
The joint Coast Guard exercise between India and the United States of America ‘Sea Defenders 2024’ is scheduled to take place on March 9-10 off the coast of Port Blair.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the continuation of Rs.300 targeted subsidy to PM Ujjwala Yojana Consumers.

News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Prime Minister dedicated and launched 52 tourism sector projects worth more than Rs 1400 crores under the Swadesh Darshan and PRASAD Scheme.
The Government of India launched the Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD) Schemes in 2014-2015.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
AI models are resource-intensive regarding energy consumption, data requirements, and high computational costs and contribute to carbon emissions.
It can be split into two phases: Training and Inference.
They work by processing and learning patterns from data, enabling them to make predictions.
How the Human Brain Process Information:
|
|---|
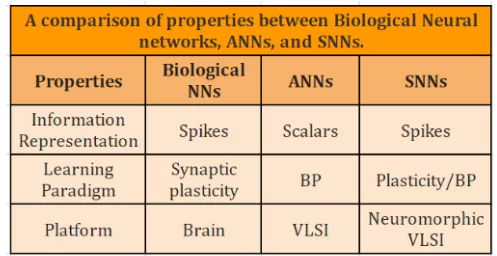
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Union Cabinet has approved the comprehensive national-level India AI mission with a budget outlay of Rs.10,371.92 crore for the period of 5 years, marking a significant step towards bolstering India’s AI ecosystem.
Compute Capacity
|
|---|
About INDIA AI:
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A committee of 18 scientists have voted down a proposal to declare the start of the Anthropocene or Human Epoch in a geologic time scale.
Geologic Time Scale (GTS)
|
|---|
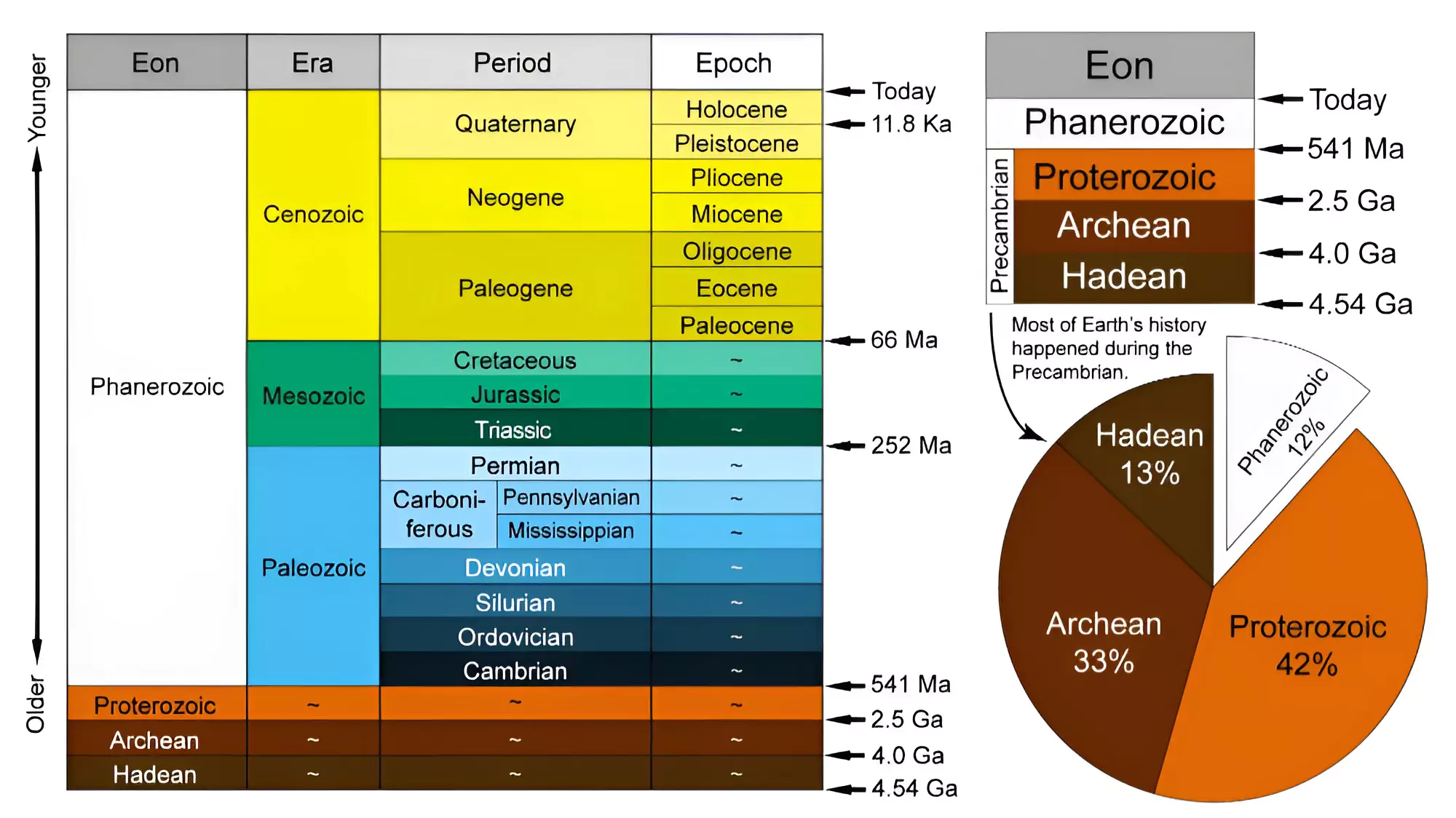
The International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS)
The International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS)
|
|---|
Holocene Epoch:
|
|---|
News Source: the Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
According to a new study, James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) captured the oldest-known dead galaxy, which stopped forming stars 13 billion years ago.

News Source: Down To Earth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Maritime Development Fund is a proposed fund in India for the ship-building industry.
 Growth of cruise tourism: The Maritime Development Fund will also encourage the growth of cruise tourism.
Growth of cruise tourism: The Maritime Development Fund will also encourage the growth of cruise tourism.News Source: TheHindubusinessline
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, The Union Government has extended the ceasefire agreement with the National Socialist Council of Nagaland/K-Khango & NSCN (Reformation) for one year.
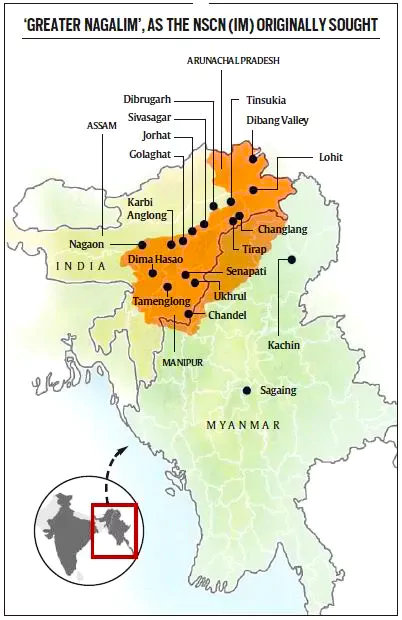

Consistent policy-making, prolonged talks for conflict resolution in the northeast, regardless of the ruling government & prioritising infrastructure development, especially roads and power.
Opening up the region will allow its people to access modern amenities and utilize its natural resources for their betterment.
Also Read:
News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This Article is based on the news “Notification of Rules framed under Section 49M of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (as amended in 2022” which was published in the PIB. Notification of Rules Framed Under Section 49M of the Wildlife Protection Act 1972 have been released by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Forests In India, BIODIVERSITY,Protected Areas, Forest Conservation, Forest Conservation Act 1980, Rising Human Wildlife Conflict, and National Parks & Wildlife Sanctuaries In India
Relevancy for Mains: Wildlife Protection Act: Provisions, Sections and Schedules. |
|---|
 The act protects wild animals, birds, and plants and matters connected with them. It extends to the whole of India.
The act protects wild animals, birds, and plants and matters connected with them. It extends to the whole of India.CITES:
|
|---|
| Prelims PYQ (2020):
If a particular plant species is placed under Schedule VI of The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, what is the implication? (a) a license is required to cultivate that plant. (b) Such a plant cannot be cultivated under any circumstances. (c) It is a Genetically Modified crop plant. (d) Such a plant is invasive and harmful to the ecosystem. Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Critically assess the enforcement mechanisms outlined in the Wildlife Protection Act. How effective are these mechanisms in deterring wildlife-related offenses? (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This Article is based on the news “India, Japan agree to make bilateral relationship responsive to emerging geopolitical, geoeconomic, geotechnological trends” which was published in the AIR. Recently, the 16th India-Japan Foreign Minister’s Strategic Dialogue was held in Tokyo, Japan.
| Relevancy for Prelims: India Japan Relations, Joint Military Exercise ‘DHARMA GUARDIAN’, Japan’s Moon Landing Mission, and Indian Diplomacy.
Relevancy for Mains: India Japan Relations: Background, Challenges, Developments, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Prominent Figures in India Japan Relations:
|
|---|
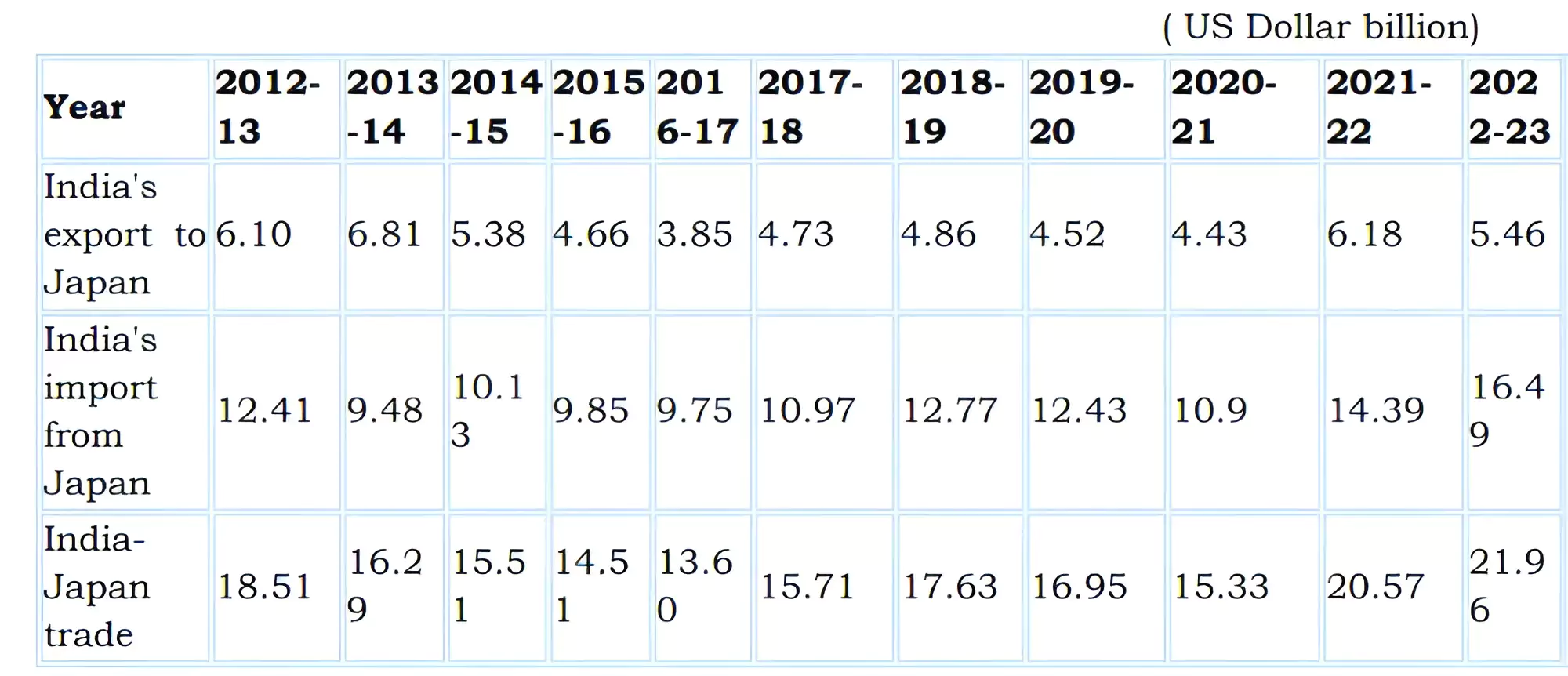
 Japanese Investment and Official Development Assistance (ODA):
Japanese Investment and Official Development Assistance (ODA):
India is significantly deepening its ties with Southeast Asian countries. India should consider taking its third-country developmental model with Japan into the sub-region of the greater Indo-Pacific at a time when resident countries are looking for alternative sources of development and security amidst the polarising dynamics of the U.S.-China power competition.
| Prelims PYQ (2019):
Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (a) Japan (b) Russia (c) The United Kingdom (d) The United States of America Ans: (b) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
