
News source: Live Mint
Governor Power to withhold assent of the bill:
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
News Source: Economic Times

India Construction Equipment Market:
|
|---|
News Source: Mint
Hydrogen Electrolyser:
|
|---|
News Source: Mint
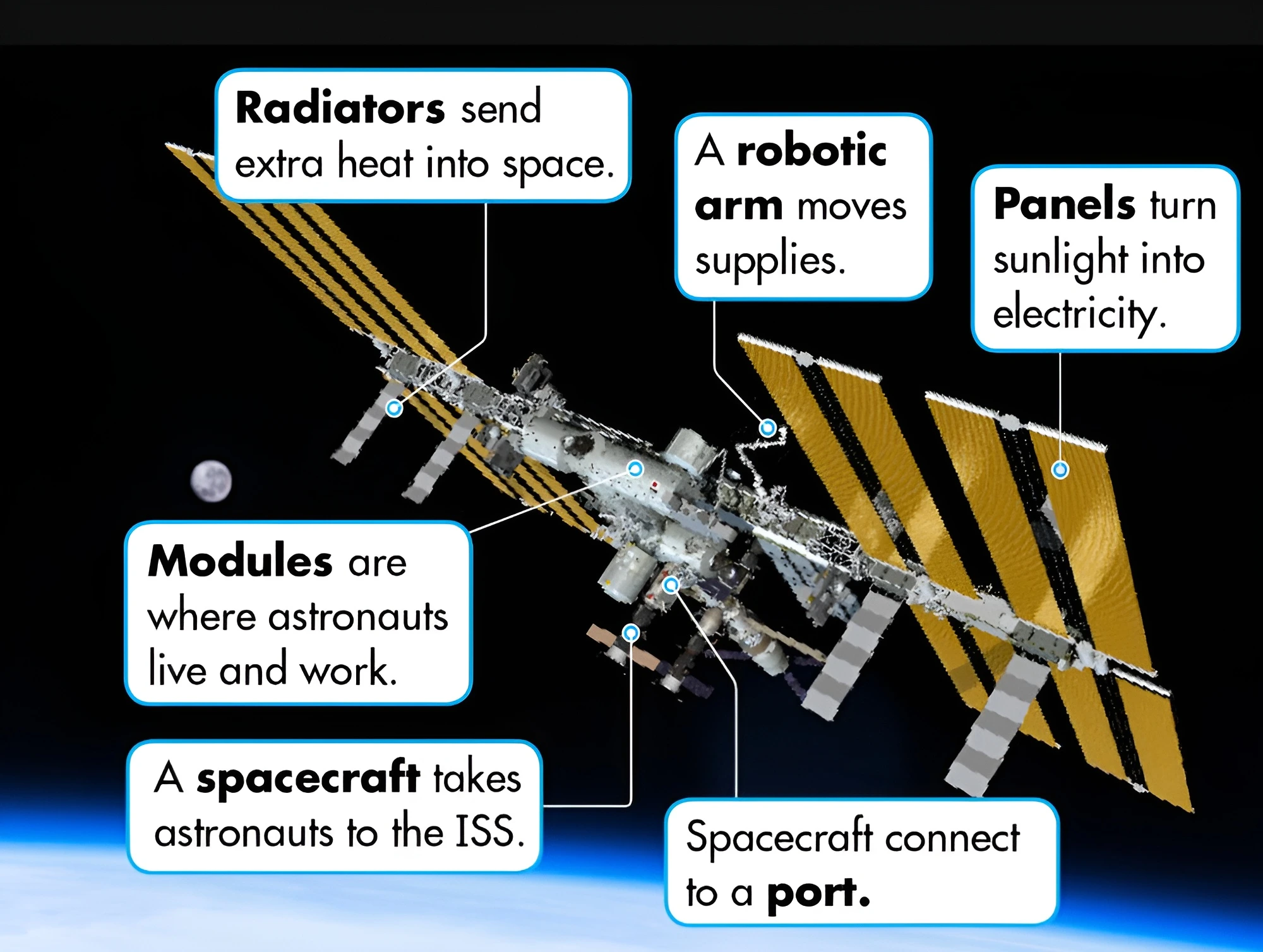
News Source: Indian Express
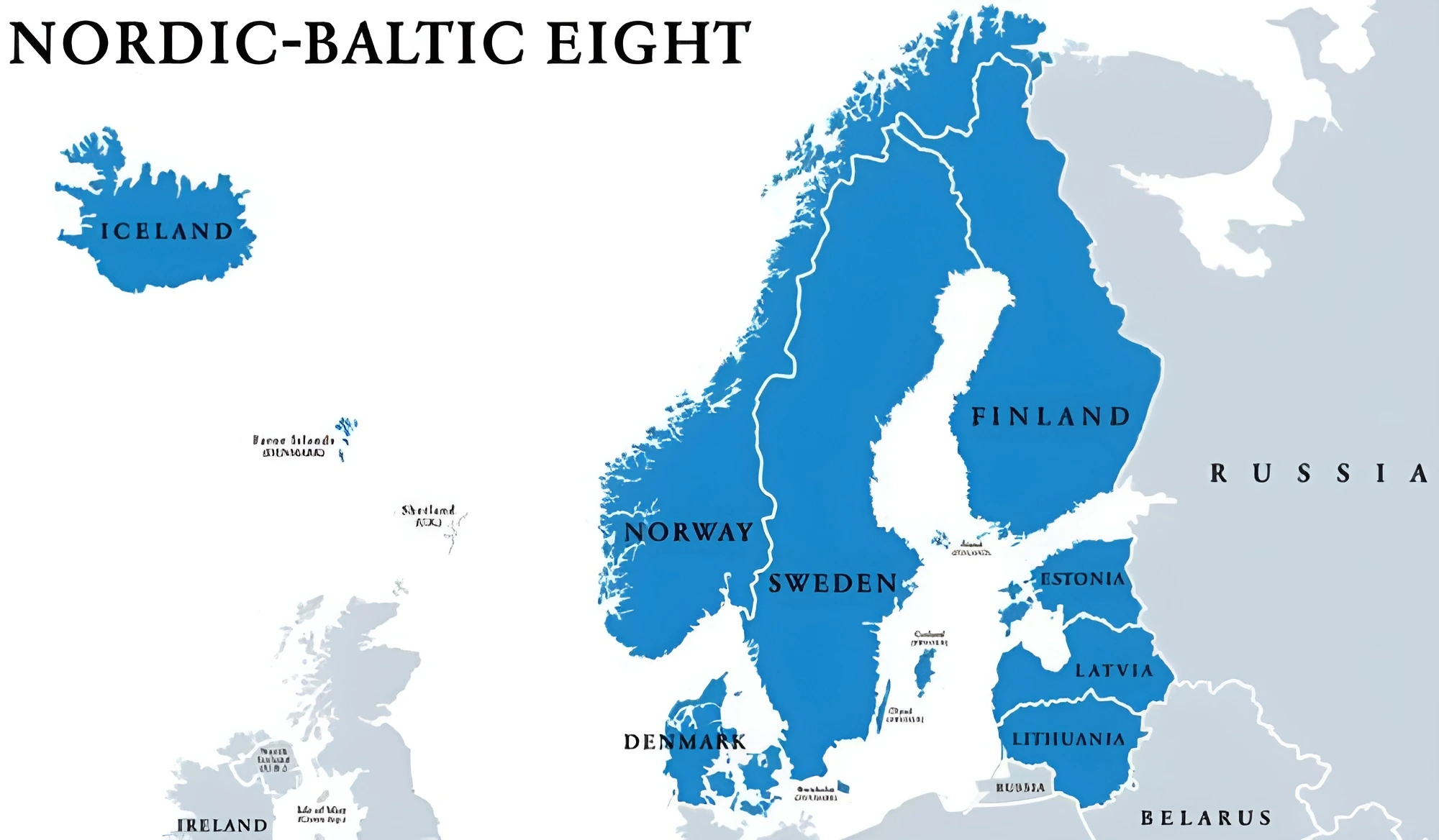
Areas Of Cooperation: The joint statement of the first India Nordic Summit in April 2018 identified four areas of cooperation between India and Nordic countries as follows:
News Source: Business Standards
The event is being organized by Tulukoota Bengaluru and buffalo racing teams from coastal Karnataka.
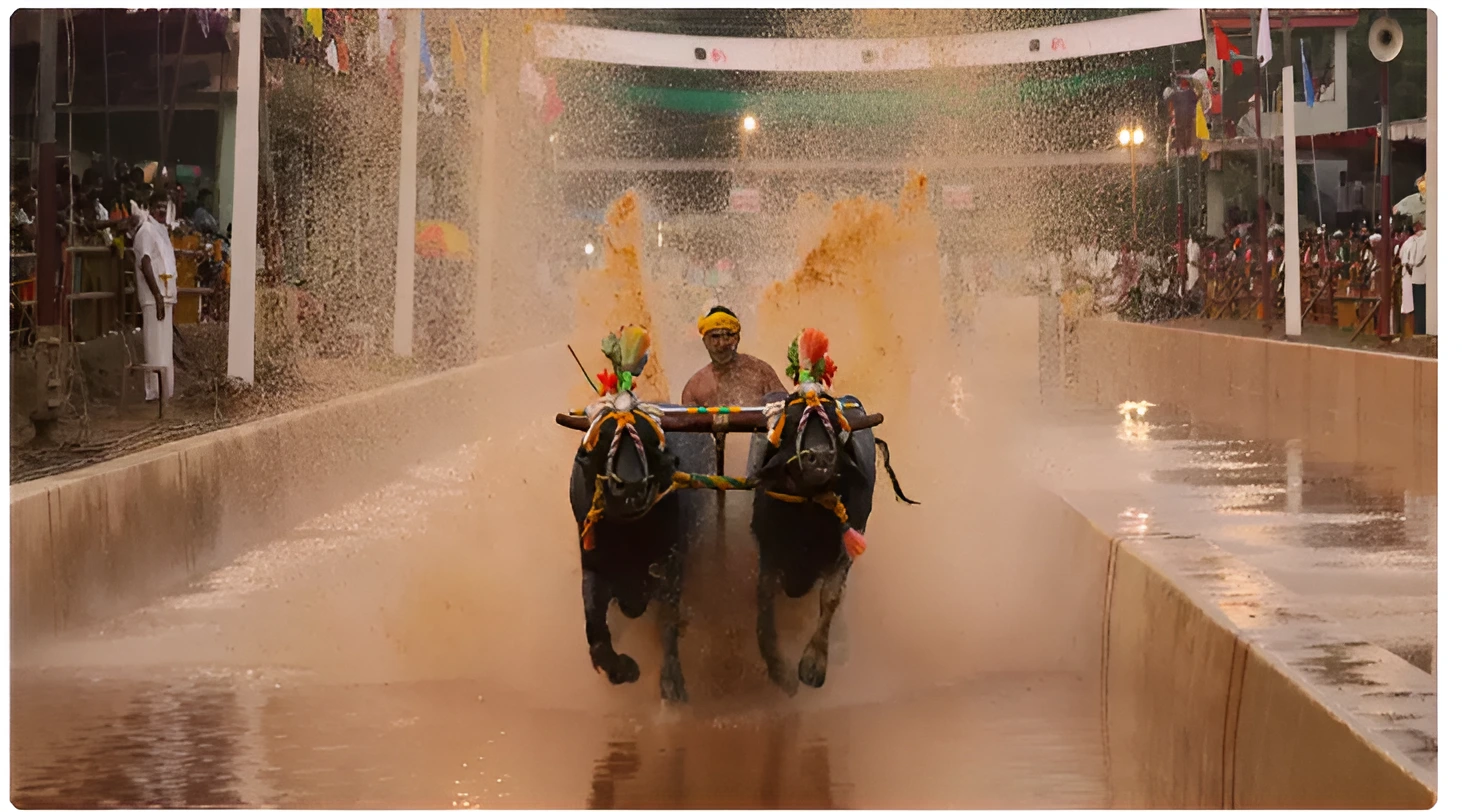

The Prevention Of Cruelty To Animals Act, 1960:
Objectives:
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
Pneumonia
|
World Health Organization (WHO)
WHO’s Regulation :
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
Rs. 525 coin
|
|---|
Bhakti Movement:
Various facets:
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
Know More About – BHAKTI AND SUFI MOVEMENT
| What Is Social Audit?
It is a process of reviewing official records and determining whether state-reported expenditures reflect the actual monies spent on the ground. |
|---|
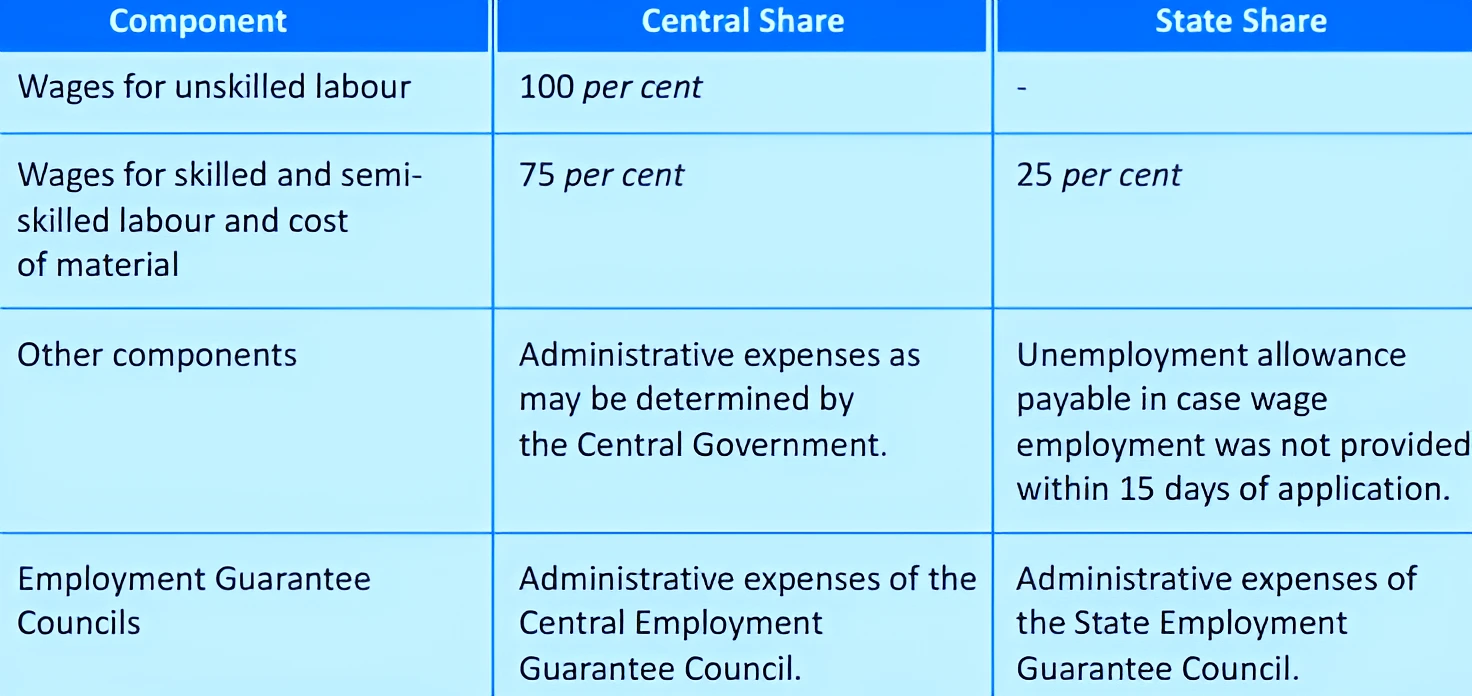
News Source: The Hindu
| What is supply chain resilience?
It is the ability to respond quickly to operational disruptions through flexible contingency planning and forecasting – from material sourcing to logistics and the final delivery of products and services. |
|---|
Balance national interests with the collaborative spirit of the IPEF. Ensure that India’s participation aligns with its economic priorities, while also contributing to the overall objectives of the framework.
| Mains Question: Discuss the factors propelling the shift of global supply chains away from China and India’s competitive advantages in becoming a key supply chain hub. (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
Critical and Emerging Technologies (CET) List:
|
|---|
| About NSC:
The three-tiered NSC of India is responsible for managing security, energy, political, and economic matters of strategic importance. Headed by: The National Security Advisor (NSA) is in charge of it. Three-tiers of hiearchy: The Strategic Policy Group (SPG), the National Security Advisory Board (NSAB), and the National Security Council Secretariat |
|---|
| What is Open RAN?
It stands for open radio access network. Specifically, Open RAN is an ongoing shift in mobile network architectures that enables service providers the use of non-proprietary subcomponents from a variety of vendors. Radio Access Network(RAN):It is a major component of a wireless telecommunications system that connects individual devices to other parts of a network through a radio link. |
|---|
| Importance of Critical and Emerging Technologies.
Economic Growth and Competitiveness:
Addressing Developmental Challenges: It can provide innovative solutions to address India’s pressing developmental challenges, including:
National Security:
Develop trusted global supply chains: The COVID pandemic exposed the world’s reliance on China as a supply source over a wide spectrum of areas, from electronics to pharmaceutical ingredients.
Setting National and Global Agenda: Global trade’s landscape is swiftly evolving, where strategic and economic imperatives intertwine, with technology at their intersection.
|
|---|
| Artemis Accords: It was established U.S. State Department and NASA with seven other founding members: Australia, Canada, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, the United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom in 2020.
NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar): It is a Joint earth observation project of NASA and ISRO. Objective: To observe natural processes, including ecosystem disturbances, ice-sheet collapse, and natural hazards such as earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, landslides, etc. |
|---|
Critical and Emerging Technology hold immense potential for India’s future growth and prosperity. India must continue to invest in research and development, foster innovation, and create a conducive environment for adopting CETs to realize their transformative power.
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
