Context: RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has kept the Repo Rate unchanged at 6.5% for 5th time in a row.
About Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)
Know more about the RBI’s Monetary Policy here. |
|---|
About Repo Rate
|
|---|
News source: Indian Express
Context: As per the Union minister of state for environment, forest and climate change, 397 Asiatic lions died in Gujarat due to various causes.
Asiatic Lions
Protection Status:
|
|---|
News Source: DTE
Context: India planning to move to the T+0 trading settlement system from the current T+1 system
Securities and Exchange Board of India(SEBI):
|
|---|
| CLEARING CORPORATION OF INDIA (CCIL)
About: The Clearing Corporation of India Ltd. (CCIL) was set up in April 2001 to provide guaranteed clearing and settlement functions for transactions in Money, G-Secs, Foreign Exchange, and Derivative markets |
|---|
News Source: Business Today
Context: Recently, an Alternative Livelihood Programme under the Amrit Dharohar Capacity Building Scheme-2023 has been launched in Sultanpur National Park.
About the Nature-tourism and Wetcomponent:
|
|---|
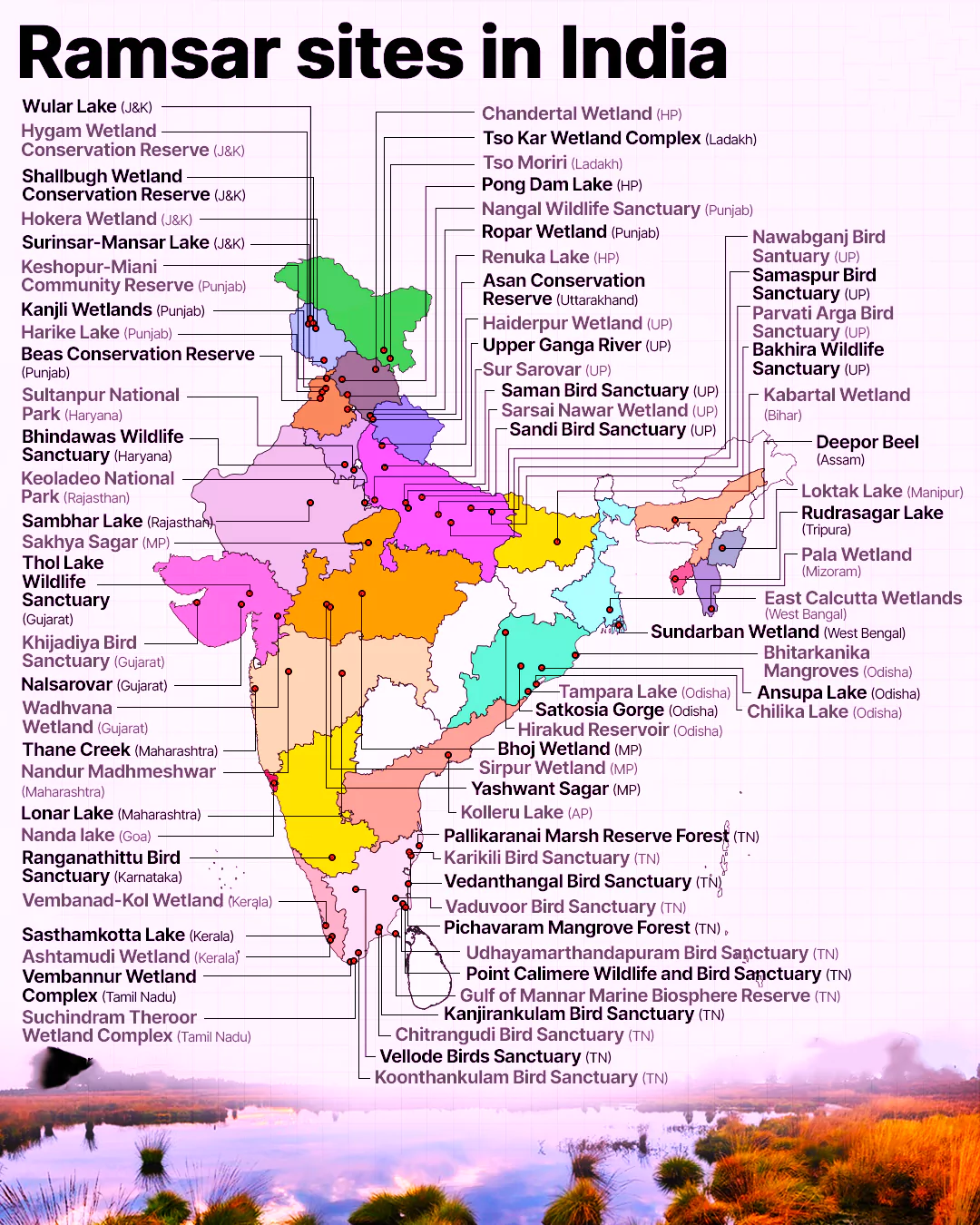
List Of Total Ramsar Sites In India 2023 here.
News Source: PIB
Context: Recently, India has ranked 7th in a report Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) 2024, published on the sidelines of the ongoing COP28 at Dubai.
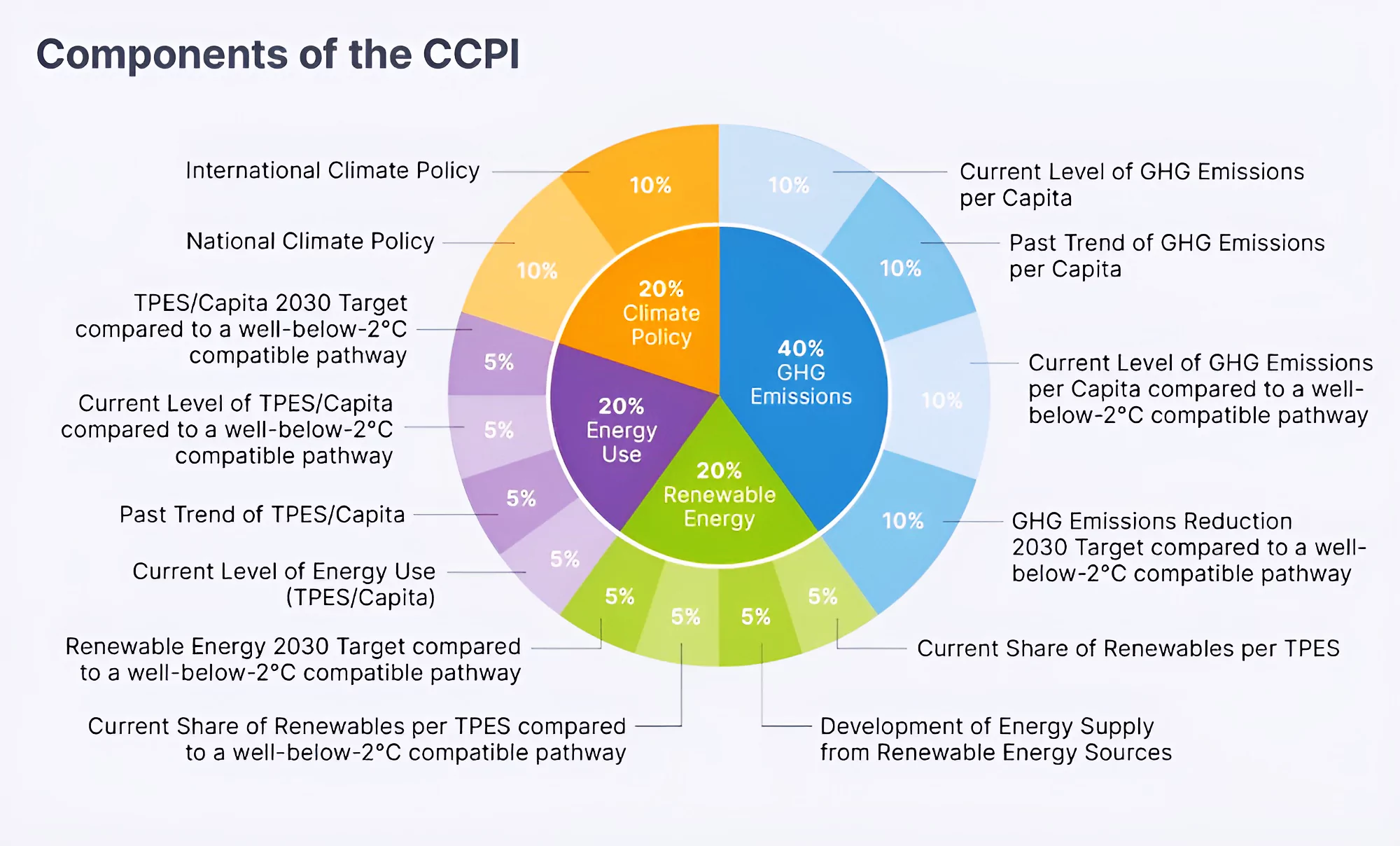
| Country | Score |
| Denmark (4th) | 75.59 Percent |
| Estonia (5th) | 72.07 Percent |
| Philippines (6th) | 70.70 Percent |
Also Read: NDC Synthesis Report For 2023: UNFCCC
| Index | Rank |
| GHG Emissions | 9th (India is on track to meet a benchmark of well below 2°C) |
| Energy Use | 10th (a low per capita benchmark) |
| Climate Policy | 10th |
| Renewable Energy | 37th (barely remaining within the ‘high’ performance category) |
Must Read: World Climate Action Summit – COP28
News Source: Down to Earth
Context: A private member bill was presented recently in Rajya Sabha which demanded a system to fix the accountability of Governors.

News Source: The Hindu
Context: According to Chinese State Media, China began commercial operations of the world’s first 4th generation nuclear reactor.
Nuclear Power Development in China
Also Read: Nuclear Power Plants In India 2023
About the Shidaowan Plant: World’s First 4th Generation Nuclear Reactor
Different Generations of Nuclear Reactors
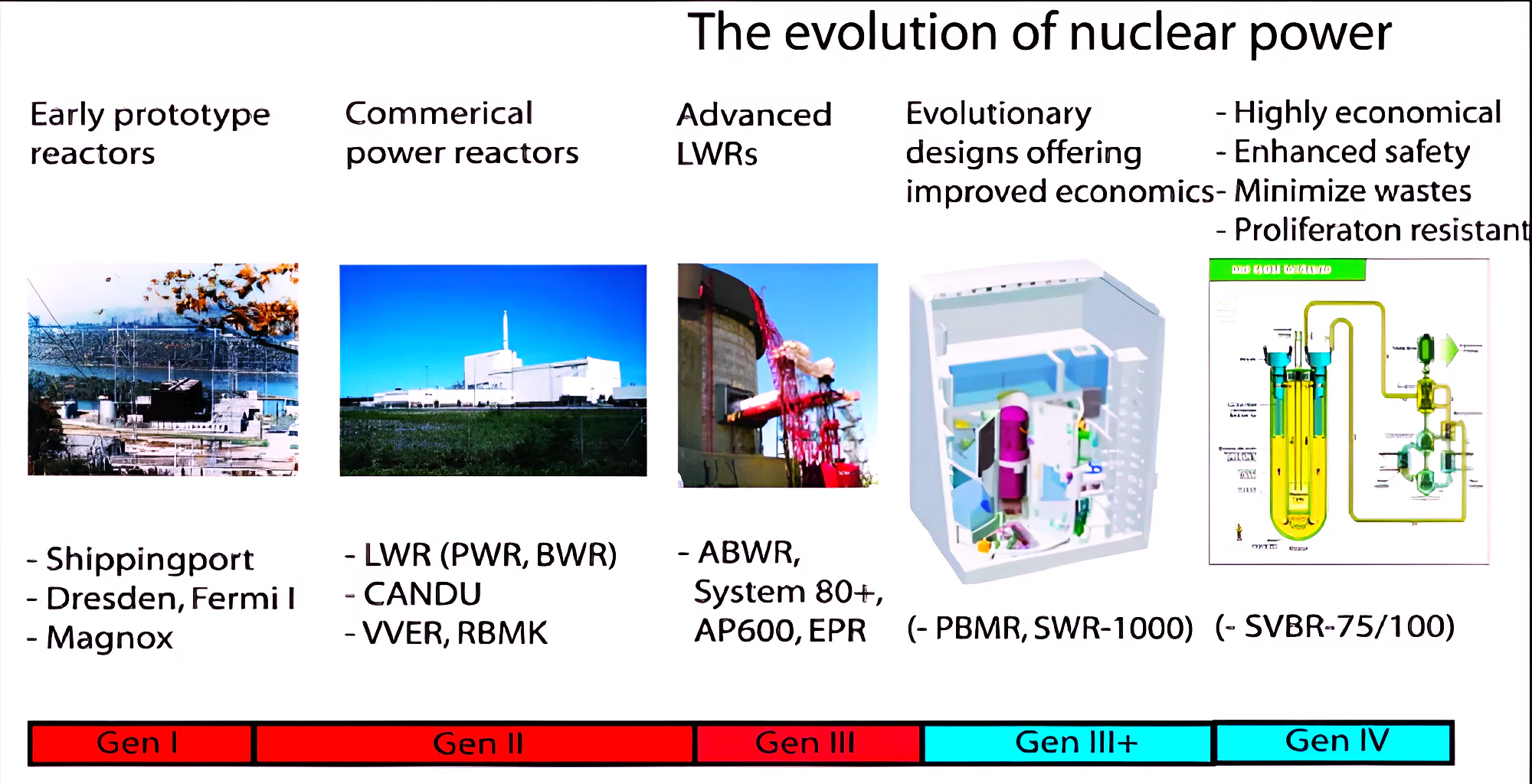
News Source: Reuters
Context: The Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) instrument on board the Aditya-L1 spacecraft has successfully captured the first full-disk images of Sun in the 200-400 nm wavelength range.
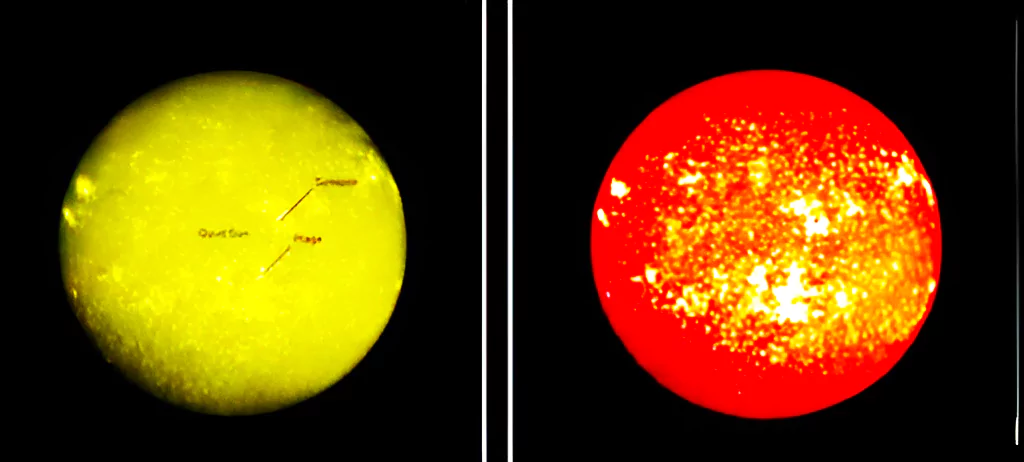
About Aditya-L1 Mission
|
|---|
Significance: SUIT observations will help scientists study the dynamic coupling of the magnetized solar atmosphere and assist them in placing tight constraints on the effects of solar radiation on Earth’s climate.
News Source: Business Standard
Context: The Char Dham project in Uttarakhand, under which Silkyara tunnel is being developed, did not require an Environment Impact Assessment, the Union government told Parliament.
Read more about the Uttarakhand Silkyara Tunnel Collapse here.
About Chardham Mahamarg Vikas Pariyojna
Silkyara Tunnel: It is around a 4.5 Km long two-lane Bi-Directional tunnel with an escape passage on Dharasu –Yamunotri.
|
|---|
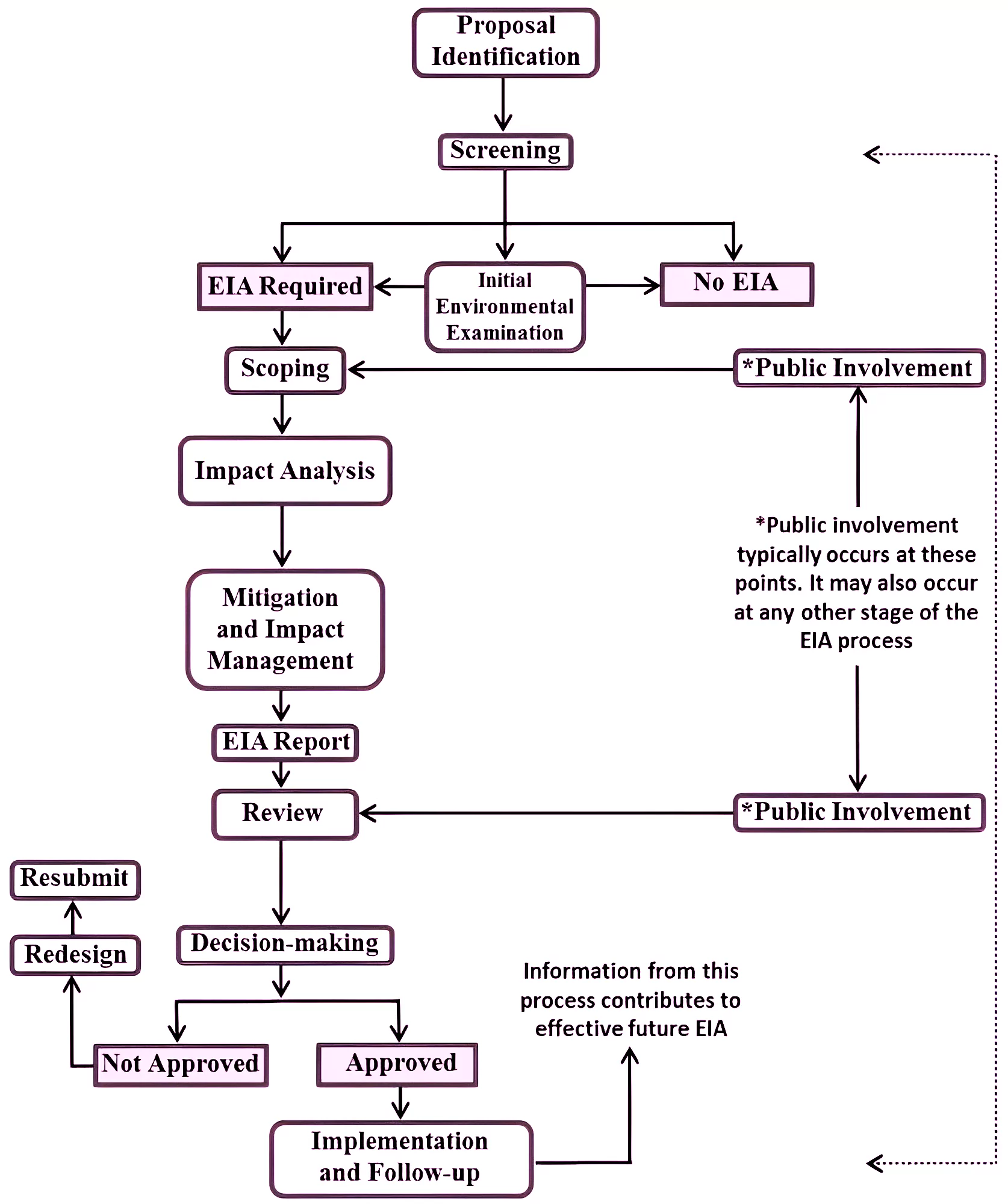
News Source: DTE
Context: Recent data from the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), shows that at least 6% of cough syrup samples from 54 Indian manufacturers failed a mandatory quality test for export.
| Deaths in the Gambia due to faulty cough Syrups
The World Health Organisation (WHO) connected the deaths of at least 70 children in the Gambia last year to medications manufactured by Indian pharmaceutical company Maiden Pharmaceuticals that were tainted with ethylene glycol (EG) and diethylene glycol (DEG), toxins typically used as antifreeze and industrial solvents. |
|---|
Must Read: India Pharma Products And Drug Safety
News Source: The Hindu
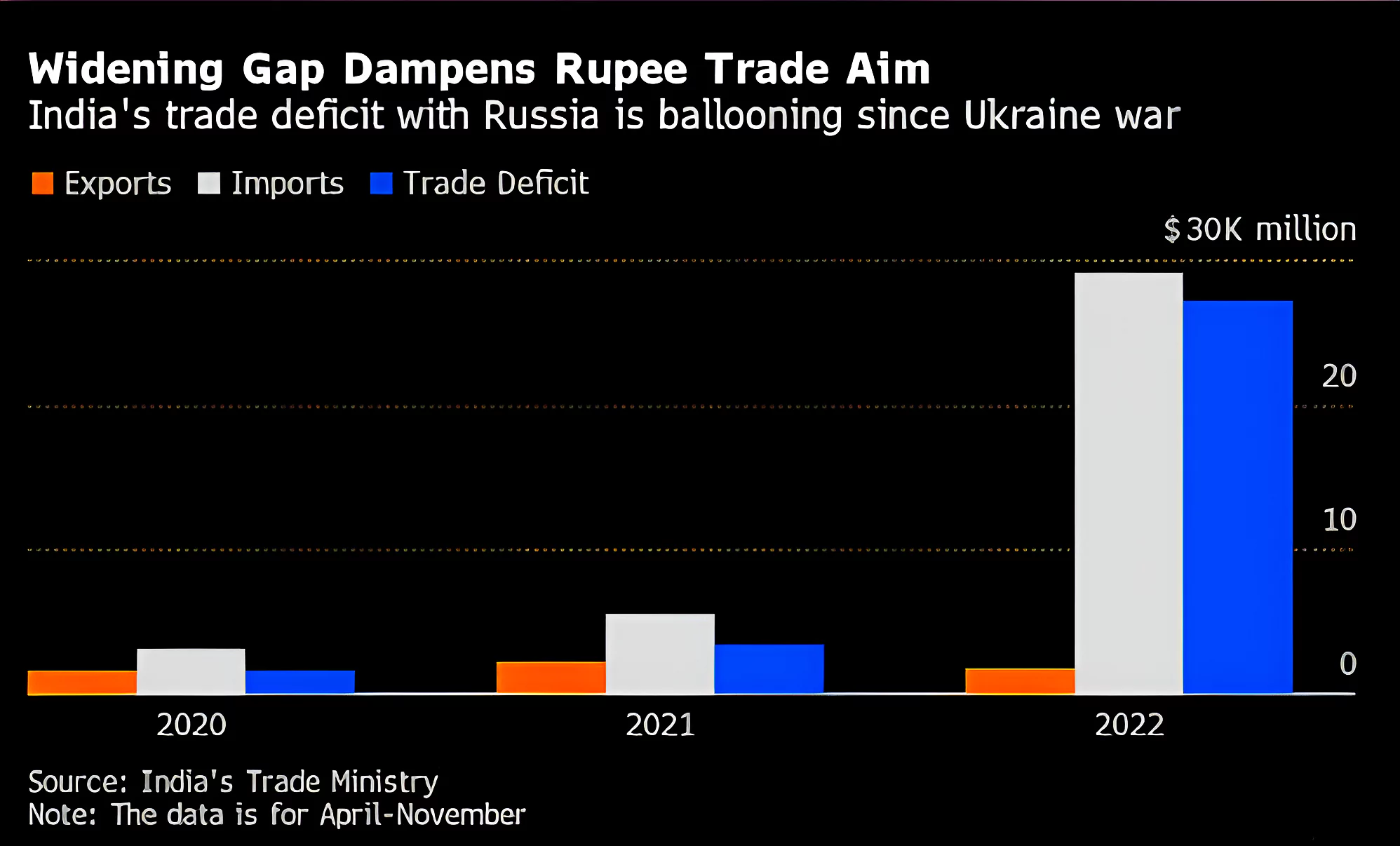
Context: This article is based on the news “India Russia trade doubled to nearly $50 billion in Jan-Sept: Russian Ambassador” which was published in the Live Mint. The bilateral trade between India and Russia has doubled to almost $50 billion during January-September 2023.
| Relevancy for Prelims: India Russia Trade Relations, Indo–Soviet Treaty of Peace, Friendship, and Cooperation, Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between India and Russia, International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), India And The Northern Sea Route (Chennai-Vladivostok Marine Corridor), and Act Far-East Policy.
Relevancy for Mains: India Russia Trade Relations: Significance, Challenges and Way Forward |
|---|
India Russia Trade: Major Trade Items
|
|---|
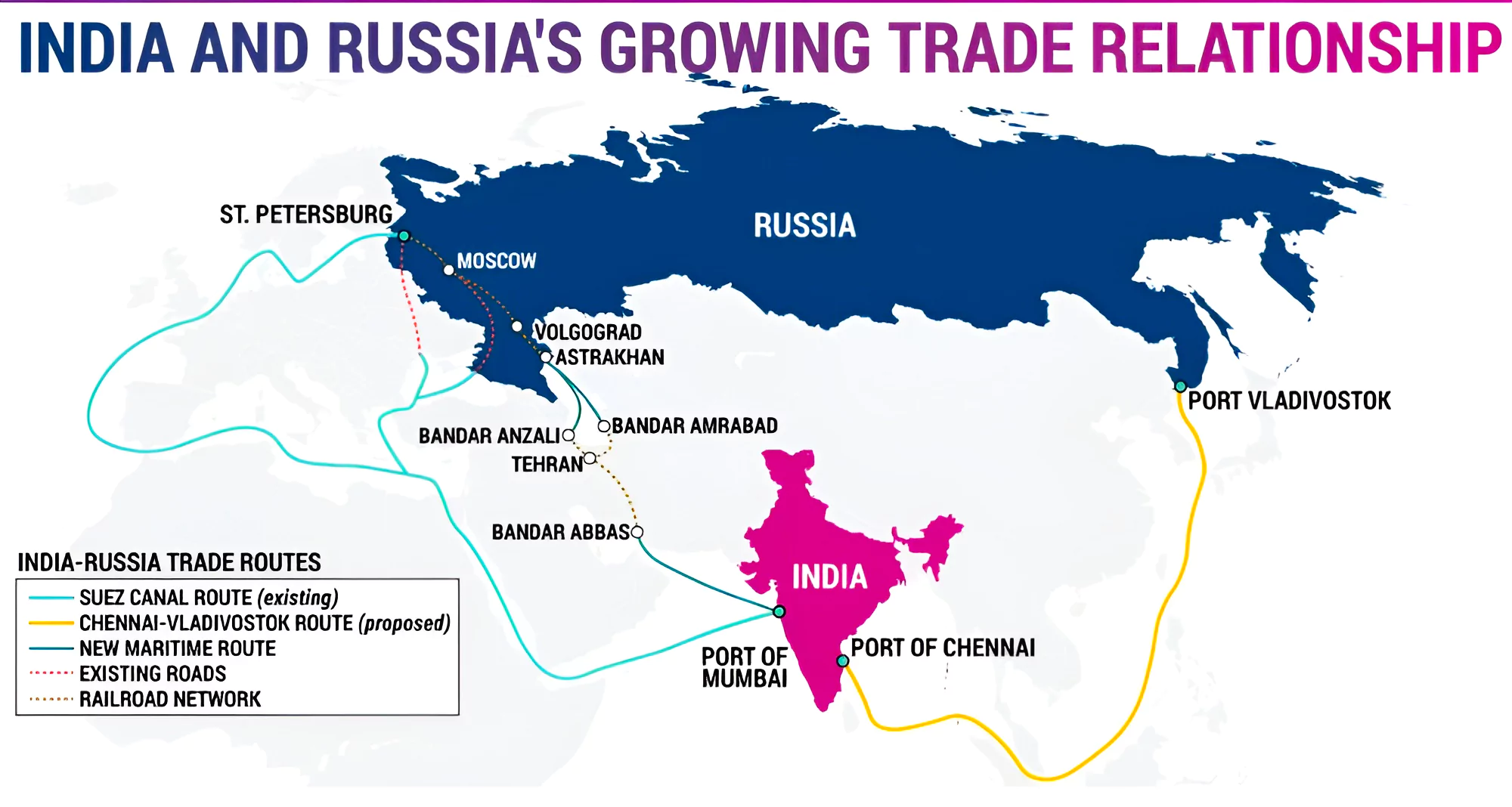
Impact of Russia- Ukraine Conflict on Bilateral Trade with India:
|
|---|
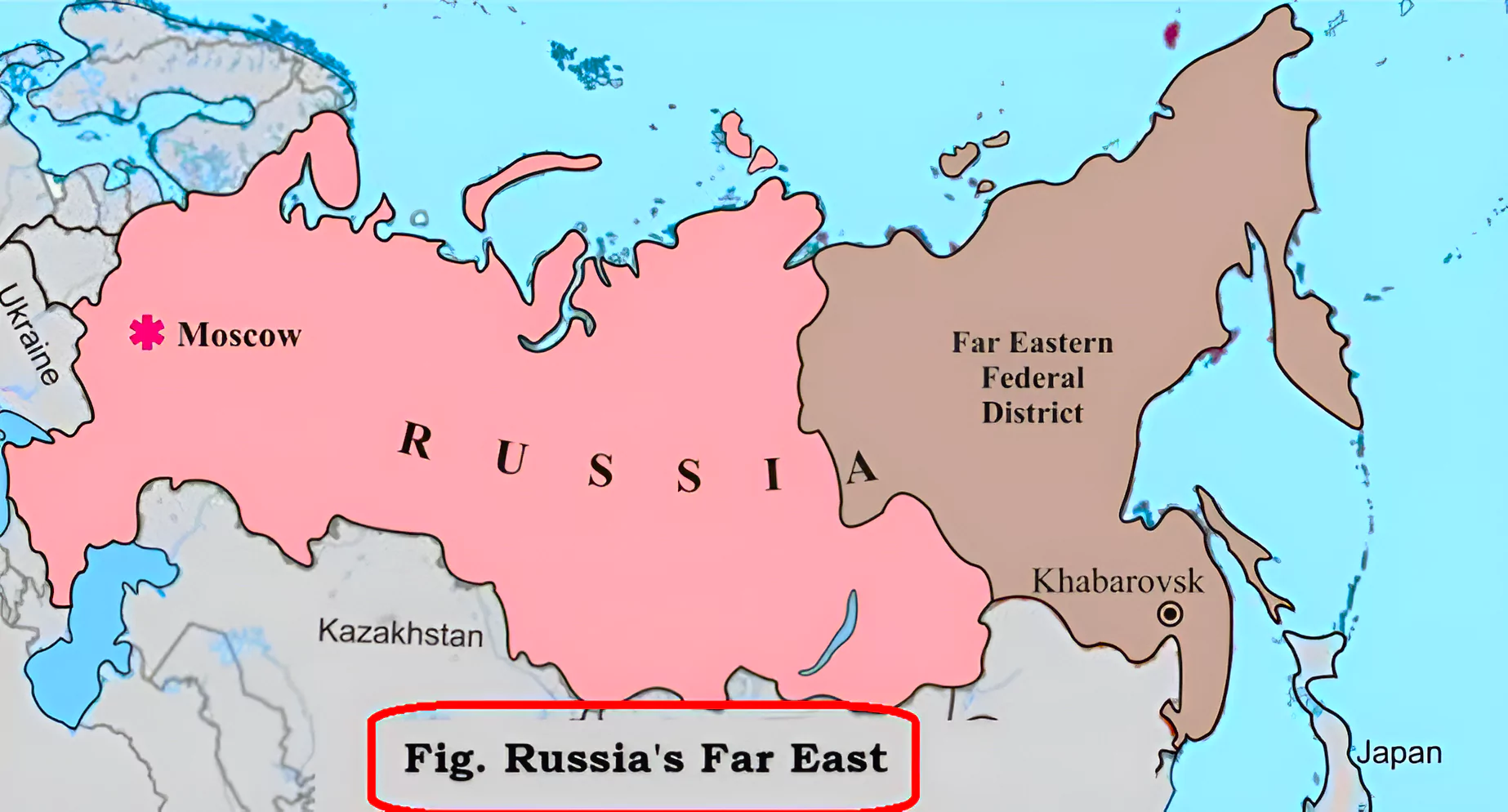
India’s Investment in Far-East Russia
|
|---|
Also Read: Russia May Pull Out From the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
The evolving dynamics of India Russia trade relations underscore the need for strategic measures to overcome challenges, bolster economic ties, and chart a path towards a more resilient and diversified partnership in the international arena.
| Prelims Question (2019)
Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (a) Japan (b) Russia (c) The United Kingdom (d) The United States of America Ans: (b) |
|---|
Context: A Member of Parliament(MP) was dismissed from the Lok Sabha after the House accepted the Ethics Committee’s report, which found her guilty of engaging in unethical conduct.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Indian Parliament, Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, Members of Parliament (MPs), Parliamentary Ethics Committee, Article 105 of the Constitution, Indian Parliamentary Privileges, and Privilege Motion.
Relevancy for Mains: Cash for Query Case, Misconduct vs. Privilege, Committee on Ethics and Privileges, Breach of Privilege, and Code of Ethics for Ministers. |
|---|
| The distinction between Privilege and Misconduct:
Privileges: They are rights and immunities given to Parliament members under Article 105 of the Constitution for effective functioning. Their misuse is a breach of privilege.
Misconduct: It describes a member acting inappropriately or participating in activities unfit for a Member of Parliament.
Privilege Committee:
Ethics Committee:
|
|---|
Know more about Lok Sabha Ethics Committee Investigates MP for Cash For Query here.
PV Narasimha Rao’s case (1998)
Cash For Query Scandal 2005/Raja Ram Pal Case
|
|---|
The expulsion of Mahua Moitra from the Lok Sabha in the Cash for Query case highlights the need for a comprehensive framework distinguishing between privileges and misconduct, advocating for a unified committee on ethics and privileges, and emphasizing the necessity of a clear Code of Ethics for elected representatives.
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
