Context: Recently a study was published in the American Meteorological Society’s Journal of Hydrometeorology which reveals that Peninsular River basins face a higher probability of widespread flooding compared to the Ganga and Brahmaputra (transboundary rivers).
About Atmospheric Rivers
|
|---|
|
Must Read: Urban Flooding: Why Are Our Cities So Flood-Prone?
News Source: Down To Earth
Context: The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Industry recommends extension of the deadline of the Faster Adoption & Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles/FAME India schemePhase II by three more years.
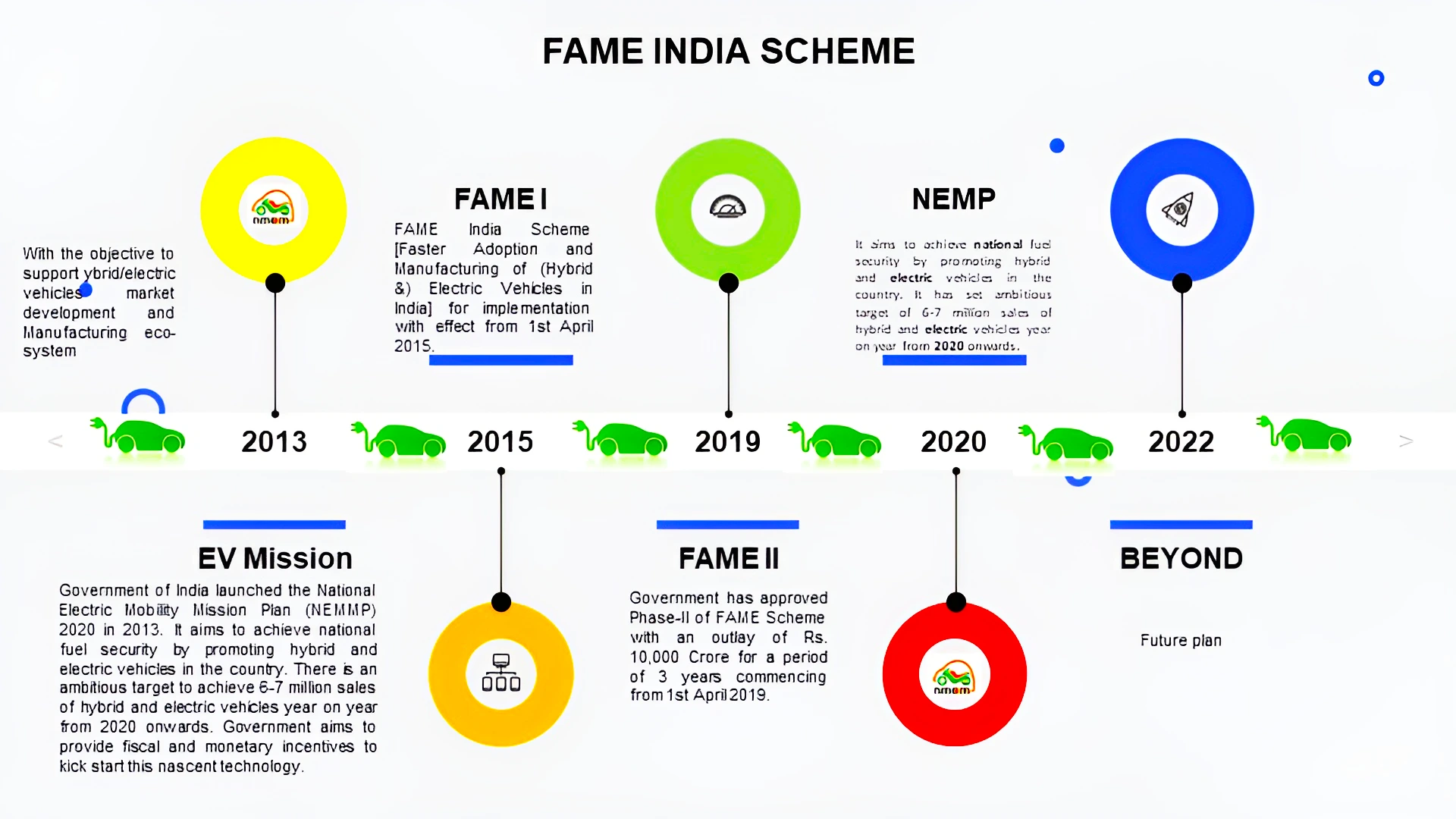
Must Read: Battery Energy Storage Systems
News Source: Down to Earth
Context: An indigenous river model BRAHMA-2D (Braided River Aid: Hydro-Morphological Analyzer) is developed by the researchers of IIT Guwahati along with the Brahmaputra Board, Ministry of Jal Shakti.
About Brahmaputra River
Majuli Island
|
|---|
News source: Economic Times
Context: Recent experiments by a team of Australian scientists show that bees can use “less than” and “greater than” to understand that zero means nothing and they placed zero correctly relative to other numbers; in particular, as less than one.
About National Bee Board (NBB)
|
|---|
News Source: Live Mint
Context: Recently, the Ministry of Mines launched the National Geoscience Data Repository or NGDR Portal.
About Geological Survey of India (GSI)
About Bhaskaracharya Institute of Space Applications and Geoinformatics (BISAG-N)
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
Context: Recently, the Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises has launched three sub-schemes under the aegis of the RAMP (Raising and Accelerating MSME Productivity) programme.
| The MSME GIFT Scheme | The MSE SPICE Scheme | MSE ODR Scheme |
| Objective: To help MSMEs adopt green technology with interest subvention and credit guarantee support. | Objective: To support circular economy projects through credit subsidy and realize the dream of the MSME sector towards zero emissions by 2070. | Objective: To synergise legal support with modern IT tools and Artificial Intelligence to address delayed payments for Micro and Small Enterprises. |
| Implementing Agency: Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) | Implementing Agency: Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) | Implementing Agency: National Informatics Centre Services Inc. (NICSI) |
Also Read: SWAMIH Investment Fund
News Source: PIB
Context: Indian Finance Minister met the World Bank Group President and discussed the possible role of Multilateral Development Banks in various sectors of India.
About World Bank
|
|---|
Must Read: Governance In Urban Cooperative Banks (UCB)
News Source: Business Standard
Context: The International Monetary Fund (IMF) reported that the central bank excessively managed the Indian currency in the period December 2022 to October 2023.
What is an Exchange Rate?
|
|---|
To read more on EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM
News Source: Live Mint
Context: R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine added to the WHO’s list of prequalified vaccines.
WHO Vaccines Prequalification
WHO Vaccines Prequalification List: Significance
|
|---|
News source: Down to Earth
Context: Missing for 42 years, the Namdapha flying squirrel resurfaces in Arunachal Pradesh.

Namdapha National Park
|
|---|
Must Read: Rising Human Animal Conflict: Reasons And Consequences
News Source: TH
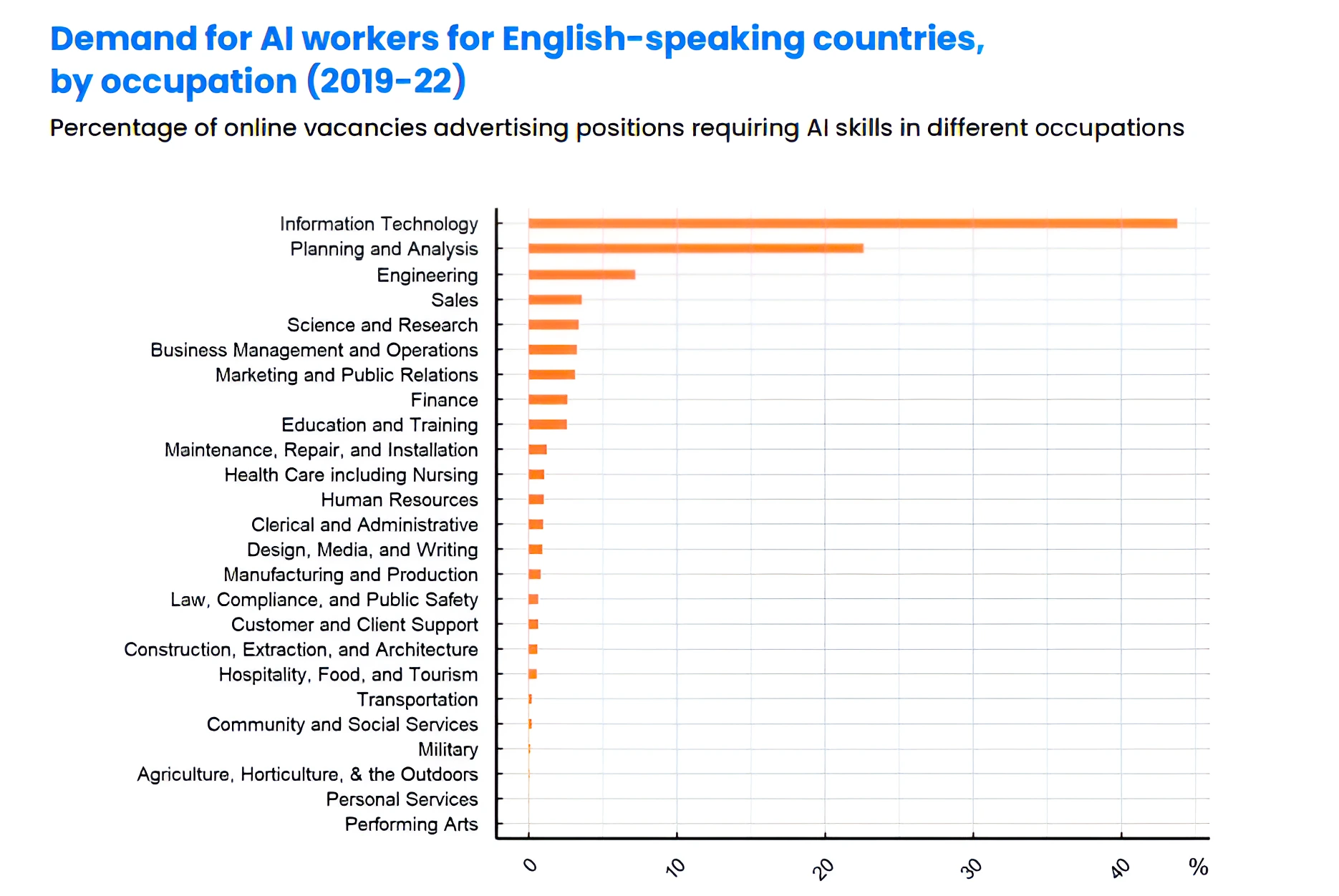
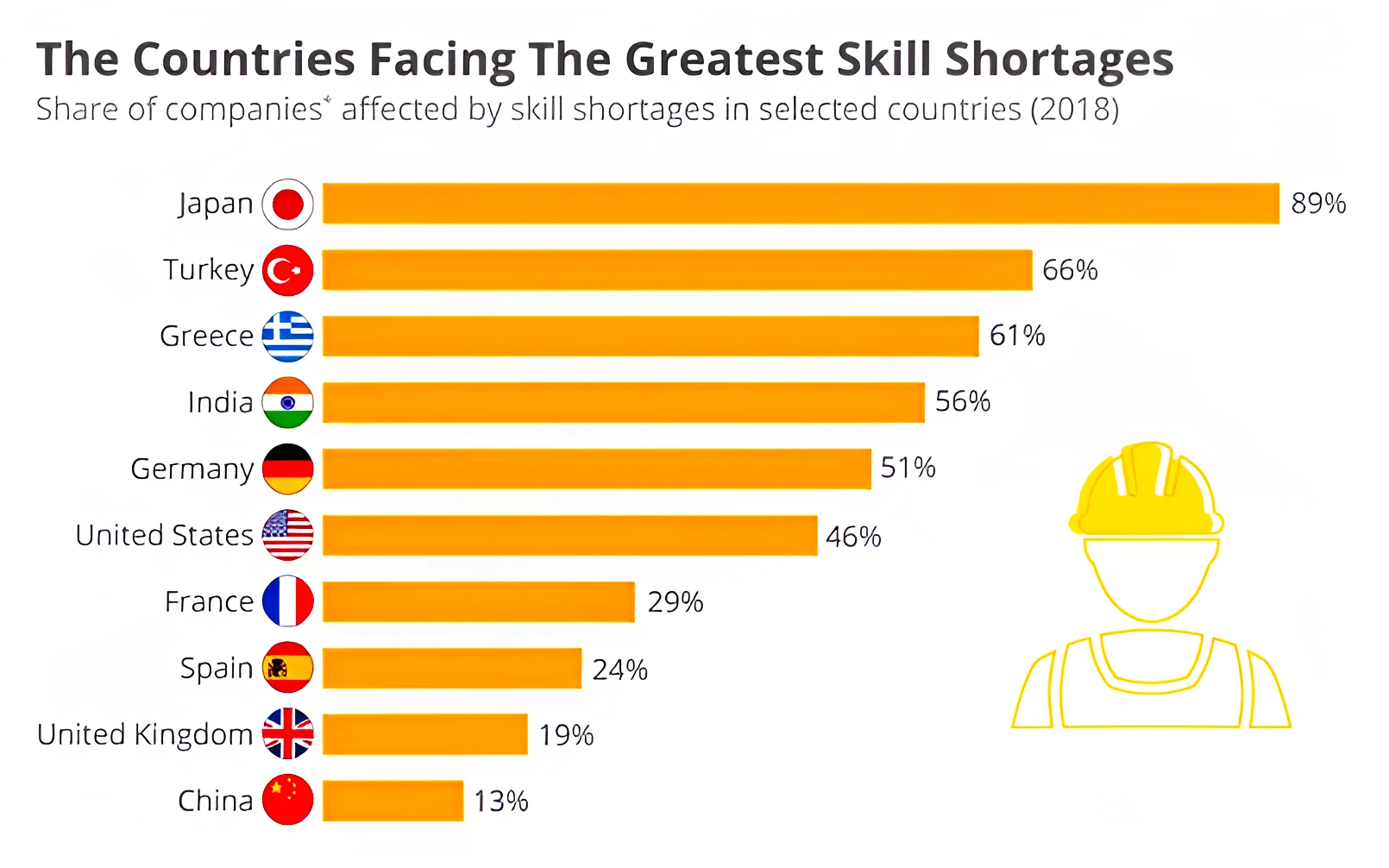
Context: This article is based on the news “India Skills Report finds Kerala the most preferred State to work” which was published in the Hindu. The talent assessment agency Wheebox recently unveiled India Skills Report 2024: “Impact of AI on the Future of Work, Skilling & Mobility”.
| Relevancy for Prelims: India Skills Report 2024, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), National Skill Development Mission (NSDM), and SANKALP.
Relevancy for Mains: Skill Development in India: Challenges, Initiatives, and Way Forward. |
|---|
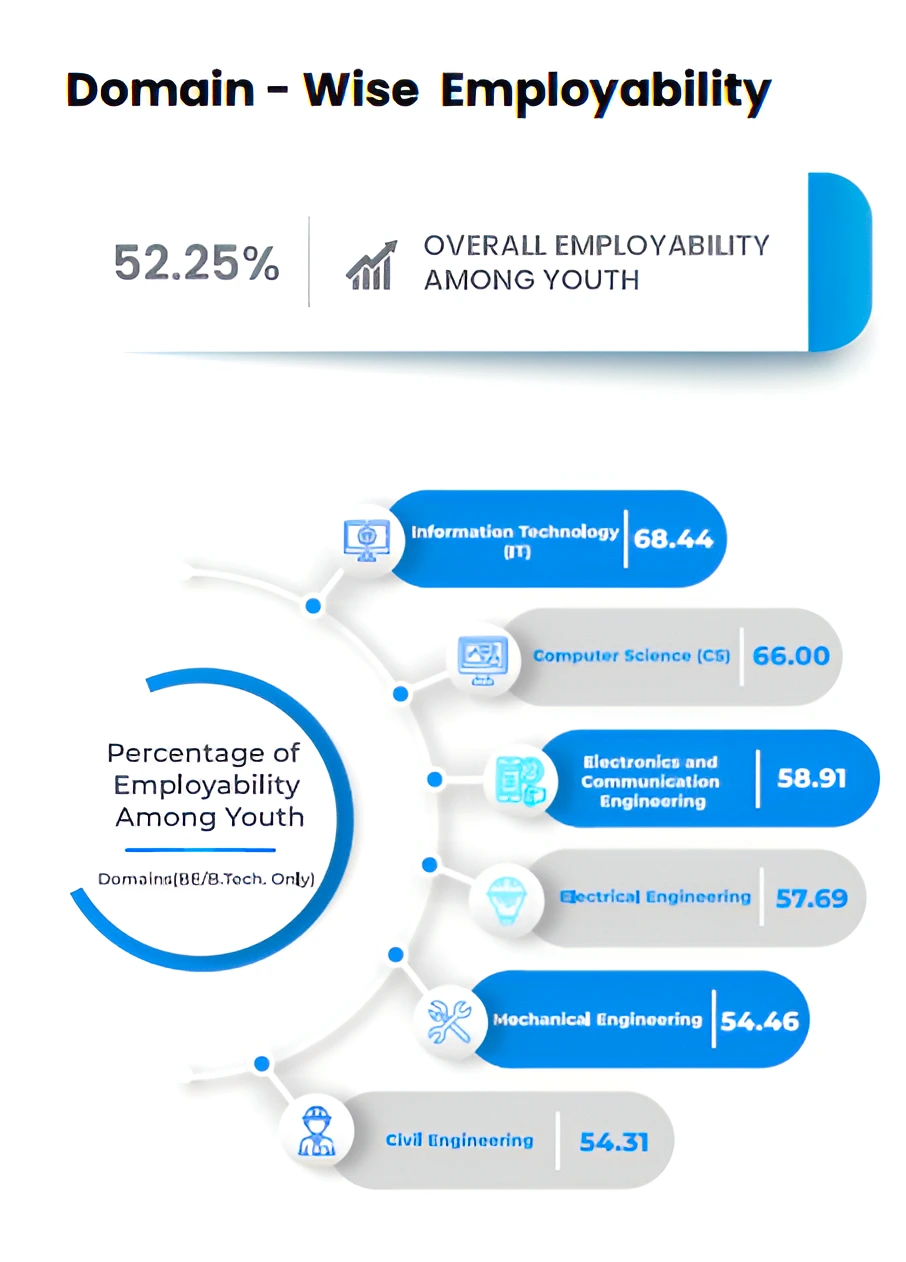 State with Maximum Employability in India Skills Report 2024: Telangana has the highest concentration of employable talent in the age group of 18-21 where 85.45% were found employable.
State with Maximum Employability in India Skills Report 2024: Telangana has the highest concentration of employable talent in the age group of 18-21 where 85.45% were found employable.
About the India Skills Report
|
|---|
Growth Story of Kerala: All Round Talent Hub
Additional Skill Acquisition Program (ASAP) Kerala
|
|---|
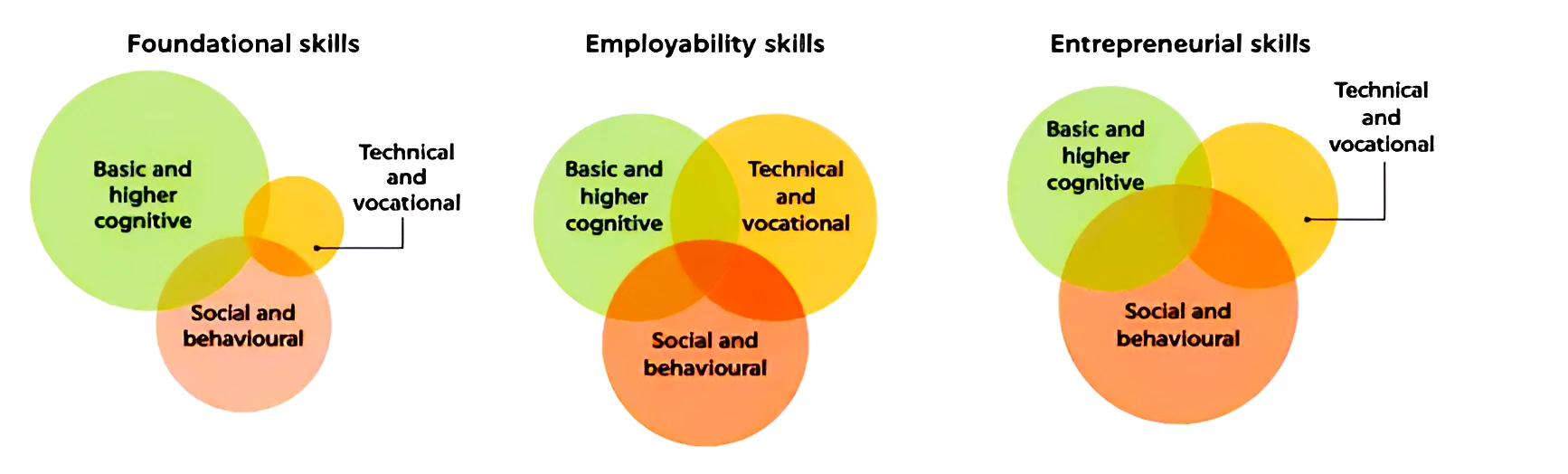
Types of skills
|
|---|
Must Read: Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) Annual Report 2022
The India Skills Report 2024 highlights improvements in employability, the transformative impact of AI, and challenges in skill development, emphasizing the need for comprehensive collaboration and proactive measures to bridge the skill gap and prepare the workforce for the evolving job market.
Context: At the recent COP28 of UNFCCC, NASA and IBM announced that an Artificial Intelligence (AI) tool called watsonx.ai would be available on the open-source AI platform Hugging Space.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Watsonx.ai Tool, NASA, and India Meteorological Department (IMD).
Relevancy for Mains: AI tool for Weather forecasting: Significance, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Must Read: Global Partnership On Artificial Intelligence – GPAI
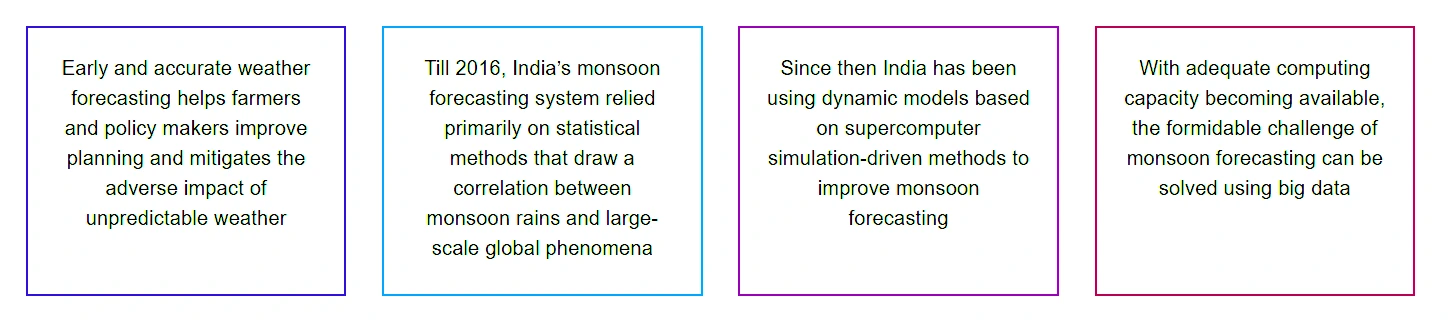
Importance of Weather Forecasting
|
|---|
About Watsonx.Ai
|
|---|
| Inductive and Deductive Reasoning
Inductive Reasoning: It aims to develop a theory and it is compatible with emerging ways of thinking, especially in the realm of machine learning forecasting. Since the climate is changing and historic data as an algorithmic variable is becoming less significant. Deductive Reasoning: It aims to draw conclusions from an existing one. It bases conclusions on accepted facts thus the future might not look like the past. |
|---|
Watsonx.ai, a joint effort by IBM and NASA, uses AI to improve weather forecasting, offering better accuracy and preparedness.
| Mains Question: Introduce the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). How does Al help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to privacy of the individual in the use of Al in healthcare? |
|---|
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
