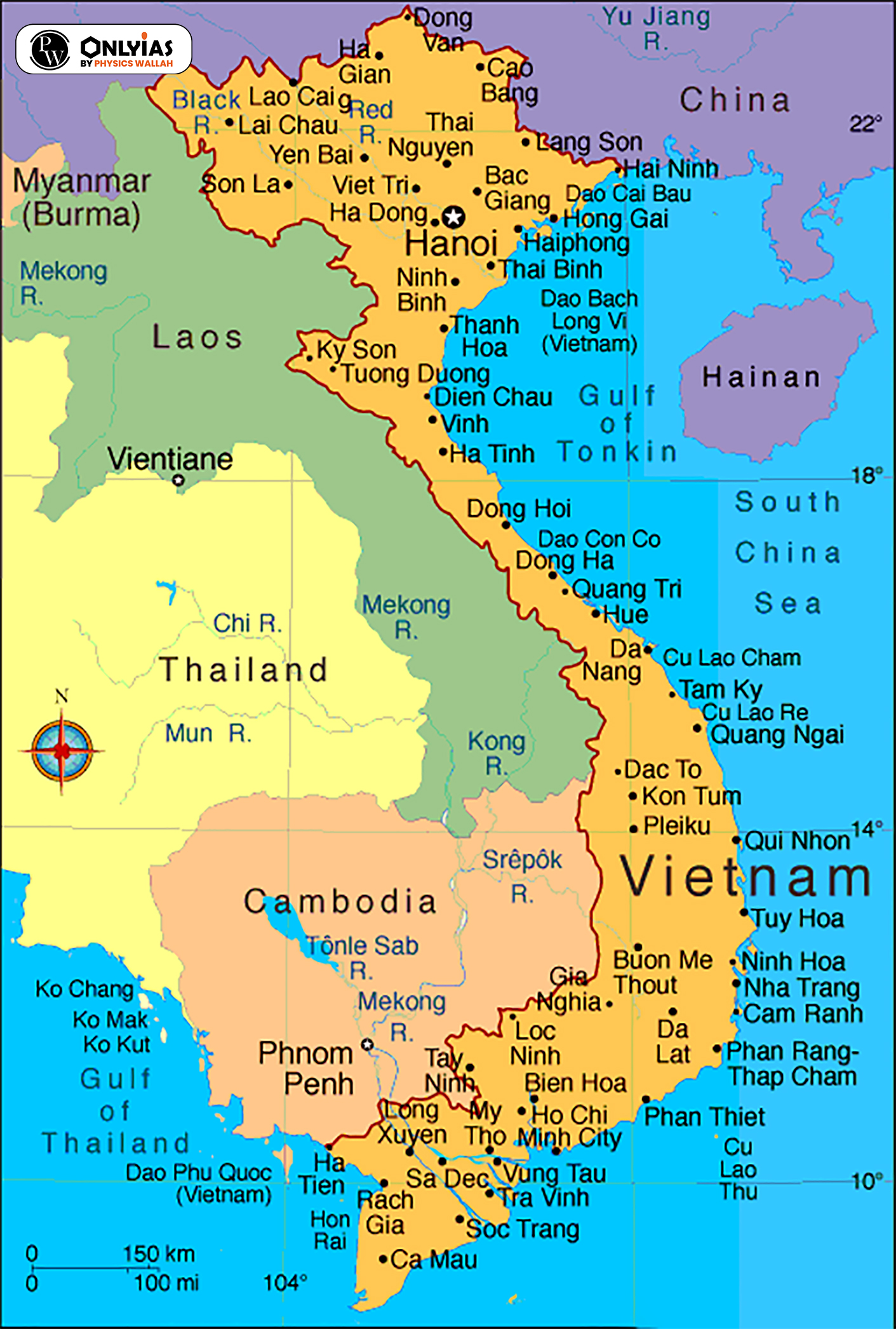
Consider the following statements: 1. Vietnam has been one of the fastest growing economies in the world in the recent years. 2. Vietnam is led by a multi-party political system. 3. Vietnam’s economic growth is linked to its integration with global supply chains and focus on exports. 4. For a long time Vietnam’s low labour costs and stable exchange rates have attracted global manufacturers. 5. Vietnam has the most productive eservice sector in the Indo-Pacific region. Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 2 and 4 (b) 3 and 5 (c) 1, 3 and 4 (d) 1 and 2 Ans: (c) |
What is the BRI?
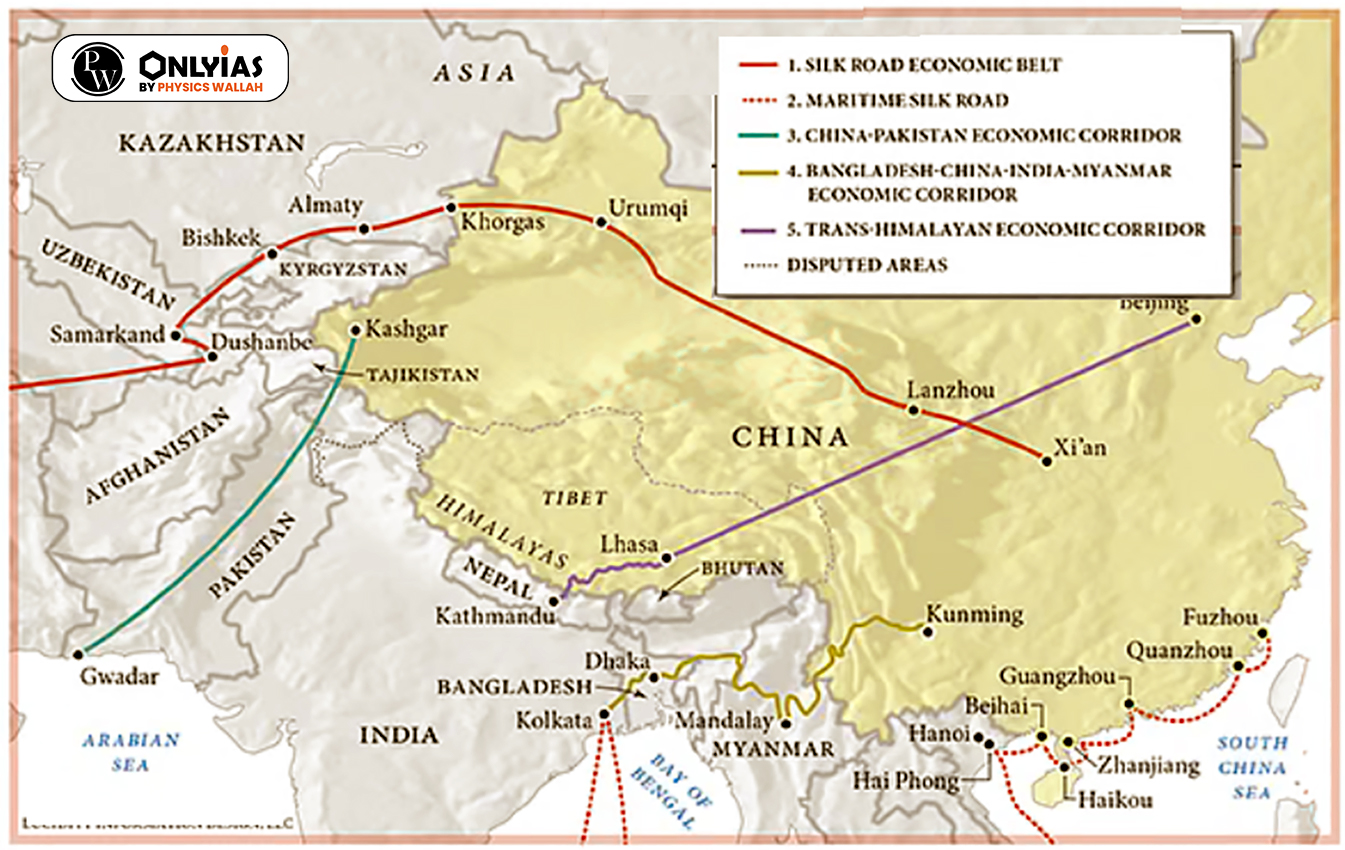
| “Belt” refers to overland routes connecting China to Europe through Central Asia, as well as to South Asia and South East Asia; while “Road” denotes a maritime network linking China to major ports through Asia to Africa and Europe. |
|---|
What are the challenges of China’s Belt and Road Initiative?
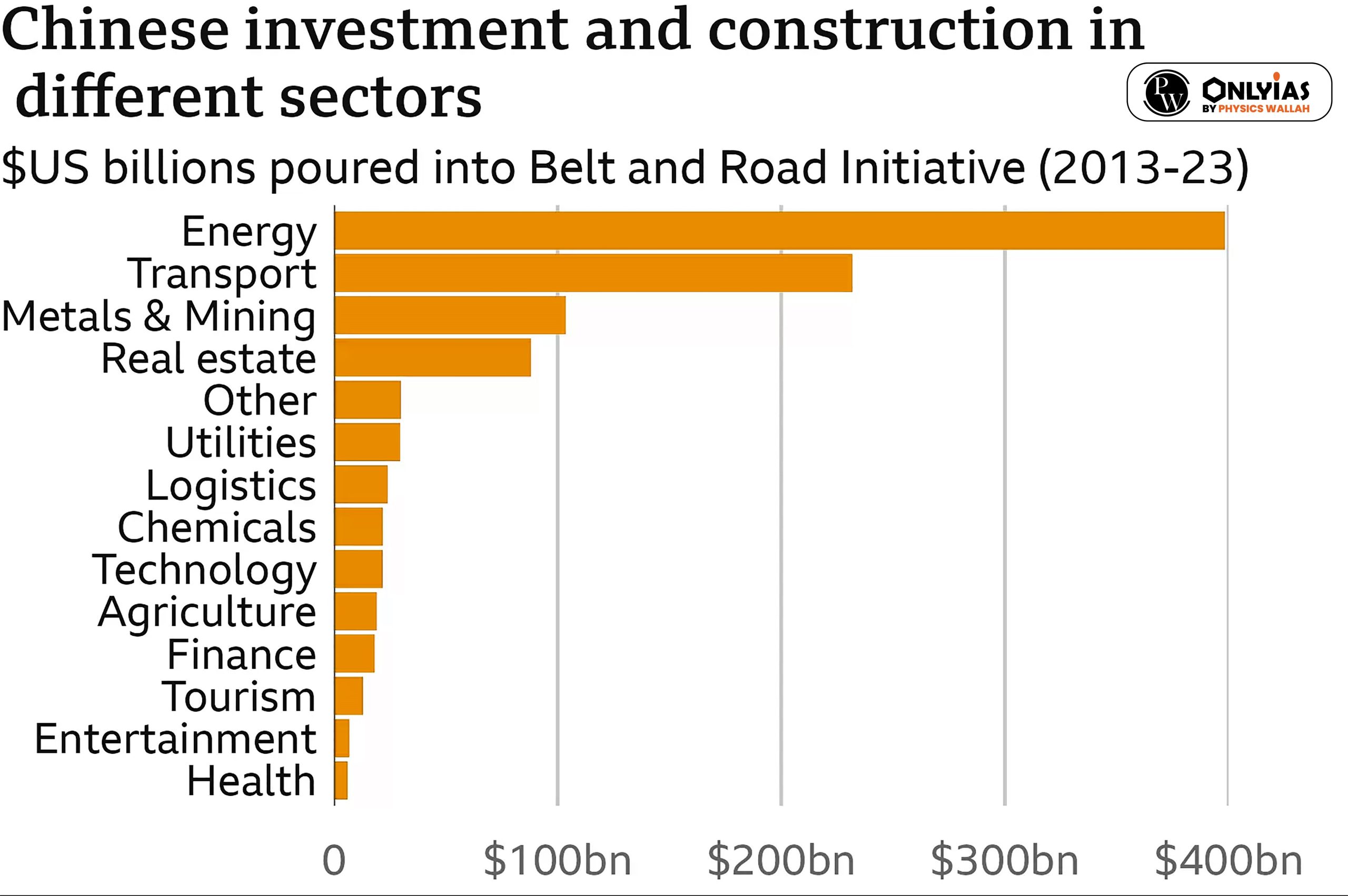
India’s Stand
News Source: Economic Times
| Prelims Question (2016)
‘Belt and Road Initiative’ is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (a) African Union (b) Brazil (c) European Union (d) China Ans: (d) |
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Prelims Question (2017)
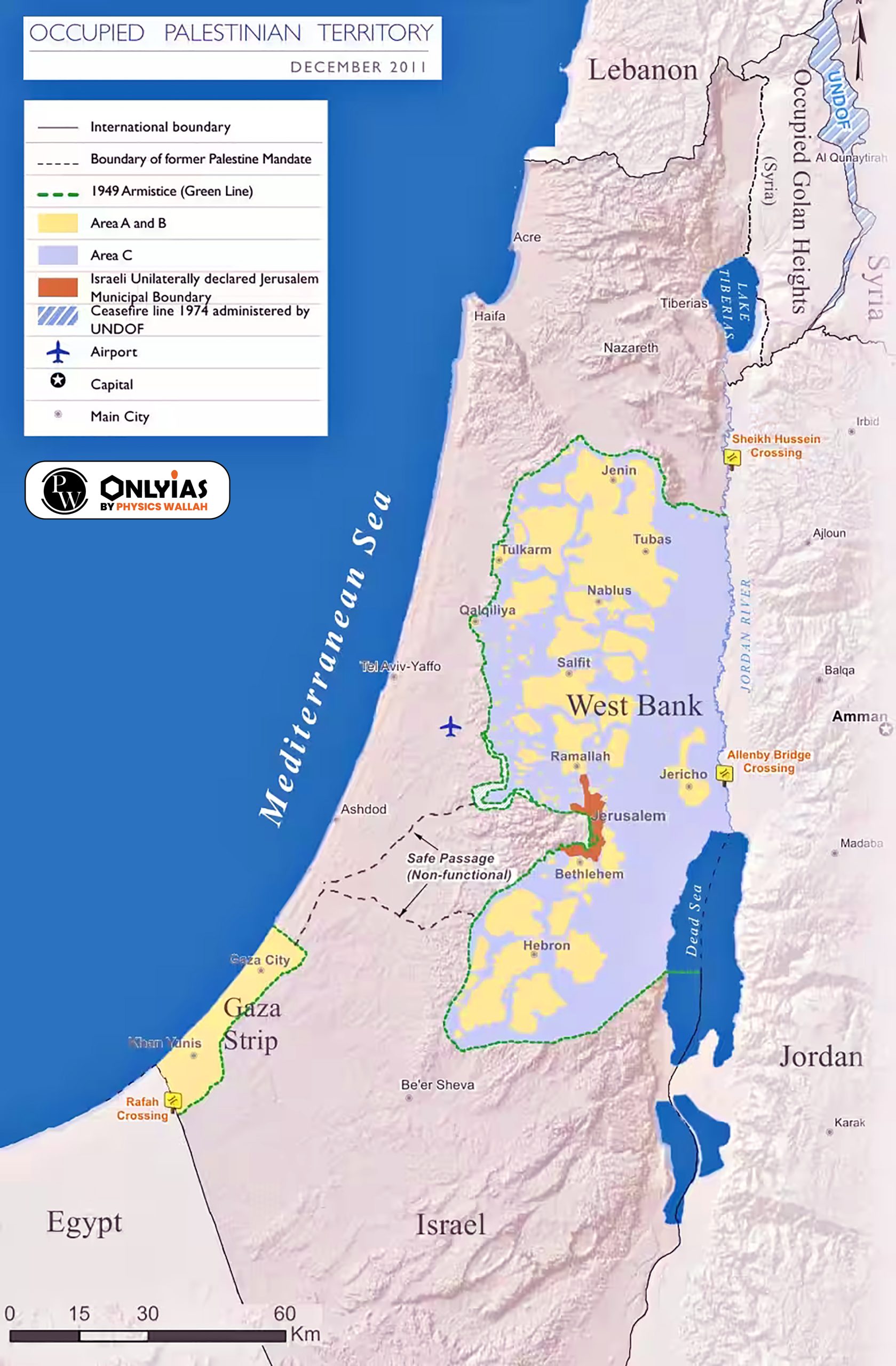
Mediterranean Sea is a border of which of the following countries? 1. Jordan 2. Iraq 3. Lebanon 4. Syria Select the correct answer using the code given below: (a) 1, 2 and 3 (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 3 and 4 only (d) 1, 3 and 4 only Ans: (C) |
|---|
About Solid Waste Management
Initiatives Related toSolid Waste Management
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Prelims Question (2016)
‘Project Loon’, sometimes seen in the news, is related to (a) Waste management technology (b) Wireless communication technology (c) Solar power production technology (d) Water conservation technology Ans: (b) |
|---|
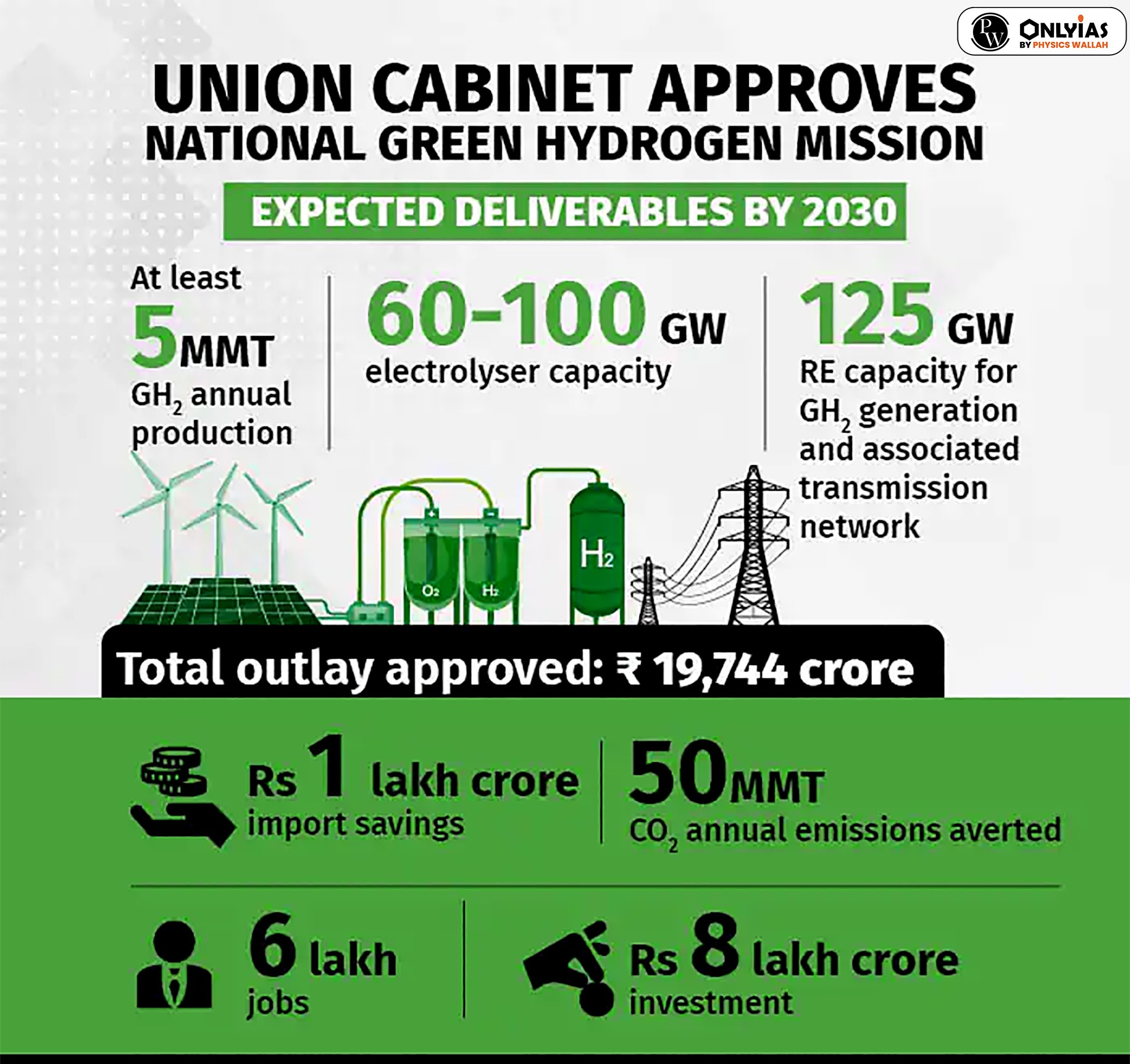
Hydrogen Consumption in India
|
|---|
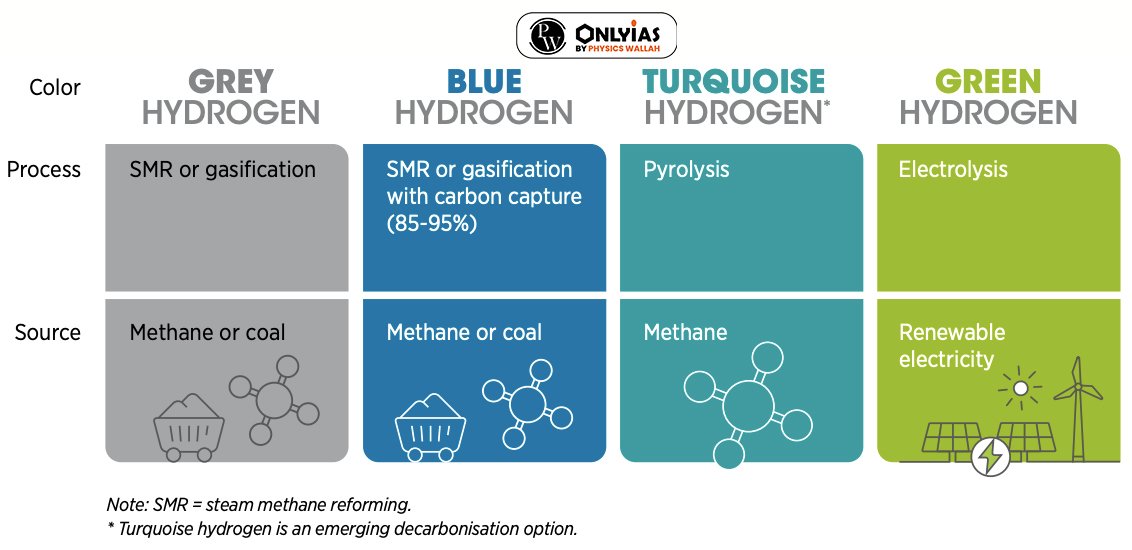
News Source: Business Standard
| Prelims Question (2019)
In the context of which one of the following are the terms ‘pyrolysis and plasma gasification’ mentioned? (a) Extraction of rare earth elements (b) Natural gas extraction technologies (c) Hydrogen fuel-based automobiles (d) Waste-to-energy technologies Ans: (d) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: Surrogacy in India, Surrogacy Laws, Surrogacy (Regulation) Act (SRA) 2021, Supreme Court, Fundamental Rights, and Human Rights.
Relevancy for Mains: Surrogacy in India, Surrogacy Law in Court, Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021, Need of Surrogacy Regulation in India and challenges associated with surrogacy. |
|---|
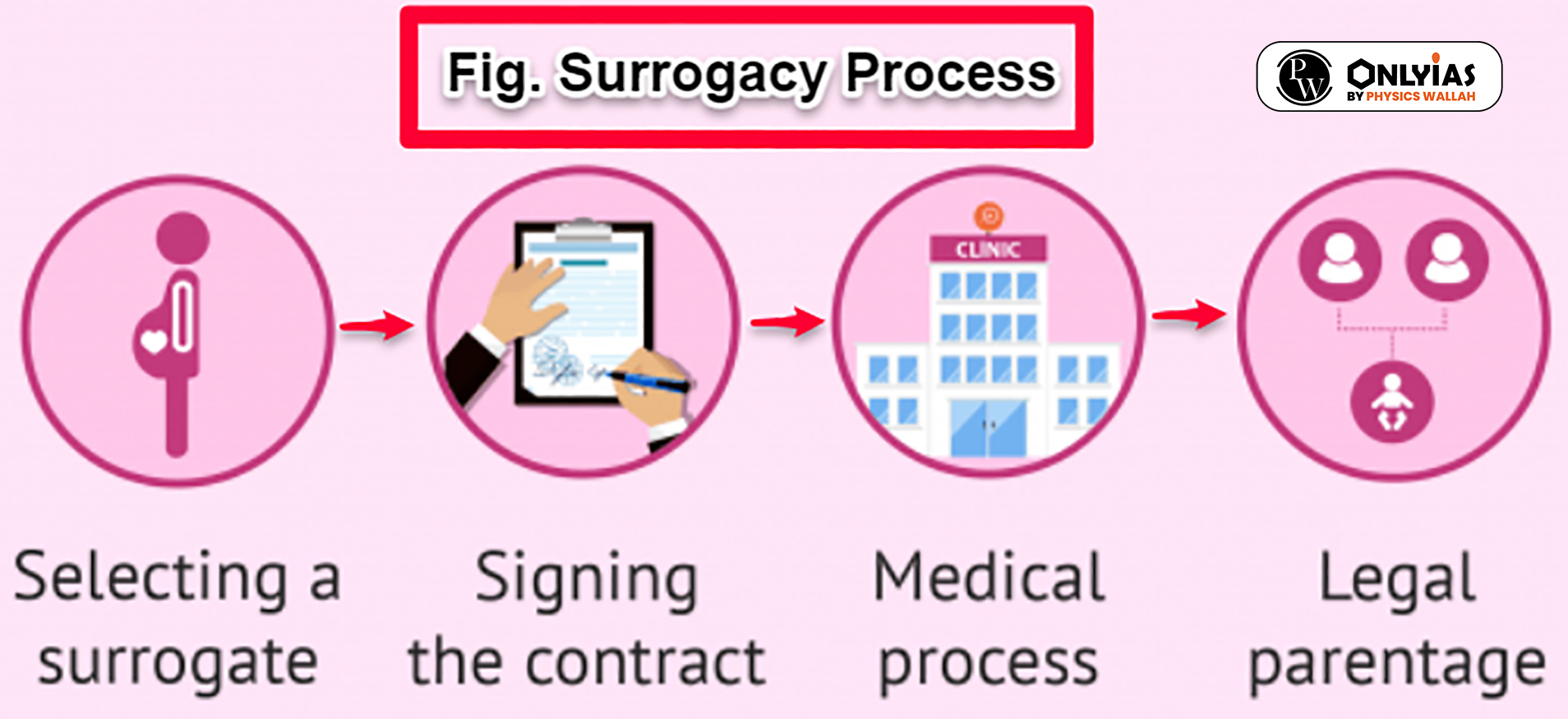

Surrogacy in India; Assisted Reproductive Technology (Regulation) Act, 2021
|
|---|
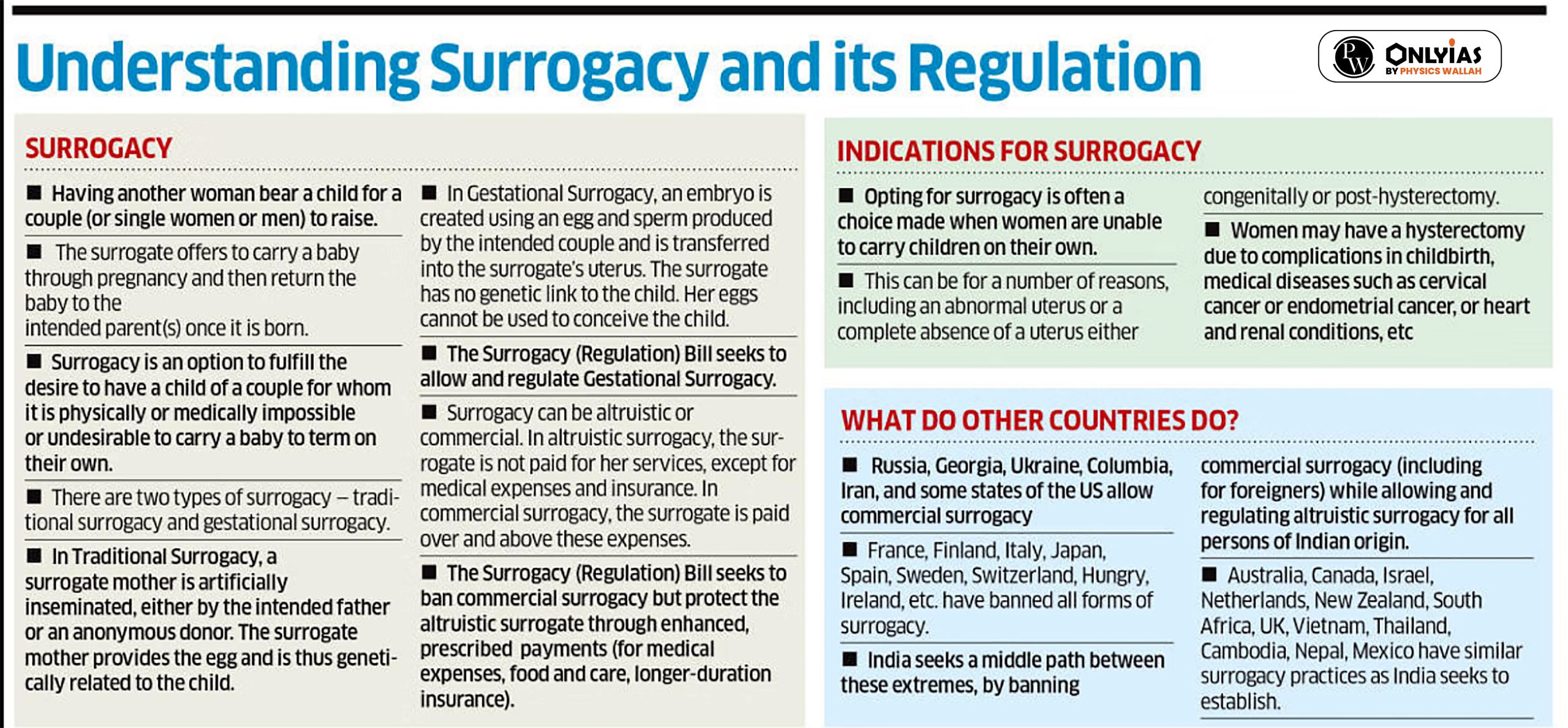
Instead of imposing a ban, the commercial surrogacy market, a balanced path by the Government would be the adoption of a rights-based approach addressing the concerns of the surrogate mother, children born out of surrogacy, and other stakeholders in the surrogacy market.
| Prelims Question (2021)
In the context of hereditary diseases, consider the following statements: 1. Passing on mitochondrial diseases from parent to child can be prevented by mitochondrial replacement therapy either before or after in vitro fertilization of egg. 2. A child inherits mitochondrial diseases entirely from mother and not from father. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Discuss the contribution of civil society groups for women’s effective and meaningful participation and representation in state legislatures in India. |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: Dedicated Freight Corridors in India, National Rail Plan, and Western and Eastern Freight Corridors.
Relevancy for Mains: Dedicated Freight Corridors; Transforming Rail Freight in India, and what are significance and challenges of dedicated freight corridors. |
|---|
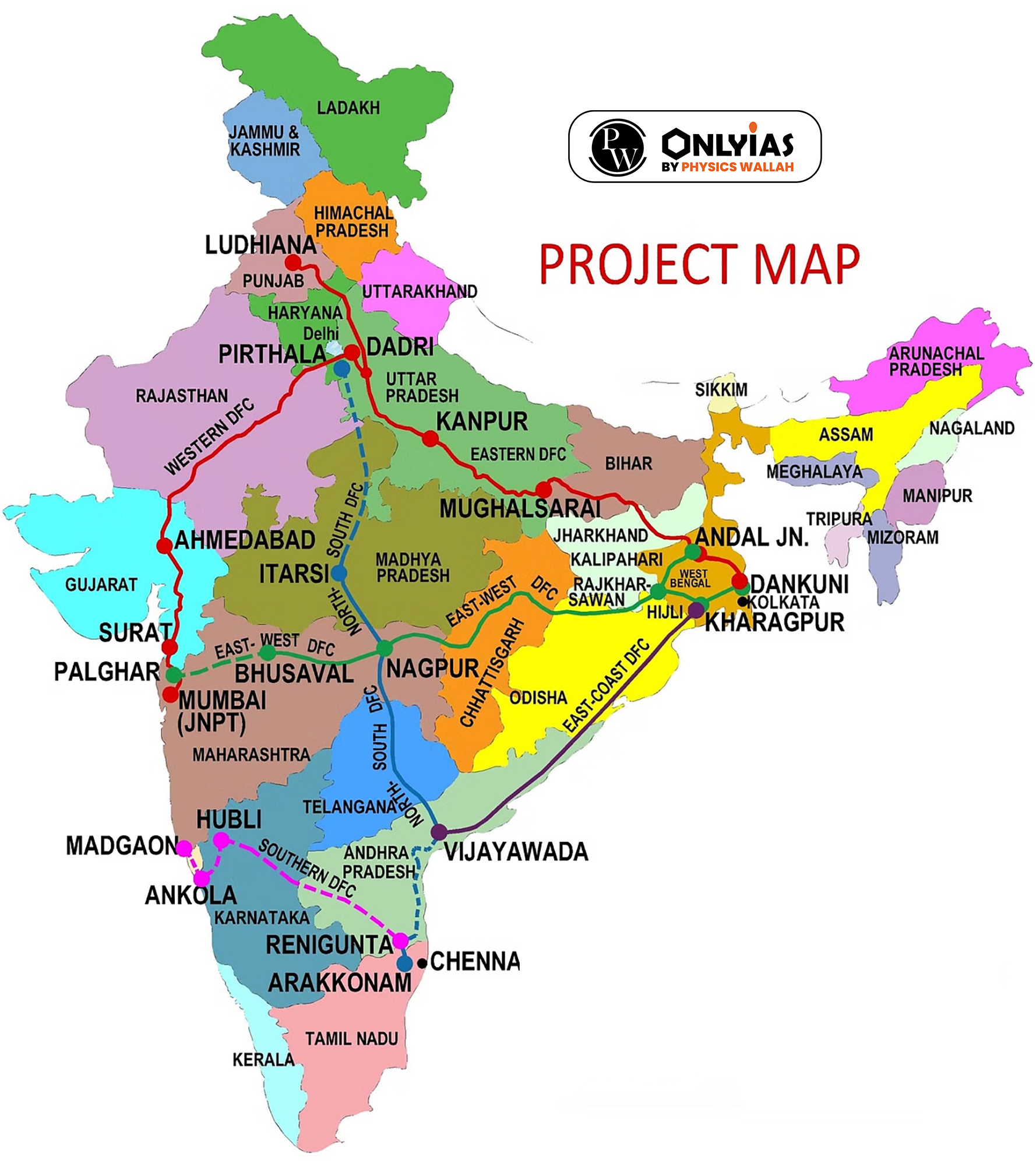

| Western Dedicated Freight Corridor | Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor |
| 1,468 km | 1,760 km |
| Dadri, U.P to Jawaharlal Nehru Port, Mumbai. | Ludhiana Punjab to Dankuni West Bengal |
| The WDFC covers Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra & Uttar Pradesh. | The EDFC route covers Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand & West Bengal |
| The Japan International Cooperation Agency. | The World Bank is funding EDFC |
Also read: Decarbonising Transport Sector
What is the significance of a dedicated freight corridor?
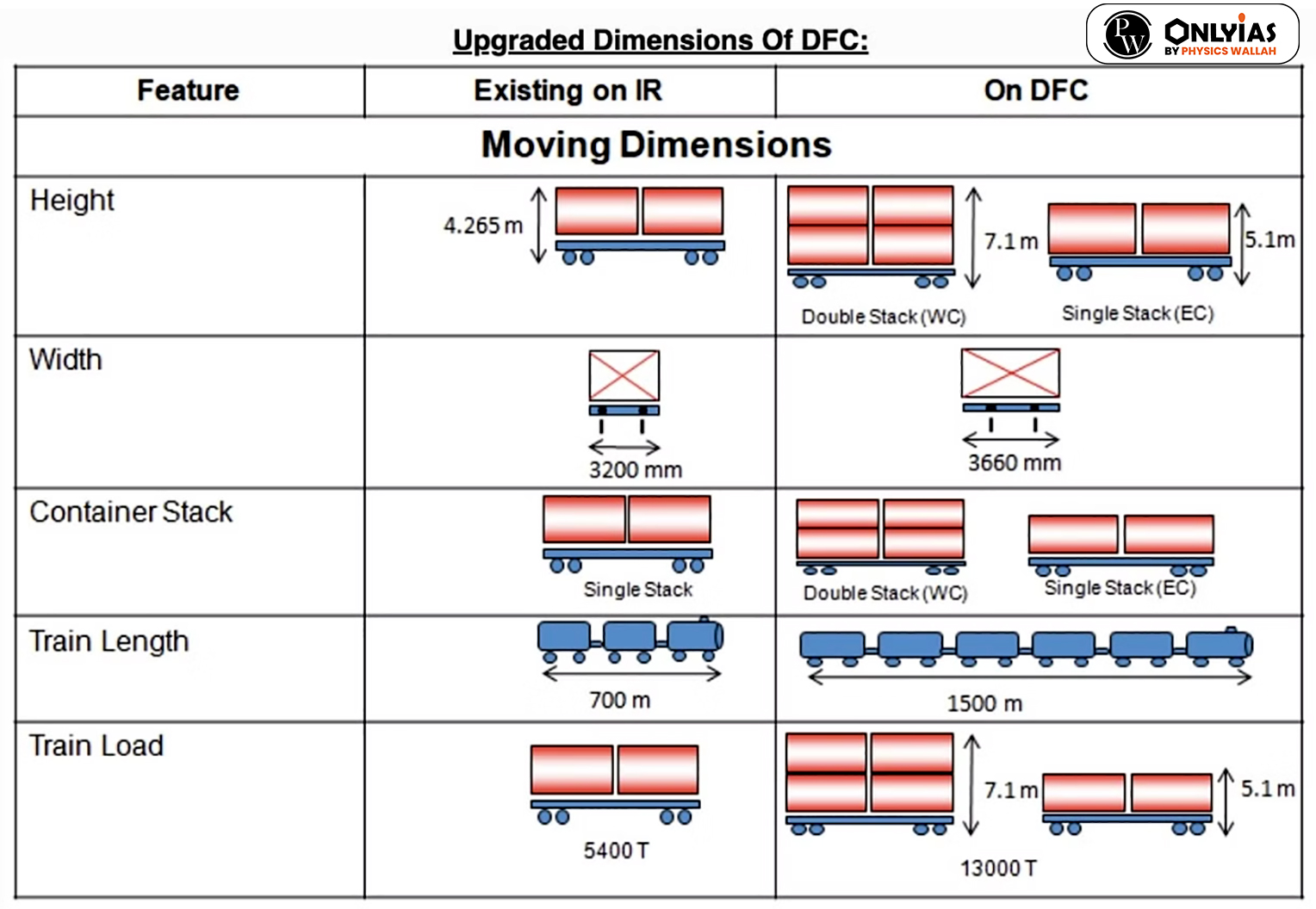
Green Impact: The corridor will rely entirely on electric locomotives, which in turn will result in a substantial reduction in carbon emissions.
Dedicated Freight Corridor Corporation of India Ltd (DFCCIL)
|
|---|
The completion of the Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor in India marks a significant step in transforming rail freight, reducing logistics costs, and promoting economic growth. Despite challenges, further expansion and strategic planning hold the key to maximizing the benefits of dedicated freight corridors for the country’s development.
| Prelims Question (2015)
With reference to bio-toilets used by the Indian Railways, consider the following statements: 1. The decomposition of human waste in the bio-toilets in initiated by a fungal inoculum. 2. Ammonia and water vapour are the only end products in this decomposition which are released into the atmosphere. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: (d) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Bring out the socio-economic effects of the introduction of railways in different countries of the world. |
|---|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
