As per the latest ENSO update from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) of the United States La Nina conditions is predicted by the end of 2024.
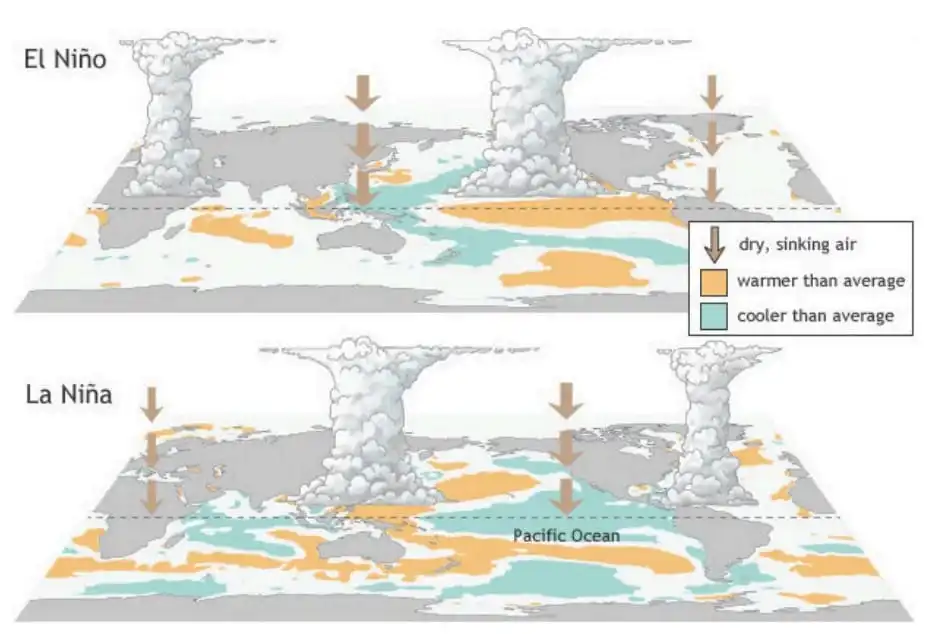
News Source: DTE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Indian Prime Minister while addressing a programme of 200th birth anniversary celebrations of Swami Dayananda Saraswati, urged people to convert the faith of Swami Dayanand Saraswati about India, into self-confidence during Amrit Kaal.

Information Need To Know
|
|---|
News Source: All India Radio
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Protest sparks over a plan for a Railway line passing through Bandipur National Park to connect Nilambur in Kerala to Nanjangudi in Karnataka.
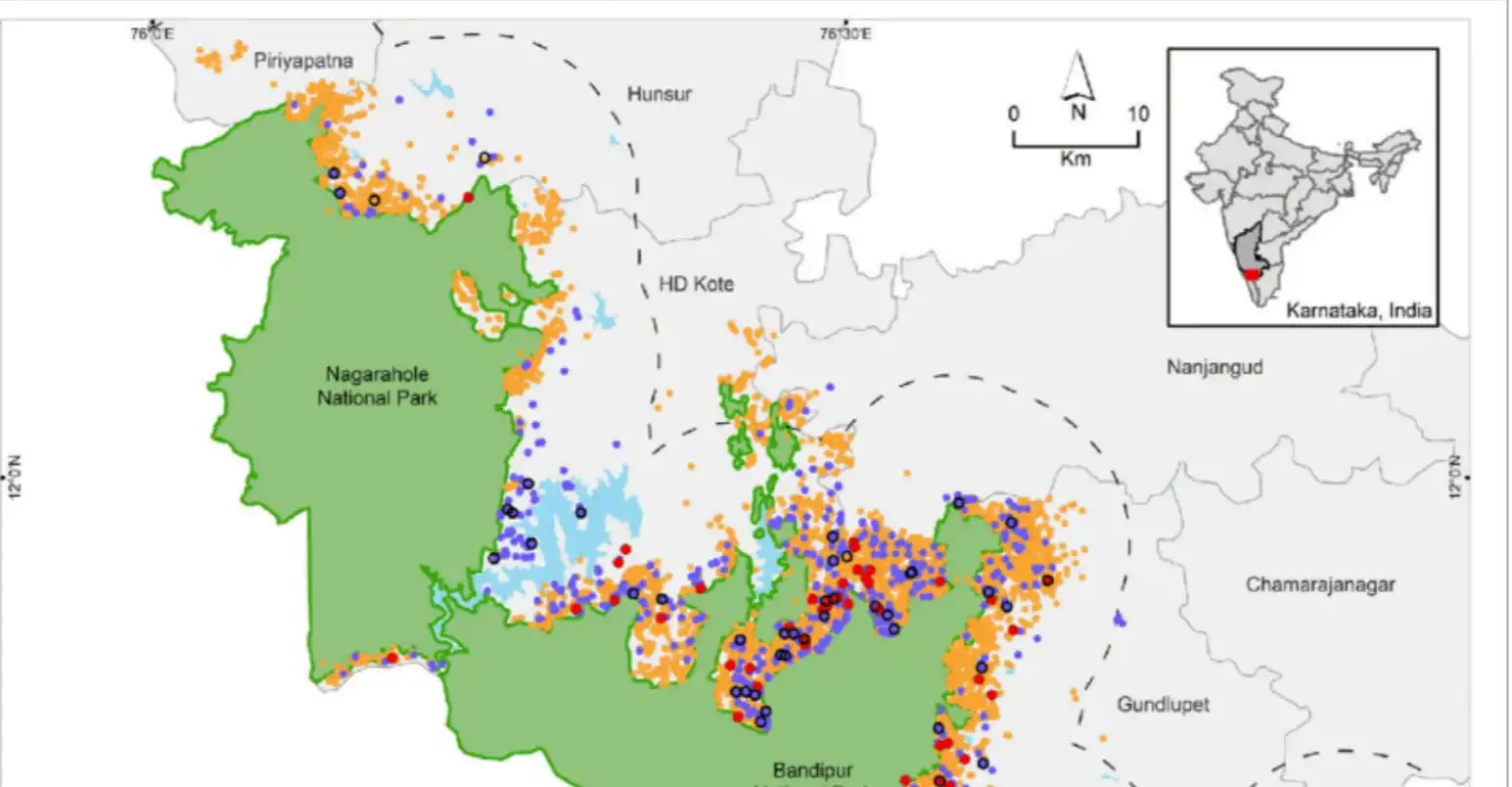
News Source: DTE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
India’s Net Direct Tax Collection rises 20.25% YOY to Rs.15.60 lakh crore, reaches over 80% of FY24 Target.
About Direct Tax
|
Corporate Income-Tax (CIT):
5 heads of Personal Income Tax (PIT):
STT ( Security Transaction Tax): It is a direct tax levied on every purchase and sale of securities that are listed on the recognized stock exchanges in India. |
|---|
Overall, the direct tax collection figures indicate robust growth revenue, with both Corporate & personal income tax contributing a steady increase. The Steady growth in tax collections reflects positively on the fiscal health of the country during the current fiscal year.
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
India’s UPI payment services launched in Sri Lanka and Mauritius and RuPay card services in Mauritius.
| Countries Accepting UPI: Bhutan (1st country), UAE (1st Gulf Country), Singapore, Nepal, Oman, France(1st European country), Sri Lanka, Mauritius.
Rupay Card Services in: Bhutan, Singapore, UAE , Nepal, Mauritius |
|---|
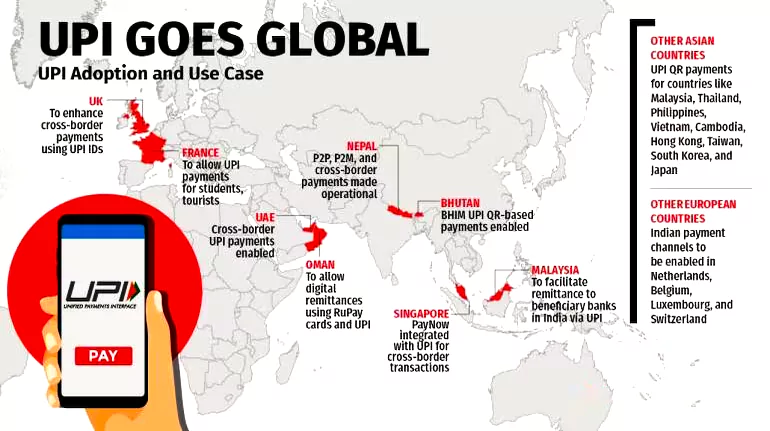 UPI Achievement:
UPI Achievement:
About NPCI
|
|---|
News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Reptiles going in the state of brumation to conserve its energy to survive harsh environmental conditions.

 They move around less and mostly stay in the darkest and coldest part of the place.
They move around less and mostly stay in the darkest and coldest part of the place. | Animals | Hibernation (Endothermic Animals) | Brumation (Ectothermic Animals) | Aestivation |
| Consumption of food | In Hibernation, animals don’t stop eating before entering inactivity | In Brumation, animals stop eating before entering inactivity | In aestivation, animals stop feeding. |
| Dormancy state | It is a state of dormancy in warm-blooded animals, | It is a state of dormancy in cold – blooded animals. | This process takes place in cold – blooded animals. |
| Activity Level | Completely inactive; no eating, drinking, or movement | May become partially active on warmer days | Animals become inactive in the summer season. |
| Metabolic Rate | metabolic rate goes down but is still active | Slowed, but not as significantly as in hibernation | metabolic activity gets low due to seeking shelter in cool underground burrow. |
| Examples | Bears, bats, groundhogs | Snakes, lizards, turtles, frogs | snails, lungfish, Desert tortoises |
| Regulation of Body Temperature | Internal | External (rely on environment) | External (rely on environment) |
News Source TheHindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
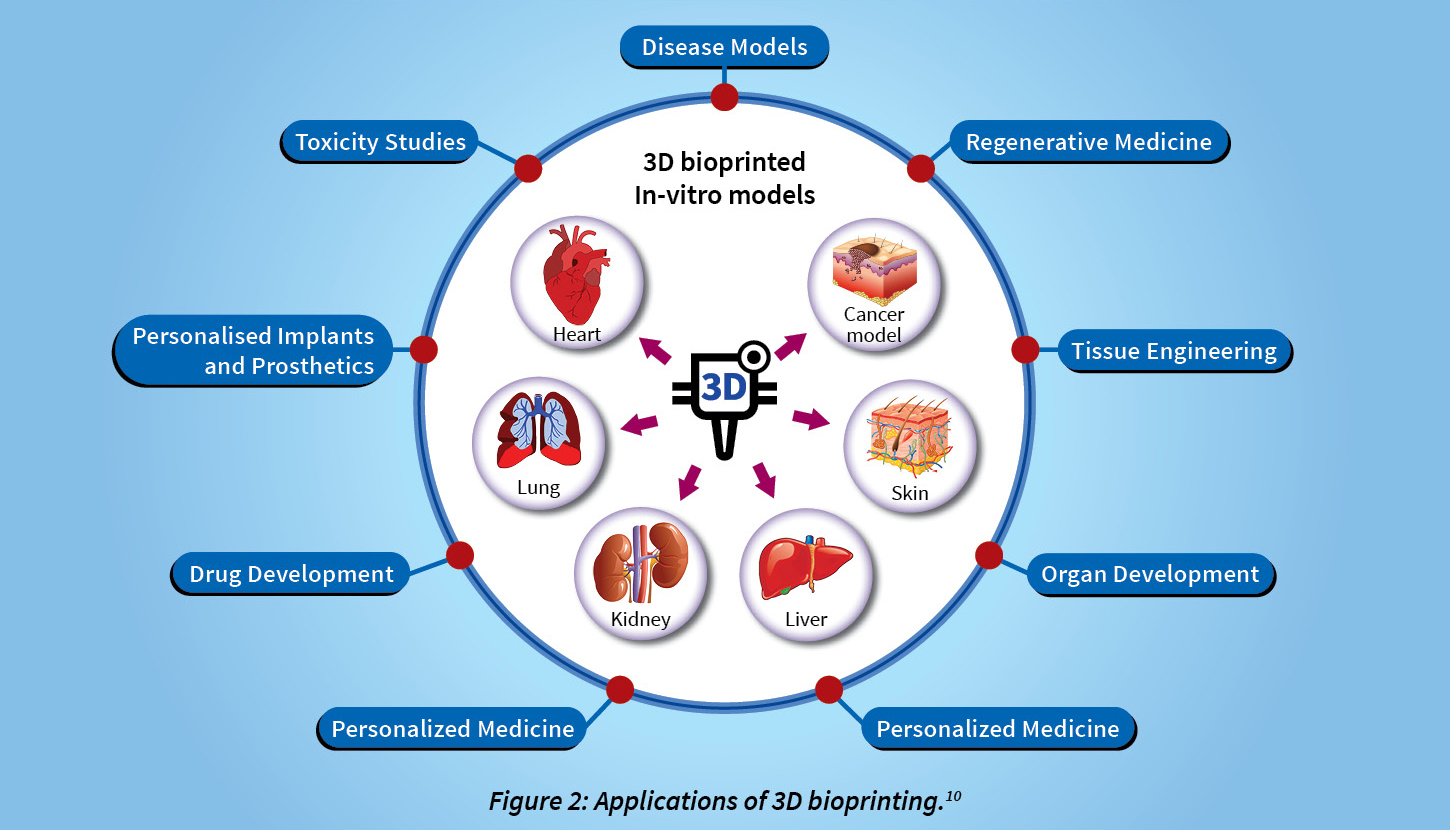
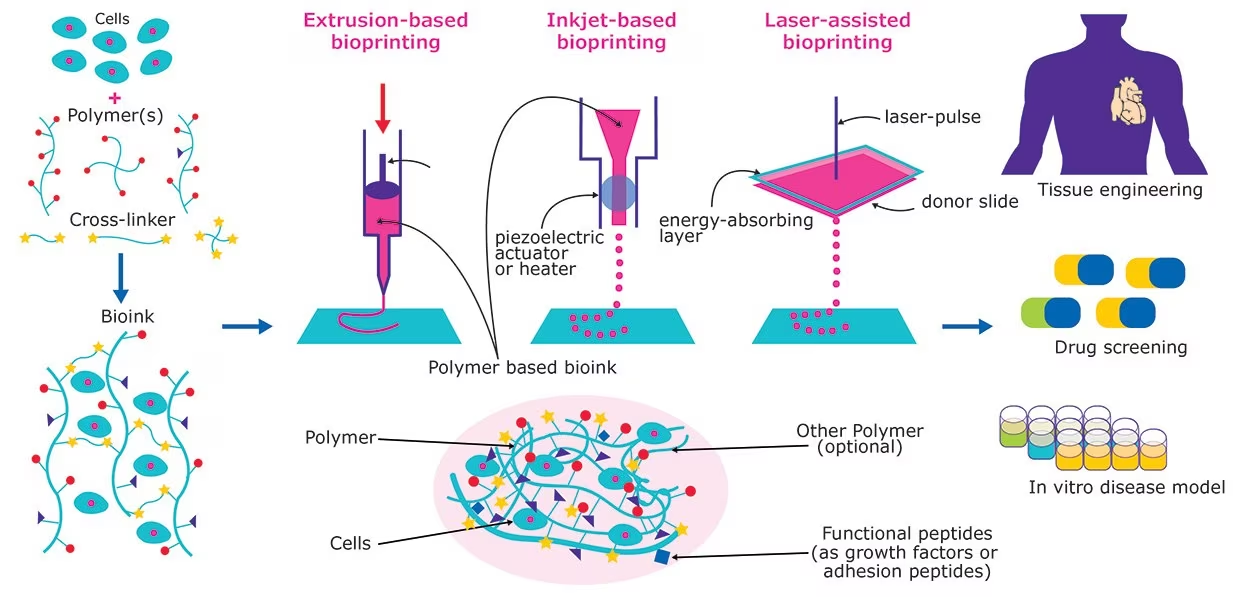
Recently, a study has been published in ‘Cell Stem Cell’ that researchers have created the first functional 3D printed brain tissue.
What is 3D Printing?
What Materials Can Be Used in 3D Printing?
3D Printing TechnologiesThere are three broad types of 3D printing technology
|
|---|
Organoids
Stem Cells
Alzheimer’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease
|
|---|
The precision of this 3D printing method allows control over cell types and arrangements, unlike miniature lab grown organs used for brain research called brain organoids. It can be used to look at the molecular mechanisms underlying brain development, human development, developmental disabilities, neurodegenerative disorders, and more. It will improve the process to create more specific brain tissues with guideable cells.
News Source: Science Alert
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Principal Scientific Advisor to the Government of India launched “SWATI Portal – Science for Women-A Technology & Innovation (SWATI)”.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “PM SVANidhi boosted annual income of street vendors by Rs 23,000: Study” which was published in the Indian Express. A recent study on the impact of PM SVANidhi, commissioned by the Union Ministry of Housing Affairs, confirmed that PM SVANidhi boosted the annual income of street vendors by Rs 23000.
| Relevancy for Prelims: PM SVANidhi Scheme, SIDBI: Small Industries Development Bank Of India, Banks In India, and Financial Inclusion.
Relevancy for Mains: PM SVANidhi: Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi Scheme: Background, Significance, Beneficiaries, and Institutions. |
|---|
The livelihood of street vendors was adversely impacted during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Who is a Street Vendor/Hawker?
|
|---|

Lending Institutions Under PM SANNidhi |
|---|
News Source: Indian Express and The Tribune
| Mains Question: COVID-19 pandemic accelerated class inequalities and poverty in India. Comment. (150 words, 10 Marks) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Vivek Katju writes: With Pakistan poll results, Imran Khan vs General Asim Munir will continue” which was published in the Indian Express. Pakistan’s emerging election results have deepened the political crisis, with implications for civil-military relations, democracy, and the economy.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Pakistan Election, Iran-Pakistan Conflict, Supreme, and Abrogation Of Article 370, Militancy In Jammu And Kashmir, and 1971 War.
Relevancy for Mains: India Pakistan Relations: Background, Current Situation, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
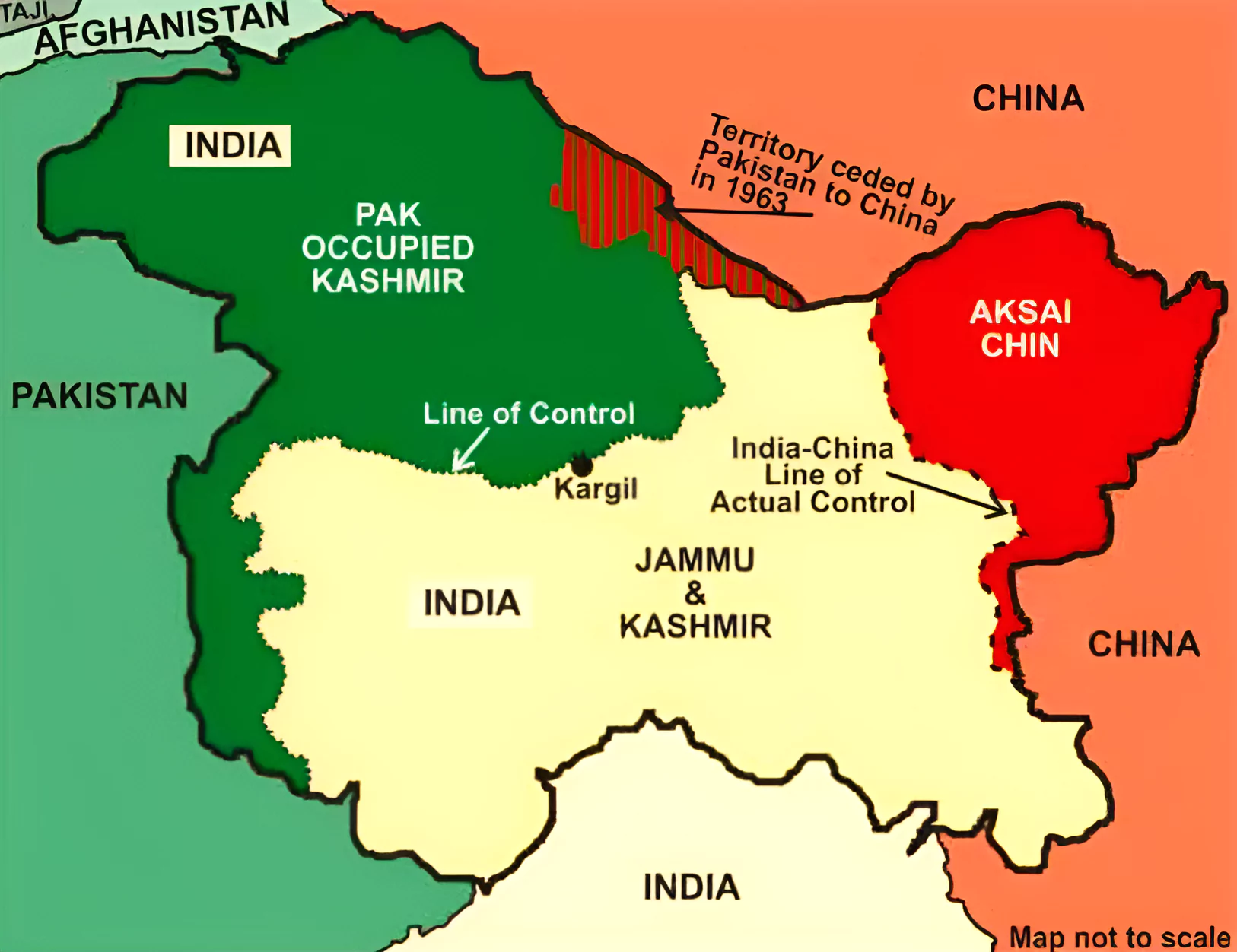 India Pakistan Wars and Agreements: Subsequent conflicts in 1965 and 1971 led to UN interventions and agreements like the Tashkent Agreement and the Shimla Agreement. India secured the Siachen glacier area in 1984 (Operation Meghdoot).
India Pakistan Wars and Agreements: Subsequent conflicts in 1965 and 1971 led to UN interventions and agreements like the Tashkent Agreement and the Shimla Agreement. India secured the Siachen glacier area in 1984 (Operation Meghdoot).
Views of Prominent Thinkers Regarding India Pakistan Relation
|
|---|
 If this state collapses, then these terror organisations will increase their network which can directly hurt India’s interests.
If this state collapses, then these terror organisations will increase their network which can directly hurt India’s interests.  Turning Tragedy into Opportunity: Reports of protests in Pakistan Occupied Kashmir (PoK) raise concerns about the potential for law-and-order issues and refugee influx. However, activists report protests in PoK with readiness to join India presents an opportunity to address regional instability and potentially expand its influence.
Turning Tragedy into Opportunity: Reports of protests in Pakistan Occupied Kashmir (PoK) raise concerns about the potential for law-and-order issues and refugee influx. However, activists report protests in PoK with readiness to join India presents an opportunity to address regional instability and potentially expand its influence.
Soft Power Dimensions for India Pakistan Relations
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
