News Source: Indian Express
| Prelims Question (2022)
The term “Levant” often heard in the news roughly corresponds to which of the following regions ? (a) Region along the eastern Mediterranean shores (b) Region along North African shores stretching from Egypt to Morocco (c) Region along Persian Gulf and Horn of Africa (d) The entire coastal areas of Mediterranean Sea Ans: (a) |
|---|
Games of Skill vs Games of Chance: Validity and Laws
|
|---|
News Source: Tribune
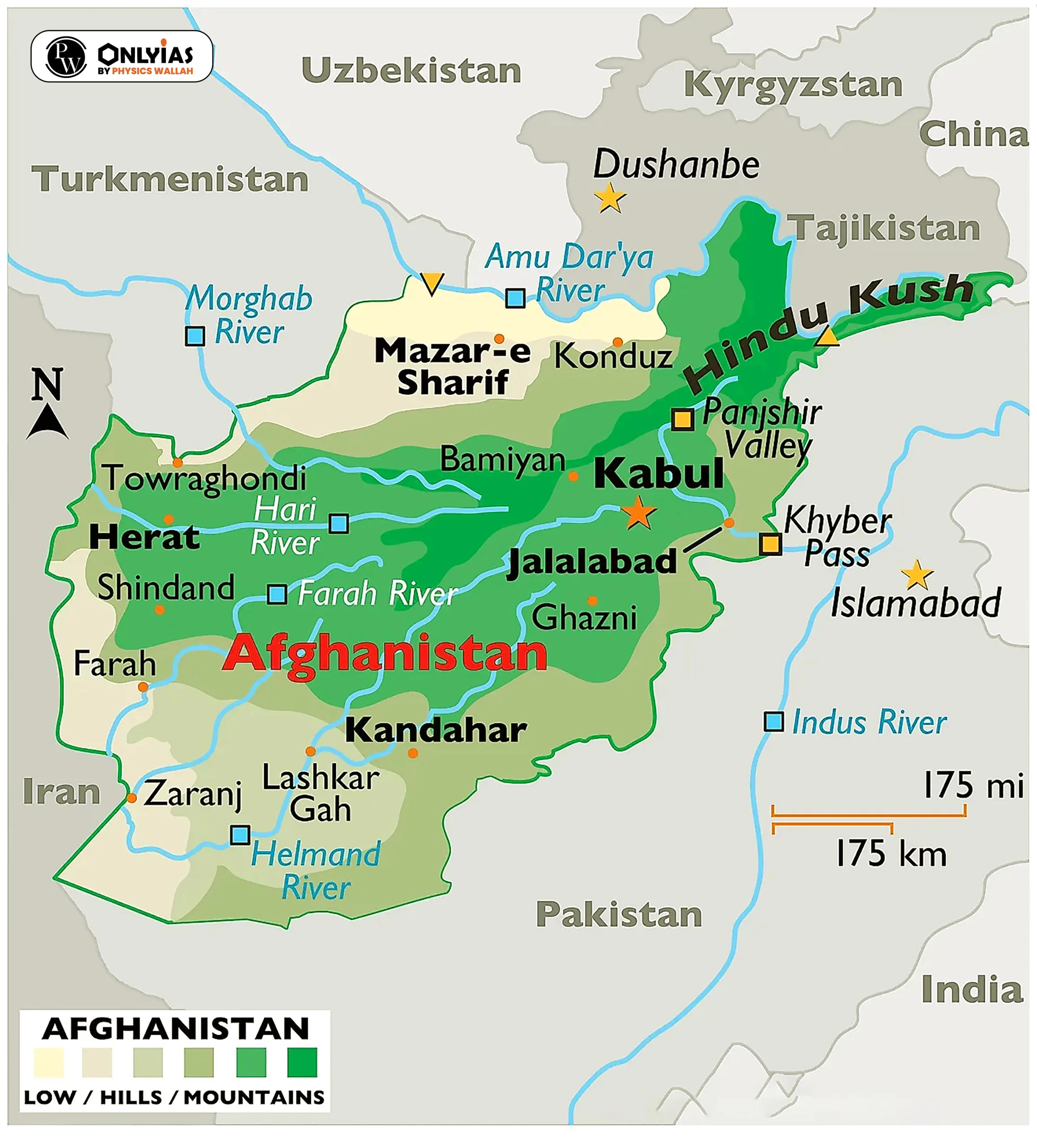
What is Fault?
Tectonic plates
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Mains Question (2021): Discuss about the vulnerability of India to earthquake related hazards. Give examples including the salient features of major disasters caused by earthquakes in different parts of India during the last three decades. |
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Prelims Question (2022)
Consider the following statements: 1. Other than those made by humans, nanoparticles do not exist in nature. 2. Nanoparticles of some metallic oxides are used in the manufacture of some cosmetics. 3. Nanoparticles of some commercial products which enter the environment are unsafe for humans. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 3 only (c) 1 and 2 (d) 2 and 3 Ans: (d) |
|---|
| Relevancy for Prelims: ISRO, Gaganyaan Mission, Flight Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1), Crew Module (CM) and Crew Escape Systems (CES).
Relevancy for Mains: ISRO conducted safety tests for Gaganyaan Mission, Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 (TV-D1), Significance and Challenges of Gaganyaan mission for India. |
|---|
What is Gaganyaan mission?
|
|---|
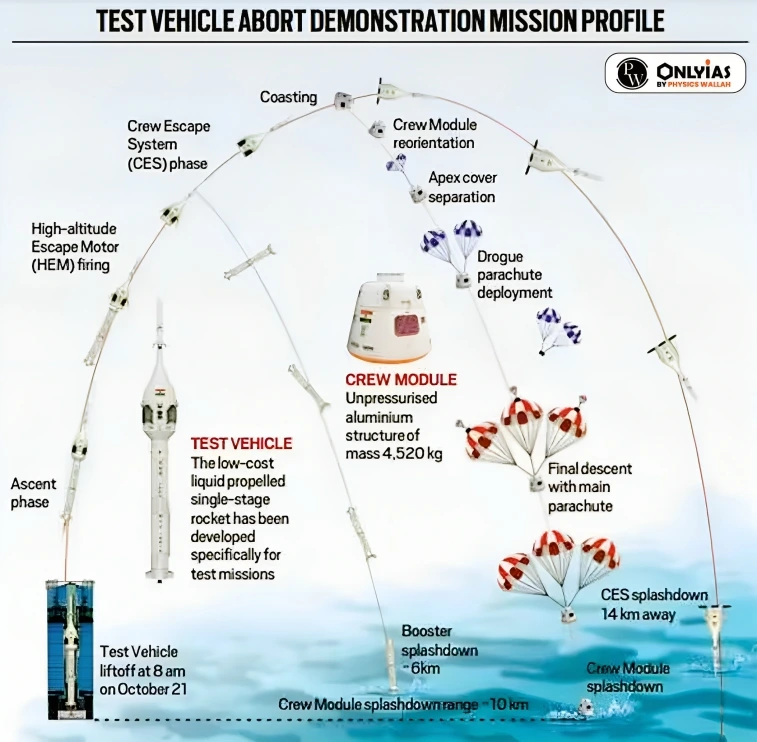
The crew escape system (also known as Launch Abort System or Launch Escape System) is an emergency exit option critical to manned space missions. It is designed to pull away the crew module, take it to a safe altitude and bring it safely back on the earth in the event of a launch abort or during the vehicle’s ascent.
Significance of test flight
|
|---|
Also read: New Targets for ISRO: Indian Space Station by 2035, Indian on Moon by 2040
The successful execution of this Flight Test Vehicle Abort Mission-1 for the Gaganyaan will mark a critical milestone in India’s journey towards achieving human spaceflight capabilities and will reinforce ISRO’s commitment to advancing space exploration. It will elevate India’s reputation as a technologically advanced nation and a player in international space exploration.
| Prelims Question (2018)
With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: 1. PSLVs launch the satellite useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites. 2. Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the samevposition in the sky, asbviewed from a particular location in Earth. 3. GSLV Mk III is a fourstaged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors; and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 (c) 1 and 2 (d) 3 only Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Mains Question: What is the importance of Gaganyaan mission to India? Discuss various challenges related to the mission. (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
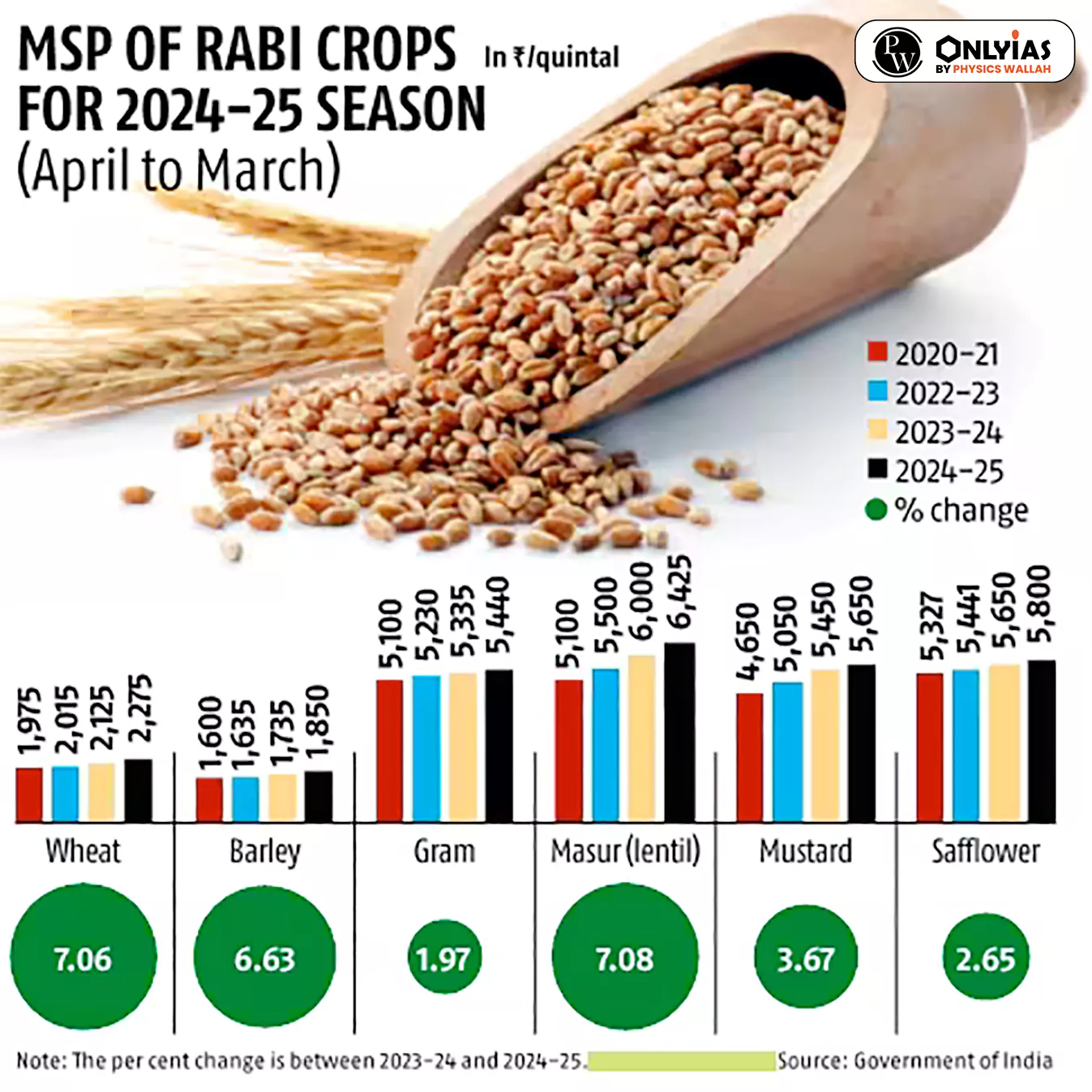
| Relevancy for Prelims: Agriculture, Minimum Support Prices, Union Budget, Swaminathan committee report, Commission for Agricultural Costs & Prices (CACP), and Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA).
Relevancy for Mains: Government Approves Minimum Support Price (MSP) for Rabi Crops, About MSP, and how it calculated and who determined it. |
|---|
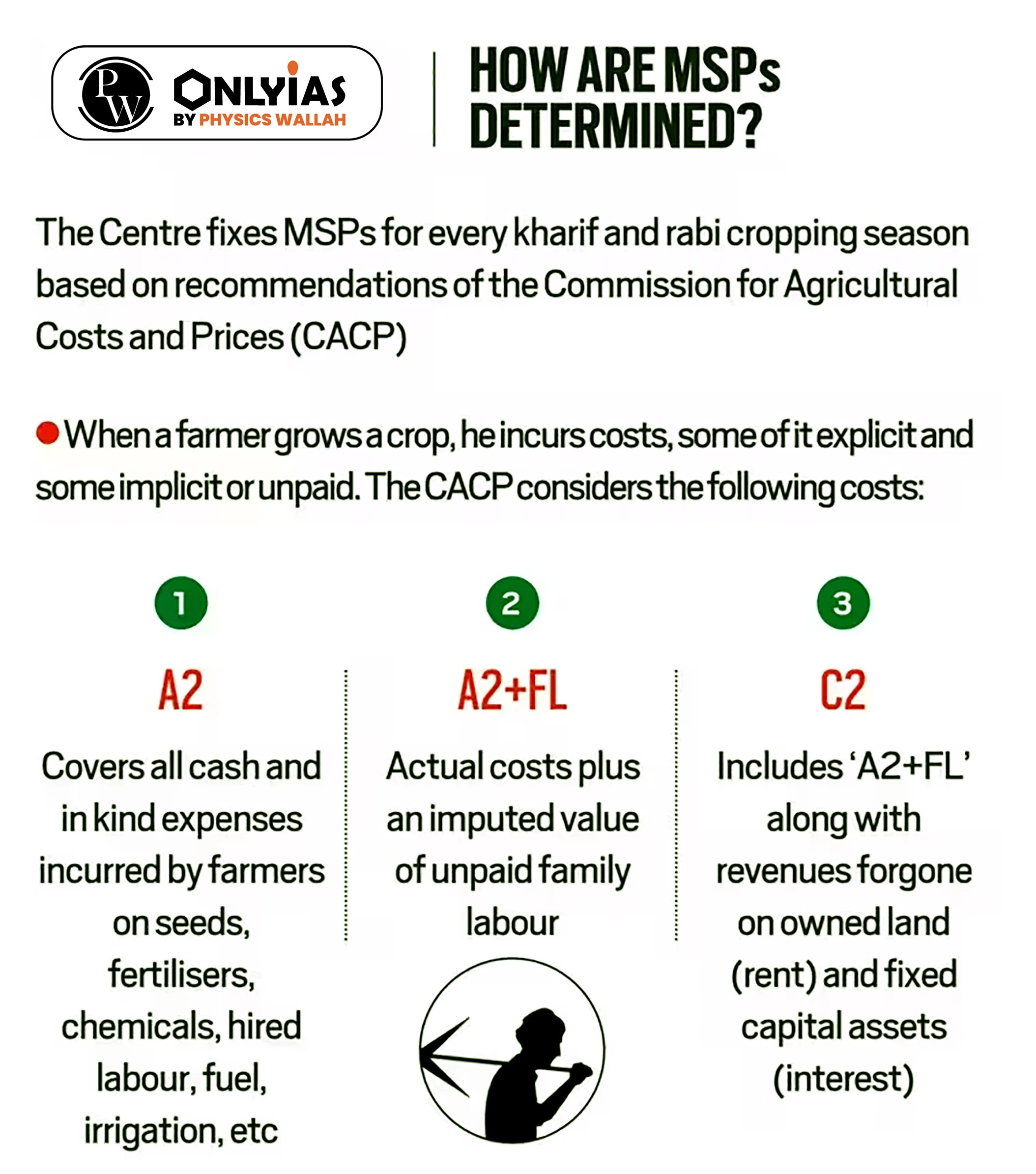
Commission for Agricultural Costs & Prices (CACP)
|
|---|
It is also known as the Swaminathan Commission, recommended that the Minimum Support Price should at least be 50 percent more than the weighted average CoP, which it refers to as the C2 cost. The government maintains that the MSP was fixed at a level of at least 1.5 times of the all-India weighted average CoP, but it calculates this cost as 1.5 times A2+FL.
| Crops | C2 | MSP announced (₹ / qtl ) | MSP acc to C2+50% |
| Wheat | 1652 | 2,275 | 2,478 |
| Barley | 1614 | 1,850 | 2,421 |
| Gram | 4547 | 5,440 | 6,820.5 |
| Lentil | 4890 | 6,425 | 7,335 |
| Rapeseed & Mustard | 4068 | 5,650 | 6,102 |
| Safflower | 5414 | 5,800 | 8,121 |
| Crops | CoP (A2) (₹/qtl) | CoP (A2+FL) | CoP (C2) |
| Wheat | 903 | 1,128 | 1,652 |
| Barley | 758 | 1,158 | 1,614 |
| Gram | 2,651 | 3,400 | 4,547 |
| Lentil | 2,543 | 3,405 | 4,890 |
| Rapeseed & Mustard | 1,957 | 2,855 | 4,068 |
| Safflower | 2,830 | 3,807 | 5,414 |
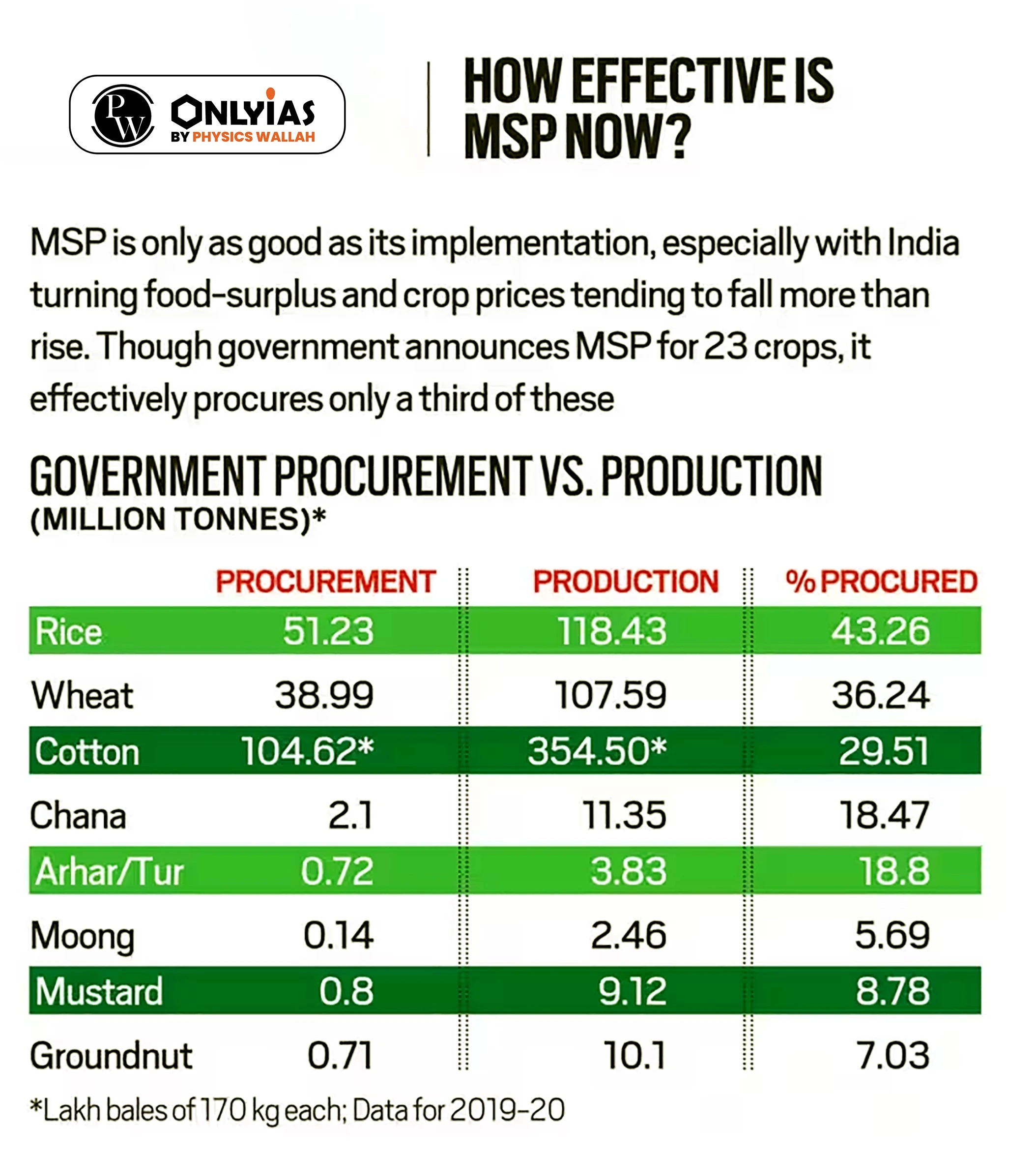
Also read: How Does Monsoon Rainfall Impact the Indian Economy?

Also read: PM-PRANAM Scheme
Dalwai Committee (2016) Recommendation for Doubling Farmers Income: The committee has observed that an increase in the Minimum Support Price could be one of the instruments for enhancing farmers’ income.
Price Deficiency Schemes: The Niti Aayog has suggested a ‘Price Deficiency Payment’ system to address the gaps in Minimum Support Price (MSP) based procurement of crops.
Direct Income Transfer: The idea here is to extend MSP benefits to the small and marginal farmers and in states where government procurement is currently insignificant.
Structural and Governance Reforms in Agriculture: It includes institutional mechanisms at district, state & national levels for coordination & convergence of various government schemes, a digital monitoring dashboard at district, state & national levels for seamless & real-time monitoring of fields, utilizing Panchayat Raj Institutions, and farm income measurement as key delivery channels for transparent and inclusive development.
Agri-R&D and agricultural-extension systems: Agricultural extension is critical to improve farm productivity and to translate the same into increased income.
Strategies for Sustainability in Agriculture: It is essential that sustainable agriculture is not limited to the practice of alternate production systems(such as Climate Resilient Agriculture, Rainfed Agriculture, Integrated Farming System, Organic Farming, etc.) in certain geographies alone, but goes beyond into larger cultivation practices by incorporating evidence-based and good agricultural practices.
Farming over the years, for the majority, especially small and marginal farmers, has not turned out to be remunerative. A rise in their income could be the long-term answer to farmers’ financial distress.
| Prelims Question (2020)
Consider the following statements: 1. The Government of India provides Minimum Support Price for niger (Guizotia abyssinicia) seeds. 2. Niger is cultivated as a Kharif crop. 3. Some tribal people in India use niger seed oil for cooking. How many of the above statements are correct? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) All three (d) None Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Mains Question: Explain the changes in cropping pattern in India in the context of changes in consumption pattern and marketing conditions. |
|---|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
