| Acharya JB Kripalani (1888 – 1982)  |
About Acharya JB Kripalani Early Life: Jiwatram Bhagwandas Kripalani was born in Hyderabad, Sindh in 1888.
Role in India’s Independence Movement:
Contribution to Constitution Making:
Later Contributions:
Key Writings: My Times: An Autobiography, Gandhi His Life and Thought, Some stray thoughts. |
| Maulana Abul Kalam Azad (1888 – 1958)  |
Early Life: He was born in Mecca, Saudi Arabia.
Role in India’s Independence Movement:
Contribution to Constitution Making:
Later Contributions
Key Writings: An Autobiographical Narrative. Other important books include Gubar-e-Khatir, Azad on Pakistan, and Tazkirah. |
News Source: Indian Express
News Source: Live Mint
News Source: The Hindu
Global Tiger Recovery Program (GTRP)
Global Tiger Recovery Program 2.0 (2023-34)
CITES (the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora):
|
|---|
News Source: DTE
News Source: Business standard
About FAO
|
|---|
El Nino
|
|---|
News Source: DTE
| CBIC: Central Bureau of Communication is the Media Unit of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting which is the designated organization for issue of advertisements through all forms of media. |
|---|
News Source: The Indian Express
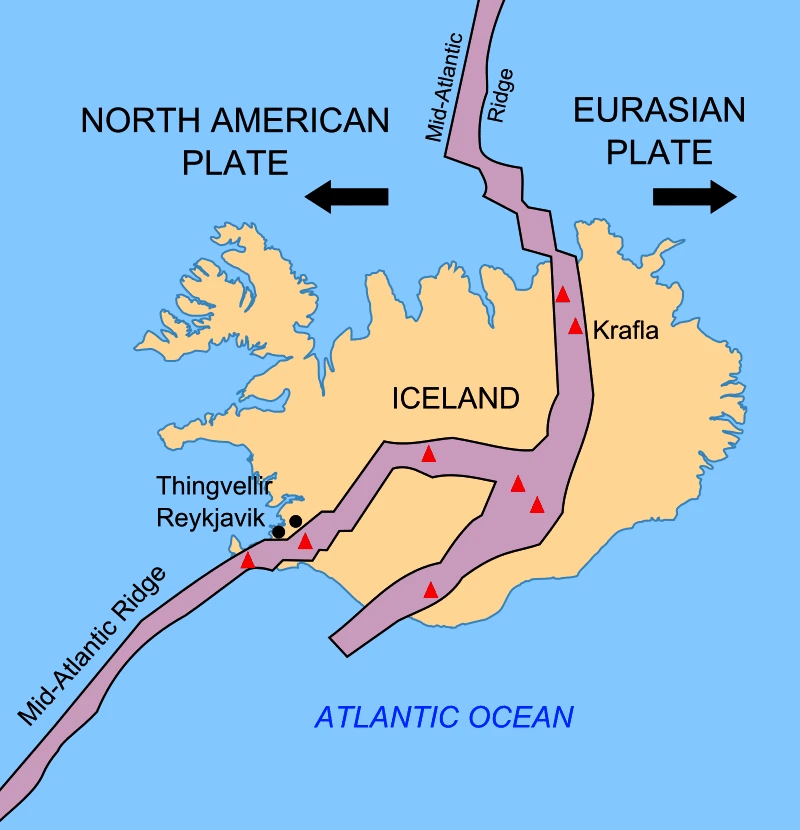
News Source: Moneycontrol
News Source: The Indian Express
News Source: The HIndu
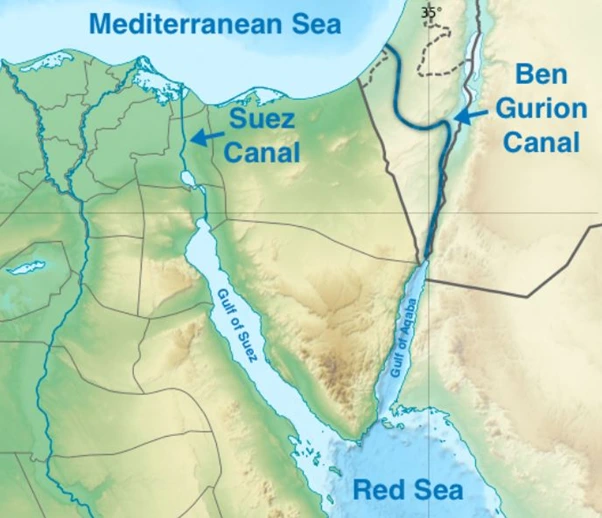
News Source: The Indian Express
| Article 131 of the Constitution empowers a state to move the Supreme Court directly in case of dispute with the Centre or any other state. |
|---|
SC Led Structural Changes: The landmark judgement in Vineet Narain v. Union of India in 1997 laid out several steps to secure the autonomy of CBI.
|
|---|
Also Read: CVC Report On Corruption
Addressing structural problems in the Central Bureau of Investigation, ensuring its independence, and making necessary improvements are crucial for making the investigative agency trustworthy and effective in upholding the law in India.
India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue
Key Outcomes of India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue
|
|---|
Know more about the India-US Bilateral Relations here.
The evolving India-US relations holds significant importance in shaping the global order of the 21st century. To fully unlock the potential of this partnership, both governments must focus on reducing bilateral and multilateral bottlenecks and embracing diplomatic flexibility and exploring innovative approaches.
| Mains Question (2020): What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. |
|---|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
