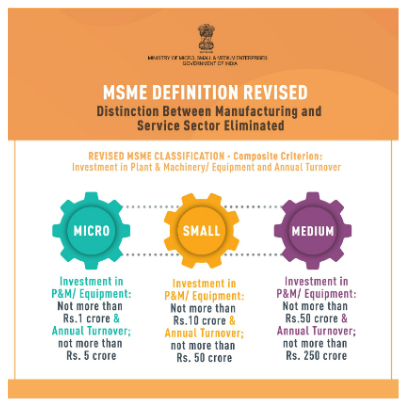
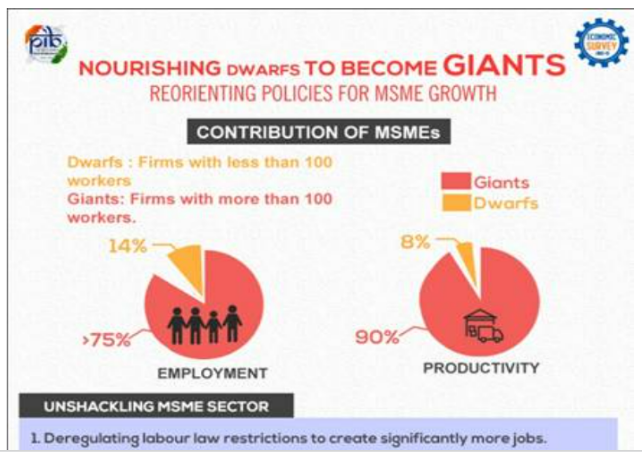
 However, to address the global market, India must aim for at least a 10 percent share of the global trade.
However, to address the global market, India must aim for at least a 10 percent share of the global trade.Schemes/ Government Initiatives for MSME Sector:
|
Source: Business Standard
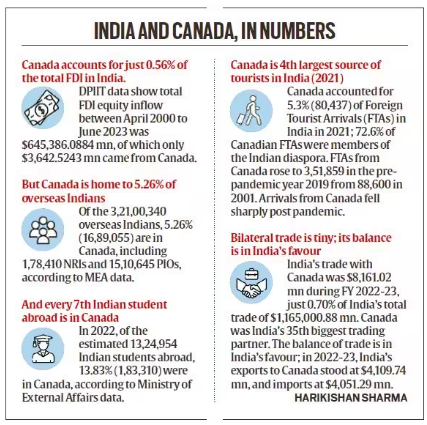 India and Canada have a long history of bilateral relations, underpinned by shared values of democracy, pluralism, and people-to-people ties.
India and Canada have a long history of bilateral relations, underpinned by shared values of democracy, pluralism, and people-to-people ties.Canada is becoming an international hub of the Anti-India movement as well as a safe haven for criminals due to the following factors:
|
Potential Implications of worsening India-Canada Relations:
|
Source: Indian Express
Subject: GS-03: Indian Economy
Non-Performing Asset (NPA):
|
News Source: Business Standard
Subject: GS-03: Environment and Ecology
News Source: Mint
Subject: GS-03: Indian Economy
News Source: The Hindu
| U.N.’s Climate Ambition Summit | The Climate Ambition Summit (CAS) convened in New York, as a part of United Nations General Assembly.
Key Points from the Climate Ambition Summit (CAS):
|
| Nadi Utsav | Recently, the fourth ‘Nadi Utsav’ has been organized by the National Mission on Cultural Mapping (NMCM) of Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA)
About ‘Nadi Utsav’ Festival:
|
| WFME Recognition for Indian Medical Graduates: | The National Medical Commission (NMC) has been granted World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) Recognition Status for 10 years.
Benefit:
The World Federation for Medical Education (WFME):
National Medical Commission (NMC):
|
| AI chatbot for PM-Kisan scheme | The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare’ unveiled AI chatbot- the first integration of its kind with a major flagship scheme of the central government — the PM-KISAN scheme.
Key Features:
|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
