Meitei MPs & MLAs representing valley areas of Manipur meet the leaders of radical Meitei group Arambai Tenggol after a summons is issued to them.
Supreme Court intervention to stop Manipur Violence:
|
|---|
Also Read:
News Source: Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Union Minister of Road and Transport ‘Ropeway: Symposium-Cum-Exhibition’ in New Delhi announced over 200 Ropeway Projects Worth 1.25 Lakh Crore under the ‘Parvatmala Pariyojana’.
What are Ropeways?
Regulation of Ropeways in India
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
536 Compressed Biogas (CBG) Plants and 1193 Biogas Plants have been registered on the Unified Registration Portal for GOBARdhan scheme since the launch of the initiative.
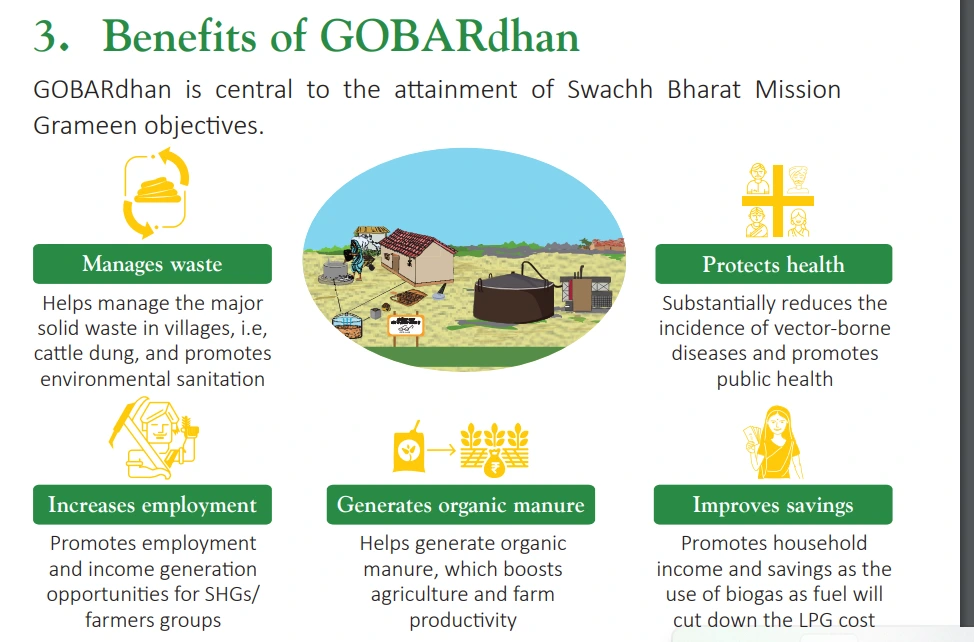
What is Compressed Biogas (CBG)?
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
For the second consecutive year the hands of the ‘Doomsday Clock’ remained at ‘100 seconds to midnight’.

News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Turkey Parliament supports Sweden’s NATO membership.
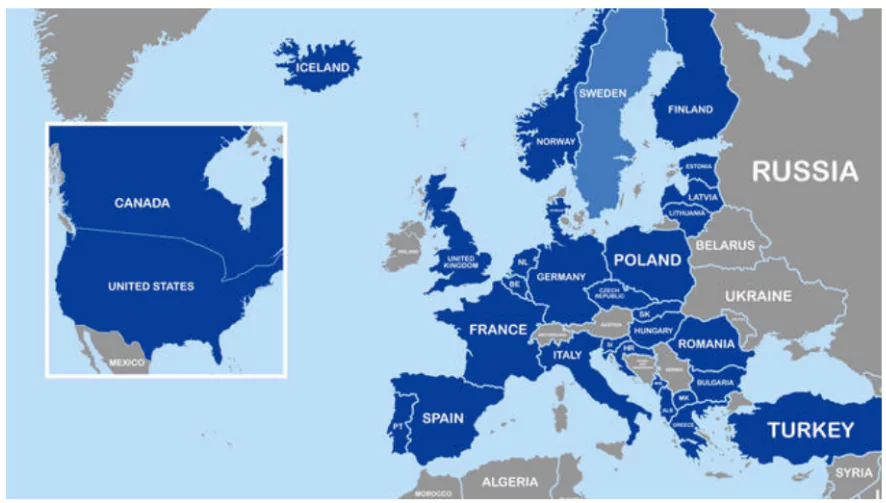
India, a NATO state? India is not a member.
|
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The National Voters Day has been celebrated on January 25 every year since 2011 to mark the foundation day of the Election Commission of India.

Abraham Lincoln’s idea and philosophy of Democracy i.e. Democracy is the government of the people, by the people and for the people, can be translated to reality only through electoral participation.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Odisha Government is establishing a melanistic tiger safari.
Pseudo-melanism.
|
|---|
Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR)
|
|---|
Also Read:
News sources: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Lake Retba is disappearing in Senegal.
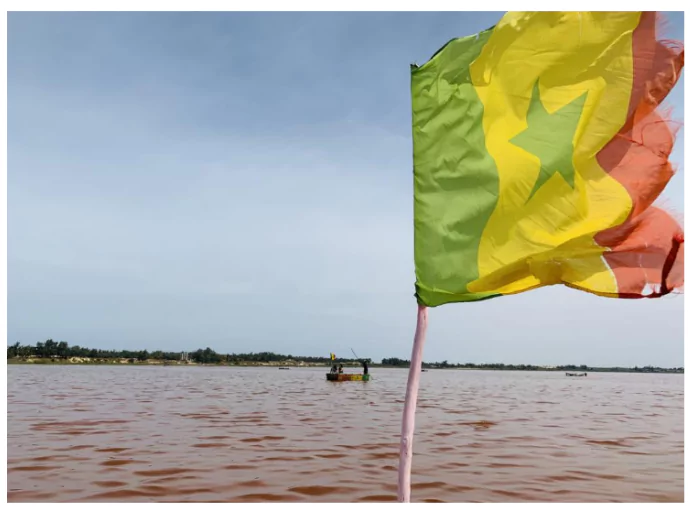

Lake Retba
| The World Health Organization (WHO) deems water potable when nitrate levels are below 50 mg/l. |
|---|
News Source: DownToEarth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Ministry of Science and Technology announced the Vaishvik Bhartiya Vaigyanik(VAIBHAV) fellowship to 22 scientists of Indian origin.
News Source: The Economic Times
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Union Health Ministry asked all states and UTs about the total number of couples and single and unmarried women who have availed surrogacy successfully since the Surrogacy Act, 2021 came into force.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
In recent years, Kaziranga National Park has been battling the highly invasive species such as – Mimosa, Siam and Ludwigia peruviana.
News Source: Down to Earth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Ministry of Health Affairs has decided to implement a new treatment regimen for leprosy.
SDG Target 3.3:
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Madhika, a language with just two speakers in Kerala with no scripts is on the brink of extinction.
Madhika is a language spoken by the Chakaliya community, It is a blend of Telugu, Tulu, Kannada, and Malayalam.
About Chakaliya Community
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Union Cabinet approves Rs 8,500 cr incentive for coal gasification projects” which was published in the Business Standards. Recently, The Union Cabinet approved a viability gap funding (VGF) scheme of ₹8,500 crore for coal gasification projects for public and private sector companies.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Conventional Sources Of Energy In India, Coal Gasification, Coal India Limited (CIL), Coal Mines In India, and Production And Challenge Of Coal & Petroleum.
Relevancy for Mains: What is Coal Gasification?: Its Methods, Need, Significance, Targets, Challenges and Related Schemes. |
|---|
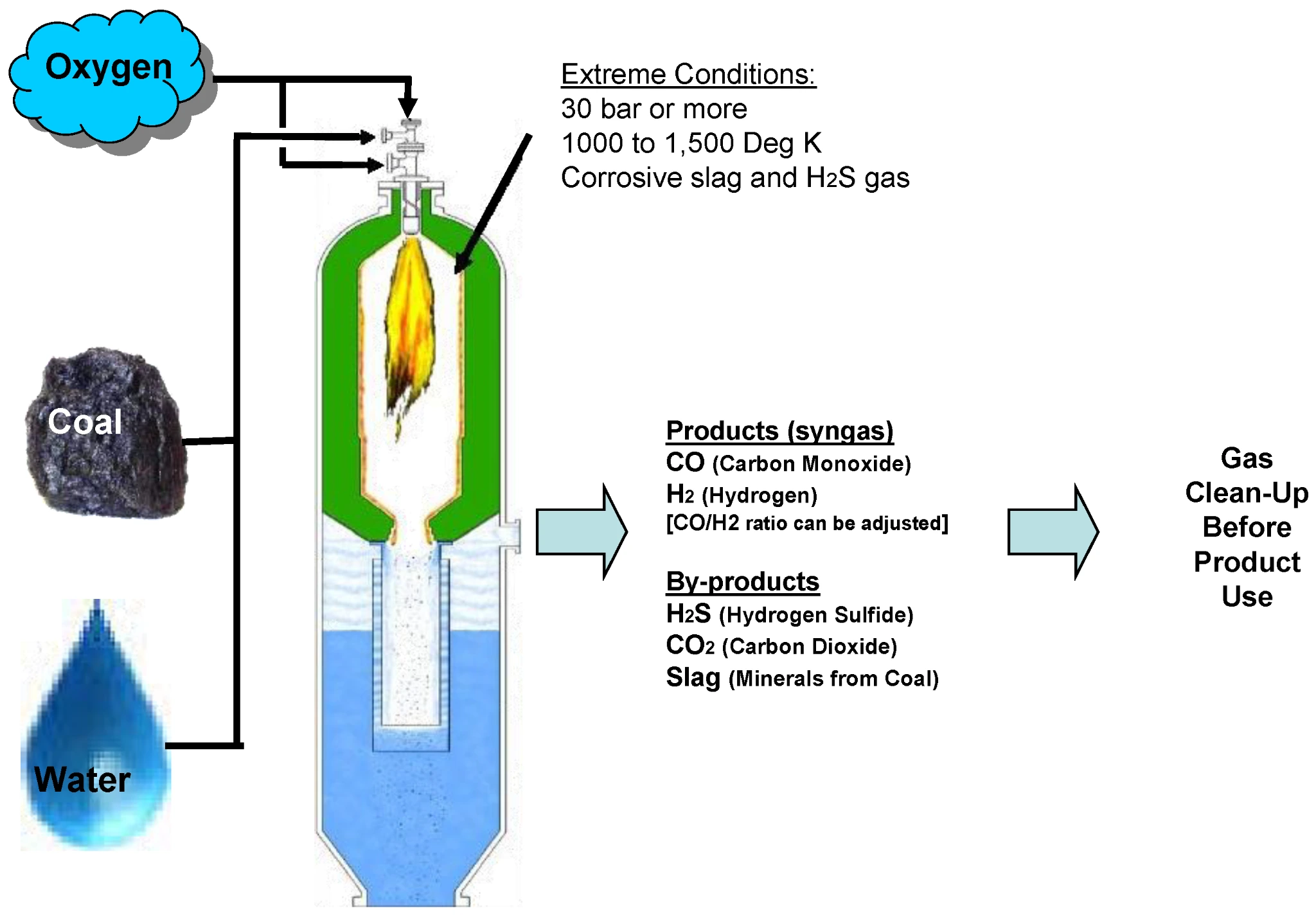
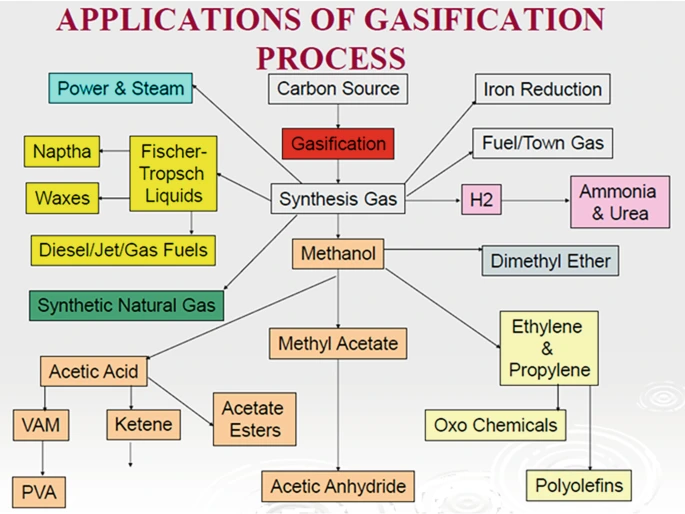 Pharmaceutical Industry: India plans to produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) domestically rather than importing them from China.
Pharmaceutical Industry: India plans to produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) domestically rather than importing them from China. The deployment of coal gasification will support India’s ‘Aatmanirbhar‘ vision, stimulate job creation and significantly reduce imports by 2030. Moreover, it presents a solution for environmental concerns, promising to lower carbon emissions and promote sustainable practices, aligning with worldwide commitments towards a greener future.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
