Context: The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has formed a committee headed by Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) Director-General Anish Dayal Singh to probe the parliament security breach on 13th December 2023.
Previous attack on Parliament
|
|---|
Source: The Hindu
Context: Recently, “Krutrim AI”, an indigenous AI model, was launched in Bengaluru.
Large Language Model (LLM)
|
|---|
News source: Business Standard
Context: Two Siberian Tigers (Lara and Akamas) arrived at Darjeeling’s Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park from Cyprus.
About Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNHZ)
|
|---|

About Cyprus
|
Also Read: Tiger Reserves In India 2023
News source: Hindustan Times
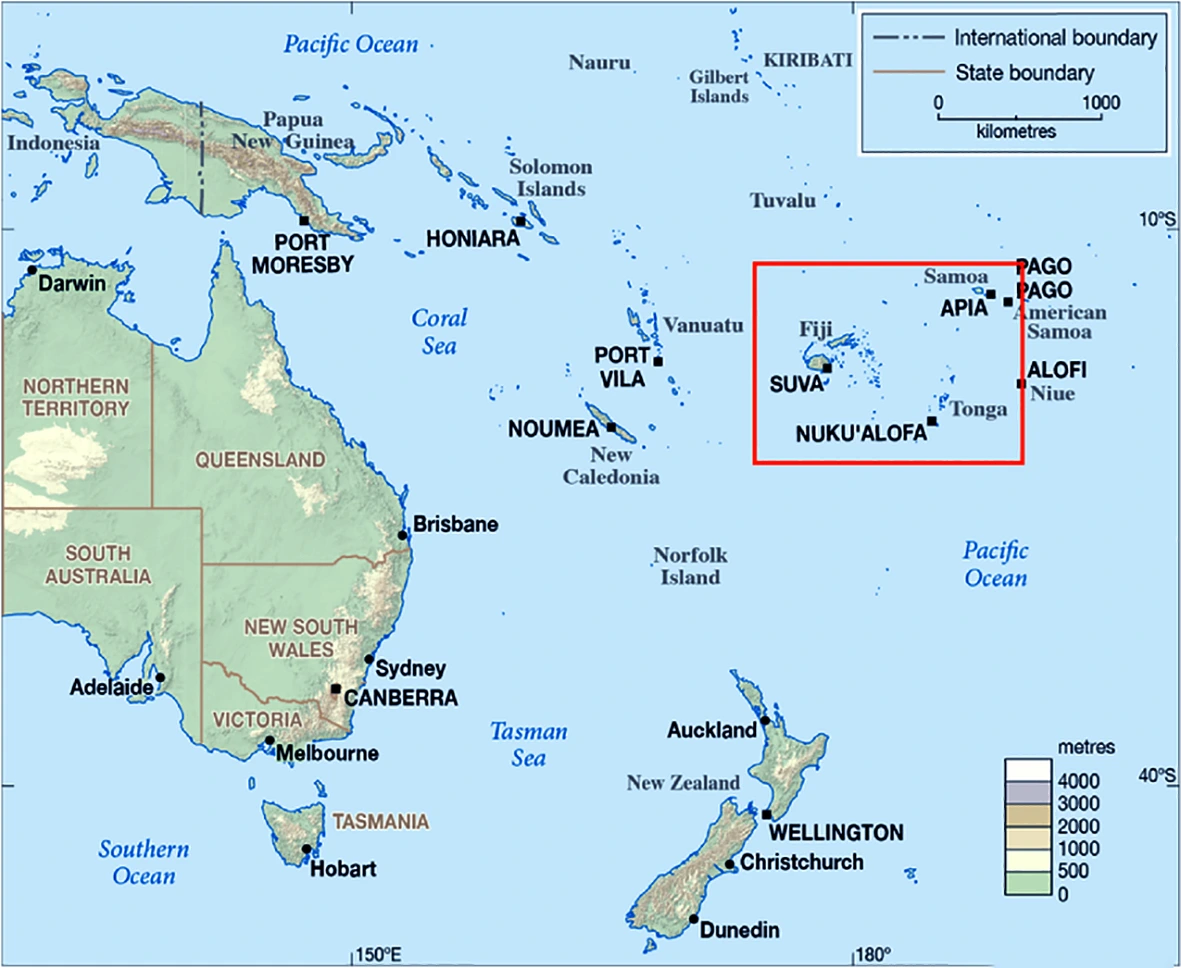
Context: An Indian Delegation in Fiji, led by a joint secretary of the Ministry for External Affairs, met the Deputy PM of Fiji to discuss the proposed 100-bed super specialty hospital.
About Fiji
|
|---|
Must Read: UN Climate Summit 2023 or COP28: Outcomes, Agreements and Challenges
Source: The Economic Times
Context: Union Minister for Tribal Affairs and Agriculture & Farmers Welfare inaugurated the Manthan Shivir 2023 to finalize the implementation plan of Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN Yojana)
About Birsa Munda:
|
|---|
 Financial outlay: Around Rs. 24,000 crores.
Financial outlay: Around Rs. 24,000 crores.About PVTGs
To Read More about PVTGs, here. |
|---|
News source: PIB
Context: Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament, and Development for 2023 has been jointly awarded to Daniel Barenboim and Ali Abu Awwad
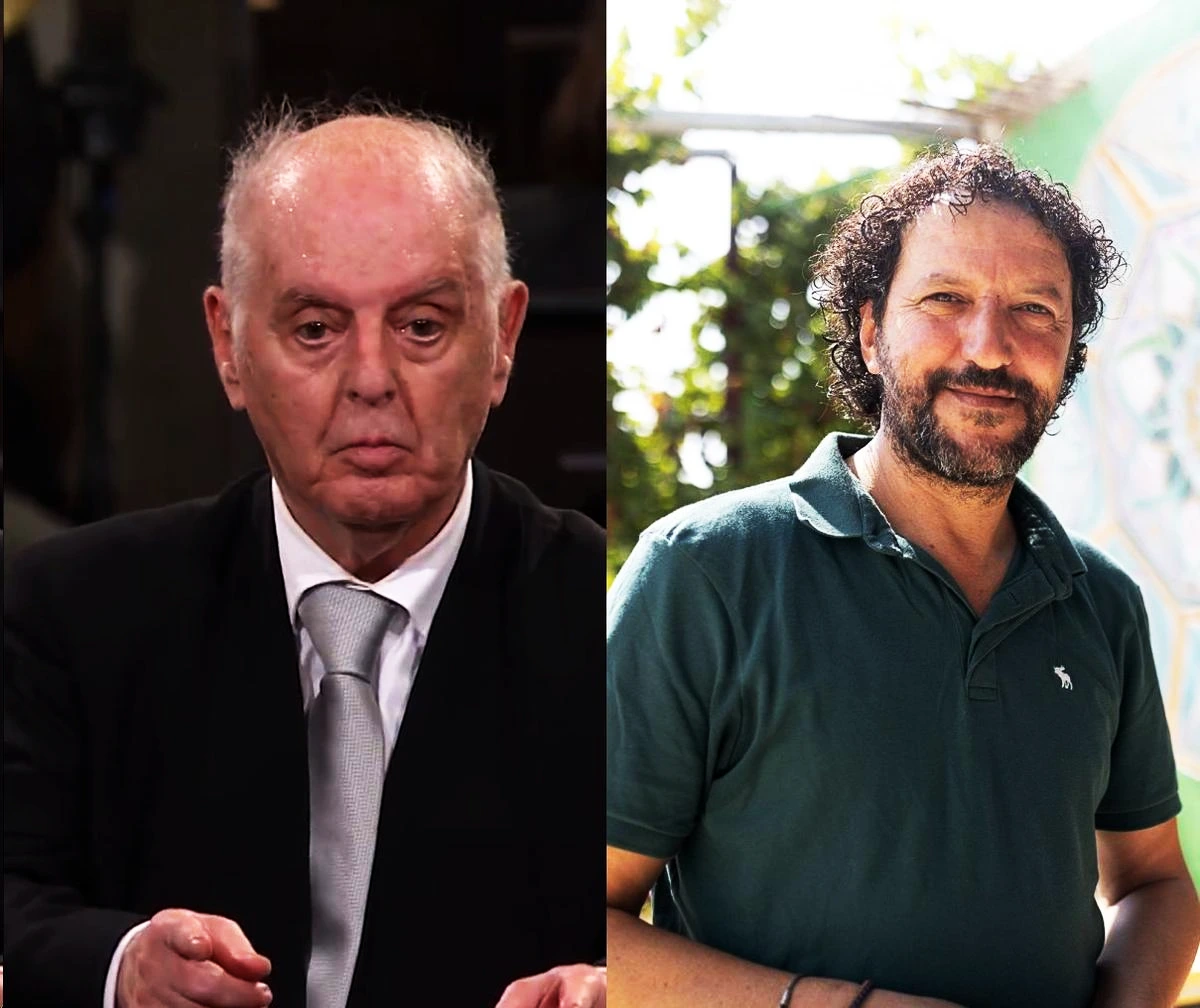

Learn more about Indira Gandhi Peace Prize Awarded To COVID-19 Warriors, here.
Source: The Hindu
Context: India has been chosen to help Saint Lucia as a partner country in strengthening its tax administration under the Tax Inspectors Without Borders (TIWB) program.
About Saint Lucia
|
Must Read: Data Point: India’s Widening Tax Base
News Source: Economic Times
Context: Recently, massive oil spillage occurred due to flood water from cyclone Michaung from the state-run Chennai Petroleum Corporation Limited’s (CPCL) refinery in Chennai.
Know more about Cyclone Michaung: Threat, Intensity, and Live Updates!
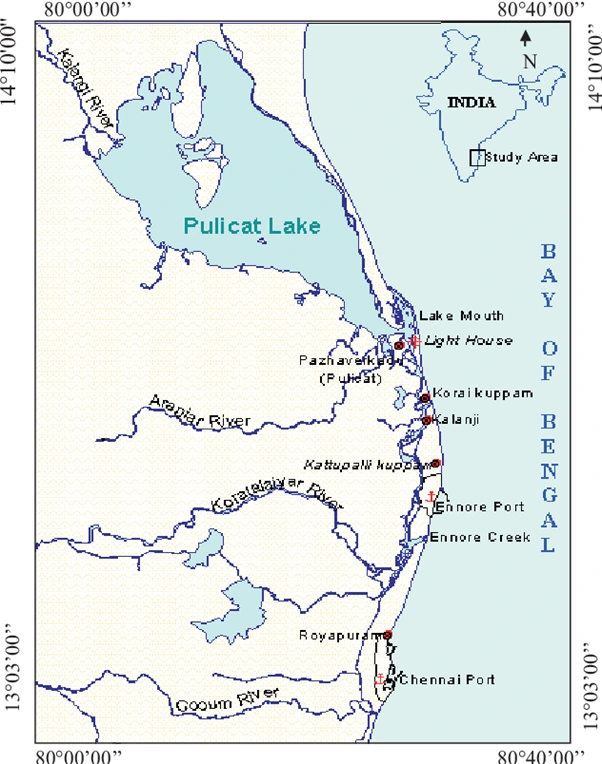
Location: Ennore Creek
National Oil Spill-Disaster Contingency Plan (NOS-DCP)
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
Context: ISRO has decided to indigenously develop the environmental control and life support system (ECLSS) for the upcoming human space flight Mission Gaganyaan.
Gaganyaan Mission
|
|---|
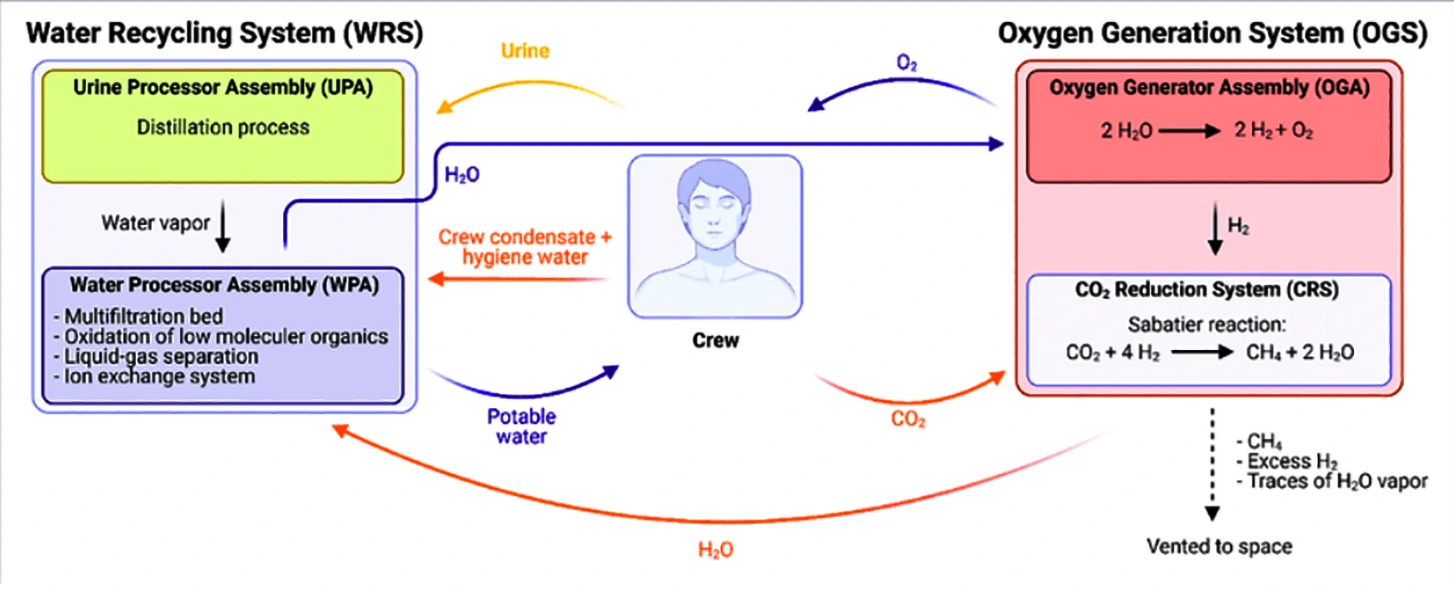 Air Management: The Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) is responsible for maintaining air quality by removing carbon dioxide, controlling oxygen levels, and filters out contaminants and particulate matter.
Air Management: The Environmental Control and Life Support System (ECLSS) is responsible for maintaining air quality by removing carbon dioxide, controlling oxygen levels, and filters out contaminants and particulate matter.News Source: Economic Times
Context: Recently, Barracuda, also known as SaurShakti was launched at the yard of Navalt Solar and Electric Boats, located in Alappuzha (Kerala). It is said to be India’s fastest solar-electric boat.
 Advanced Technology: It seamlessly integrates advanced technologies making it a pioneer in modern naval and passenger transportation.
Advanced Technology: It seamlessly integrates advanced technologies making it a pioneer in modern naval and passenger transportation.Navalt Solar and Electric Boats
|
|---|
News Source: TH
Also Read: Recently, three Anti-submarine Warfare Ships for Indian Navy Launched
Context: This article is based on the news “Escalating tiger-human conflict haunts Karnataka’s Mysuru, Chamarajanagar districts. Is big cat population spike to blame?” which was published in the Down to Earth. The Mysuru and Chamarajanagar districts in Karnataka reported five deaths in the last three months due to an increase in the number of tigers.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Wild Life (Protection) Act of India(WPA), 1972, Centre for Wildlife Studies (CWS), National Wildlife Action Plan, and National Board for Wildlife (NBWL).
Relevancy for Mains: Rising Human Wildlife Conflict (Human-Animal Conflict): Causes, Impact, and Interventions to Address Human Wildlife Conflict, and Way Forward. |
|---|
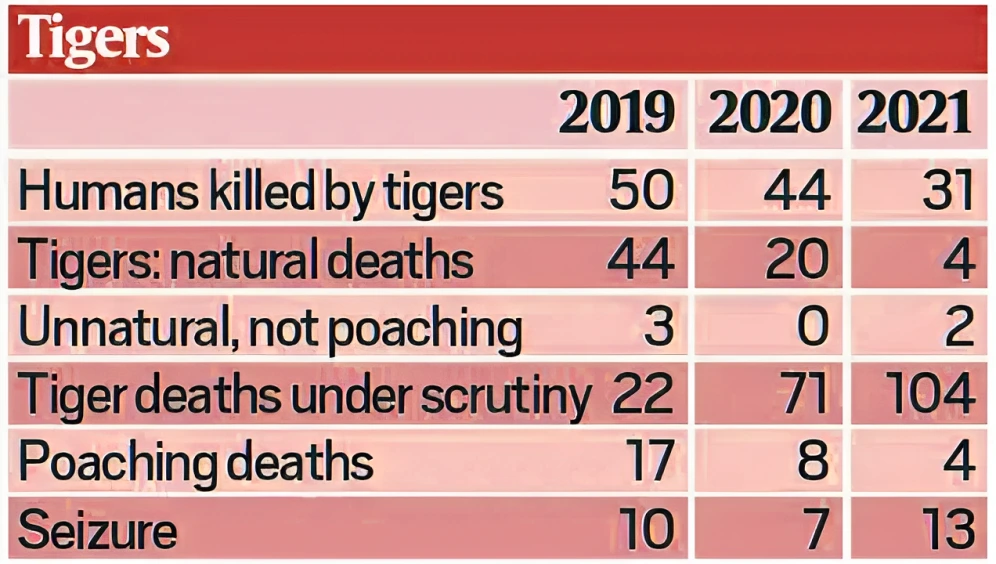 The escalating animal-human conflict in the Mysuru region worries wildlife lovers and environmentalists.
The escalating animal-human conflict in the Mysuru region worries wildlife lovers and environmentalists. 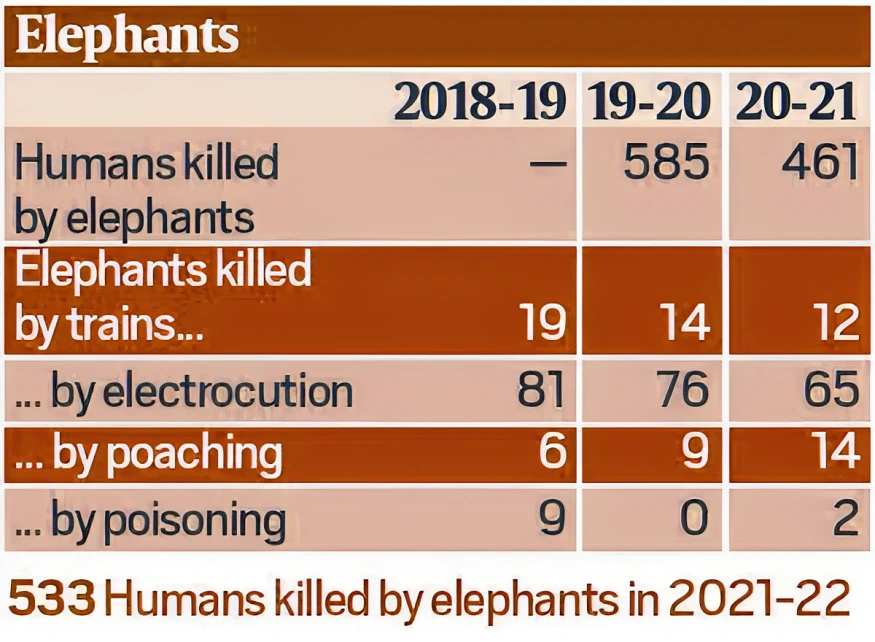 This conflict is not limited to humans, as big cats prey on numerous livestock and dogs every month.
This conflict is not limited to humans, as big cats prey on numerous livestock and dogs every month.Must Read: INDIAN WILDLIFE CONSERVATION EFFORT
| Recent Data Related To Human Elephant Conflict
As per data from the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, over 500 elephants were killed between 2014-2015 and 2018-2019, mostly due to human elephant conflict.
|
|---|
Kaziranga-Karbi Anglong Corridor
Also Read: Gajraj System: Indian Railways to Install AI-Based Elephant Protection Software |
|---|
The rising human wildlife conflict in Karnataka’s Mysuru and Chamarajanagar districts underscores the urgent need for comprehensive government interventions addressing the root causes, mitigating impacts, and fostering sustainable coexistence between humans and wildlife nationwide.
| Mains Question: Critically assess the enforcement mechanisms outlined in the Wildlife Protection Act. How effective are these mechanisms in deterring wildlife-related offenses? (250 words, 15 Marks) |
|---|
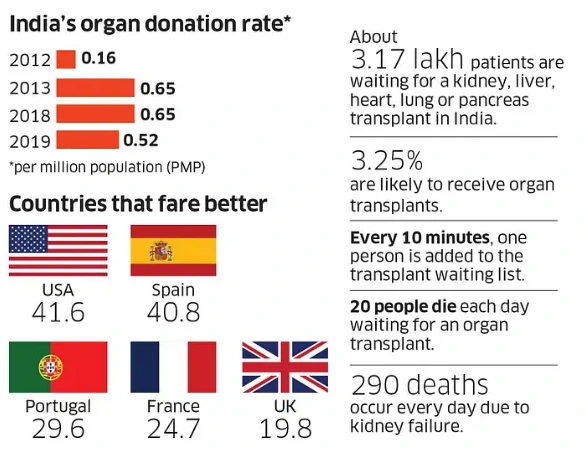
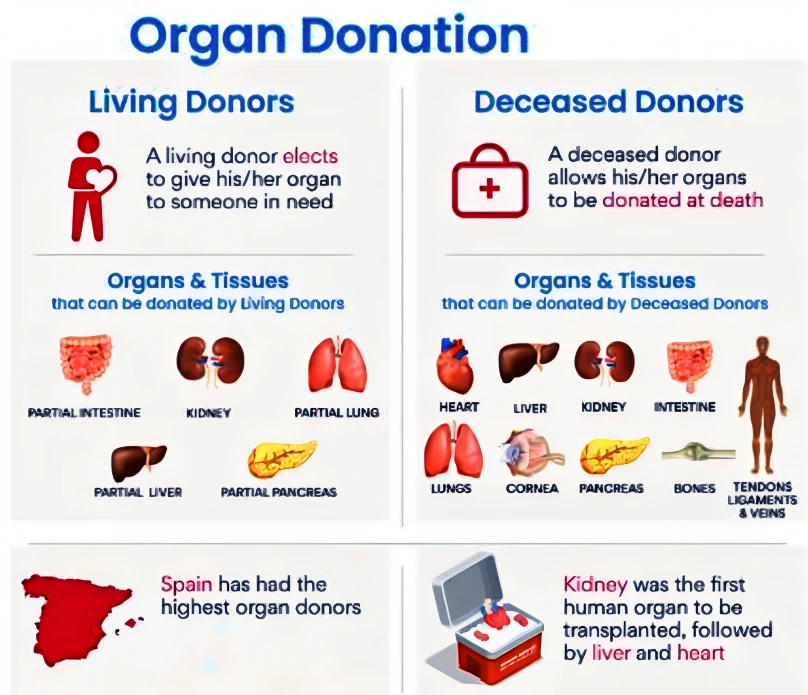
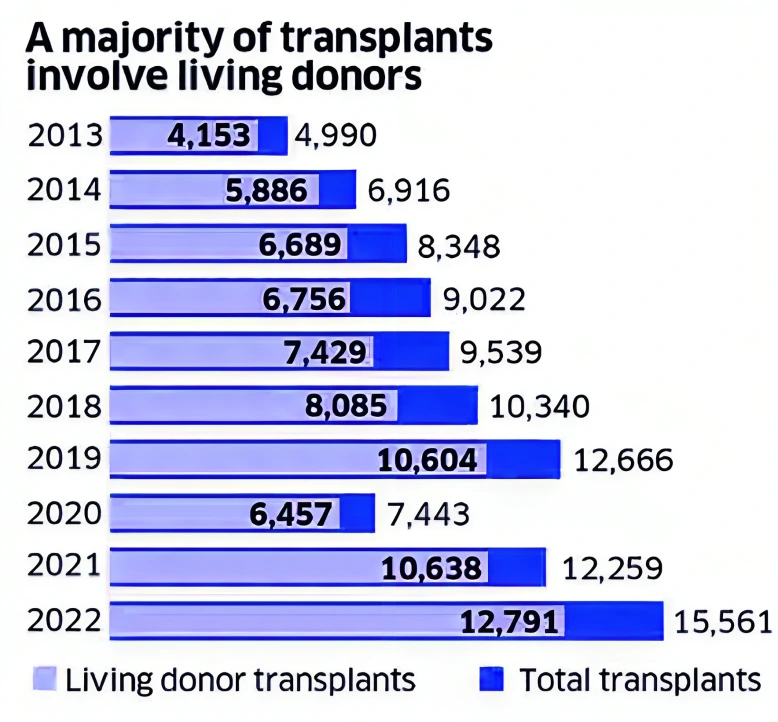
Context: This article is based on the news “The flipside of medical tourism — organ transplant rackets” which was published in the Indian Express. There is frequent news in the media on organ transplantation, ranging from uplifting stories of donors saving lives or disheartening stories, like scandals where organs are bought from vulnerable individuals.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Organ Transplants, World Health Organization (WHO), Indian Organ Donation Day, National Organ Transplant Programme, and National Organ & Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO).
Relevancy for Mains: Organ Transplantation & Medical Tourism In India: Statistics, Reasons for Increasing Medical Tourism In India, and Challenges Associated with Organ Transplants in India. |
|---|
Must Read: Organ Donation Policy
Government Initiatives Related to Organ Transplants
|
|---|
Also Read: Unveiling India’s Kidney Transplant Crisis: Challenges and Solutions
Changes in India’s Organ Donation and Transplantation Rules
|
|---|
Medical tourism in India, particularly in organ transplantation, has become a significant revenue source for private hospitals in India. According to the Global Observatory on Donation and Transplantation (GODT), India is the third-highest country in the world for organ transplantation, following only the USA and China.
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
