The Pench Tiger Reserve (PTR) in Maharashtra has been marked as India’s first Dark Sky Park and the fifth Dark Sky Park in Asia for protecting the night sky and preventing light pollution.
Light Pollution, or Artificial Light at Night:
Impacts:
|
|---|
Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO):
International Astronomical Union (IAU): The IAU’s mission is to promote and safeguard astronomy in all aspects (including research, communication, education and development) through international cooperation. |
|---|

News Source: Live Mint
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
India’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) based inflation rate touched 5.69% in December.
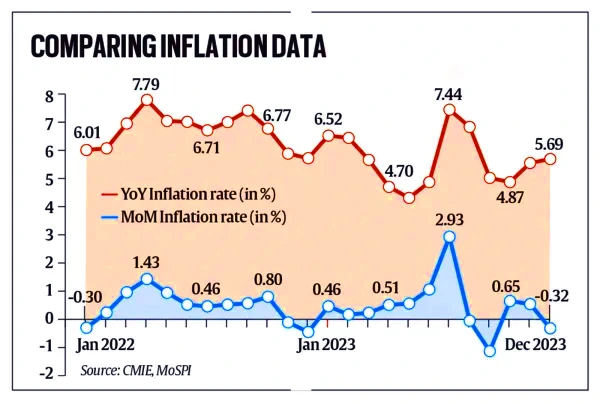
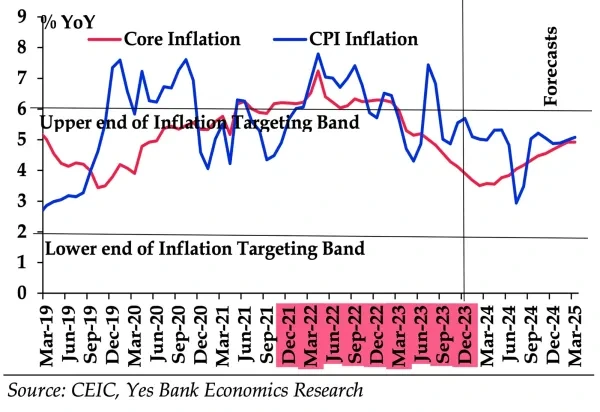 Cereals, too, were costlier by 10%.
Cereals, too, were costlier by 10%. News Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Recently, a new species of Silverline butterfly has been recognized within the biodiversity-rich regions of the Western Ghats in India.
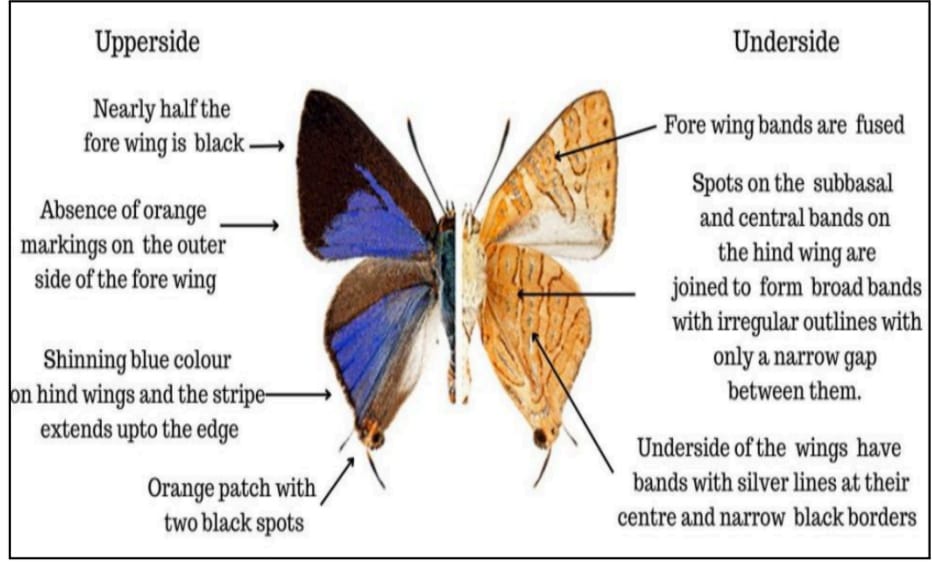
About Brahmagiri Wildlife Sanctuary
|
|---|
News Source: DownToEarth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
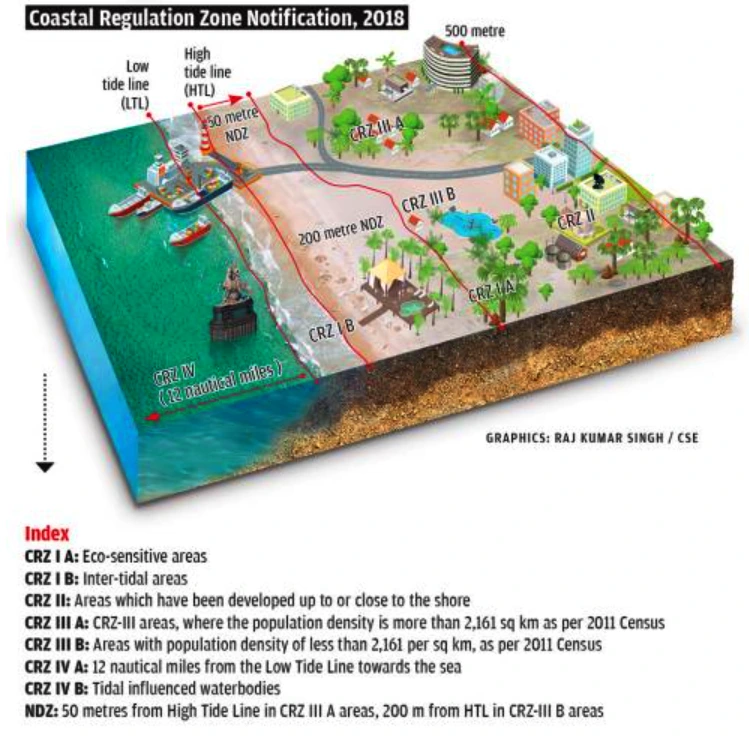
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has asked the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change to ensure that coastal States and Union Territories prepare the Coastal Zone Management Plan (CZMP).
High Tide Lines (HTL):
Low Tide Lines (LTL):
Spring Tide:
|
|---|
About National Green Tribunal (NGT)
|
|---|
Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
“The Global Cooperation Barometer 2024” has been released by the World Economic Forum (WEF).
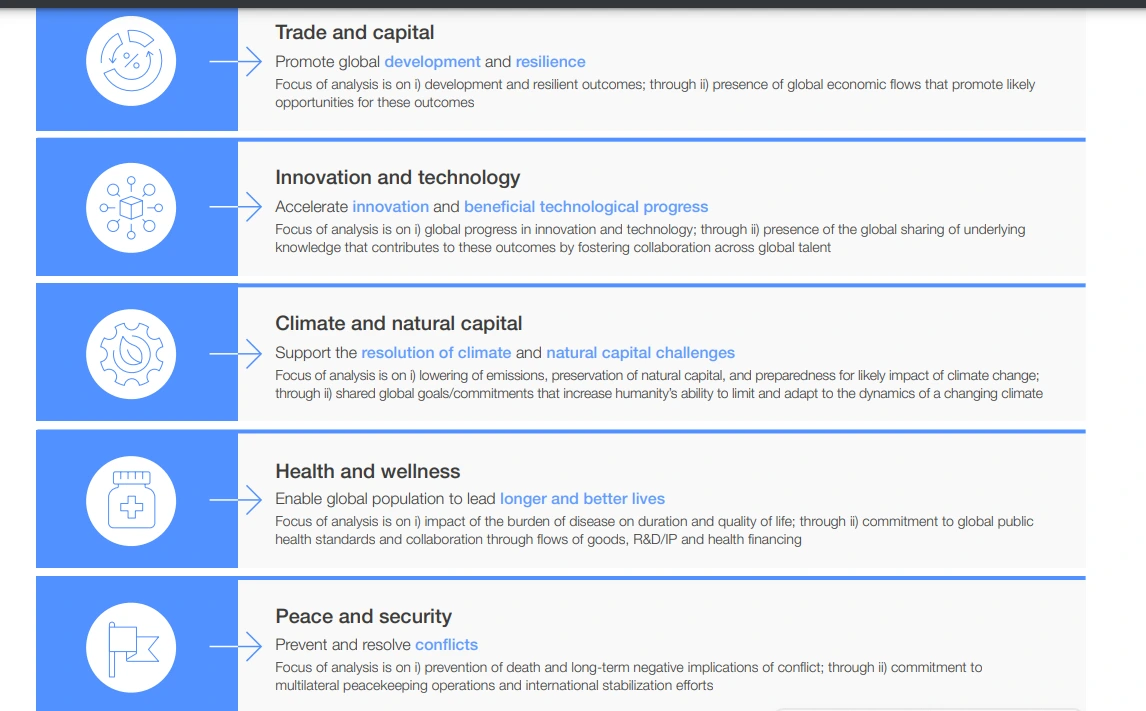
Frontier Technology
|
|---|
Also Refer: Global Risks Report 2024
News Source: DTE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
India Meteorological Department (IMD) celebrated the 150th Year of its establishment in 2024.
About India Meteorological Department
|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Recently, the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) has utilized the ‘Rejupave technology to build bituminous road sections at the world’s highest Sela road tunnel and LGG-Damteng-Yangste (LDY Road) road section near the China border in Arunachal Pradesh.
 Bituminous Road: It is also known as the asphalt road, is a type of road construction that involves the use of bitumen as a binding agent to hold together a mixture of aggregates.
Bituminous Road: It is also known as the asphalt road, is a type of road construction that involves the use of bitumen as a binding agent to hold together a mixture of aggregates. | Sela Road Tunnel: It aims to provide “all-weather” connectivity to Tawang, a remote and strategically significant district in the region. It will be the world’s longest bi-lane tunnel at an altitude above 13,000 feet. |
|---|
News Source: Times of India
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Recently, a ‘Vulture restaurant’ has been set up in Koderma district, Jharkhand to conserve the vulture species.
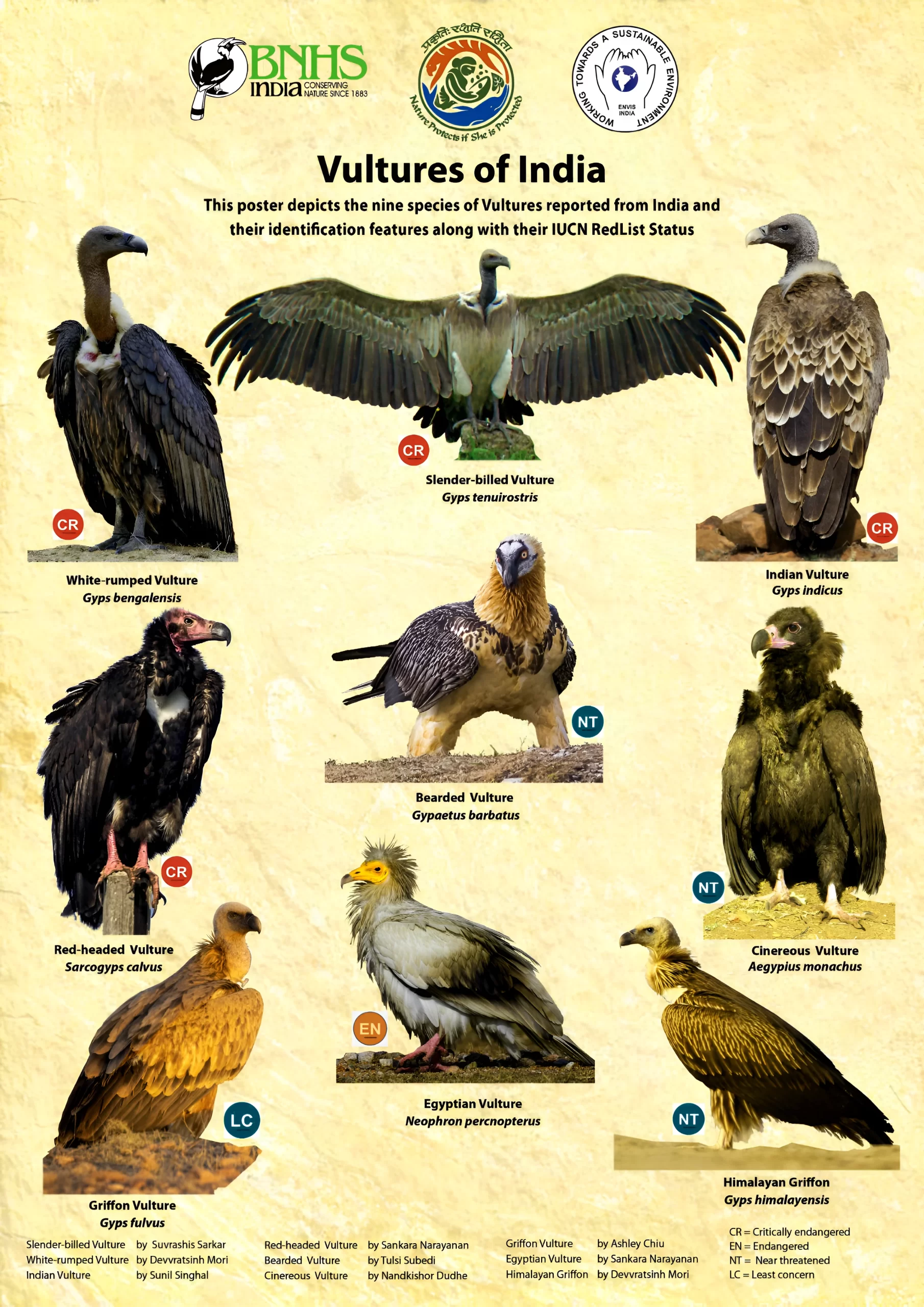

Also Refer: IUCN Red List Update At COP28
News Source: Deccan Herald
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Recently, India’s first National Highway (NH) steel slag road section on NH-66 (Mumbai-Goa NH) was inaugurated.
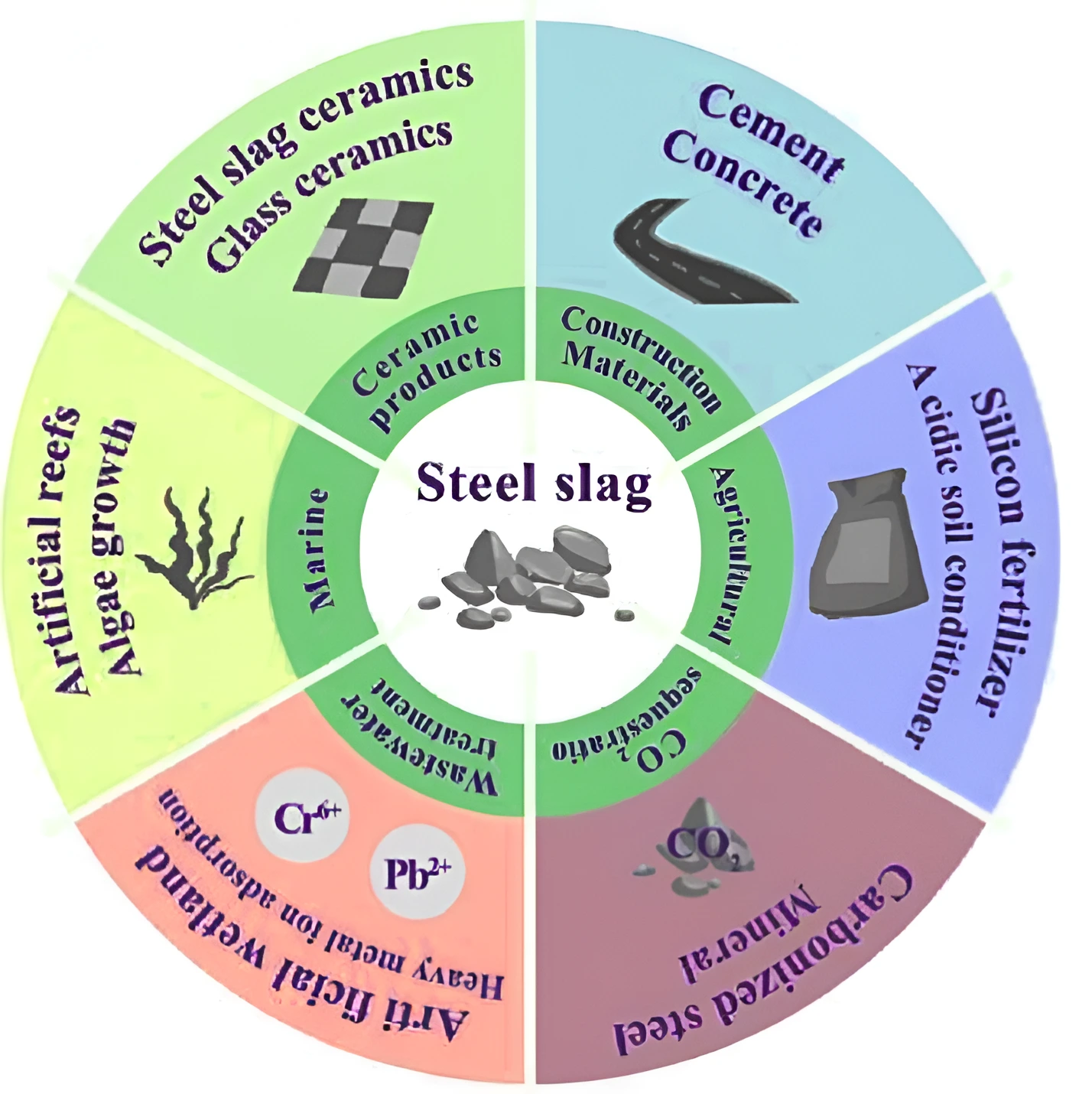
Also Refer: Road Accidents In India-2022′ Report Released By MoRTH
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
This article is based on the news “Jaishankar in Iran, discusses Chabahar Port, Red Sea attacks” which was published in the Indian Express. The External Affairs Minister of India visited Iran during the ongoing high-level exchanges between the two sides.
| Relevancy for Prelim: Red Sea Crisis, Chabahar Port, International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), and Turkmenistan–Afghanistan–Pakistan–India (TAPI).
Relevancy for Mains: About India-Iran Relations: Historical, Political, Economic and Cultural, Challenges in India-Iran Relations, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Also Refer: UN Resolution Calling for ‘Humanitarian Pauses’ in Gaza
About Chabahar Port
Significance of Chabhar Port
Continue To Read: Chabahar Port Project – Why It Significant To India? About INSTC Project
|
Must Read: How Are Houthi Attacks On Ships In The Red Sea Affecting Global Economy?
| Mains Question: What are the maritime security challenges in India? Discuss the organisational, technical and procedural initiatives taken to improve maritime security. (150 words, 10 Marks) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
This article is based on the news “India’s multidimensional poverty rate down to 11.28% in 2022-23 from 29.17% in 2013-14” which was published in the Indian Express. According to a discussion paper ‘Multidimensional Poverty in India since 2005-06’ released by NITI Aayog, the share of India’s population living in multidimensional poverty is estimated to have fallen to 11.28% in 2022-23 from 29.17% in 2013-14.
| Relevancy for Prelims: NITI Aayog, Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI), National Family Health Surveys (NFHS), Suresh Tendulkar Committee (2009), World Bank, MGNREGA, and Public Distribution System.
Relevancy for Mains: About Poverty, Evolution of Poverty Estimation in India, Government Multi-Dimensional Approach for Poverty Reduction, Challenges and Way Forward. |
|---|
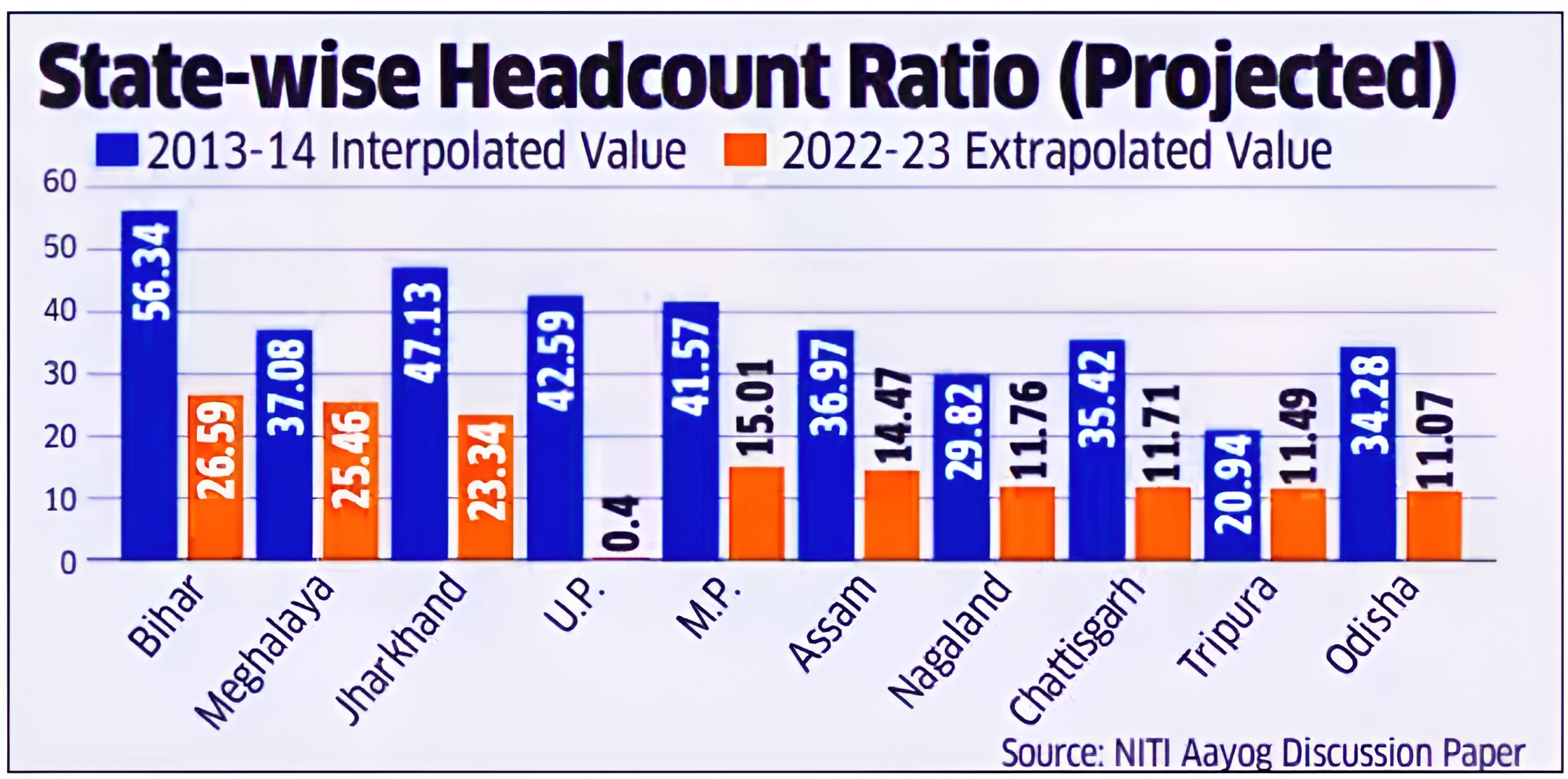 State-wise Estimates: States like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan recorded the sharpest decline in people classified as poor based on the Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI).
State-wise Estimates: States like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan recorded the sharpest decline in people classified as poor based on the Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI).
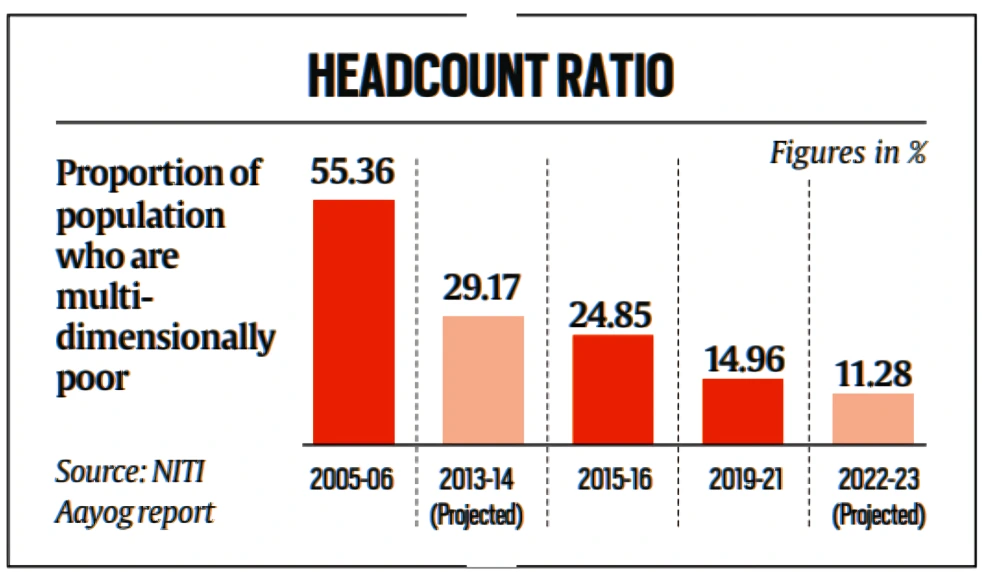 Within the standard of living dimension, the highest levels of deprivation in 2005-06 were found in indicators such as Cooking Fuel (74.40%), Sanitation (70.92%), and Bank Accounts (58.11%).
Within the standard of living dimension, the highest levels of deprivation in 2005-06 were found in indicators such as Cooking Fuel (74.40%), Sanitation (70.92%), and Bank Accounts (58.11%).
Evolution of Poverty Estimation in India
|
|---|
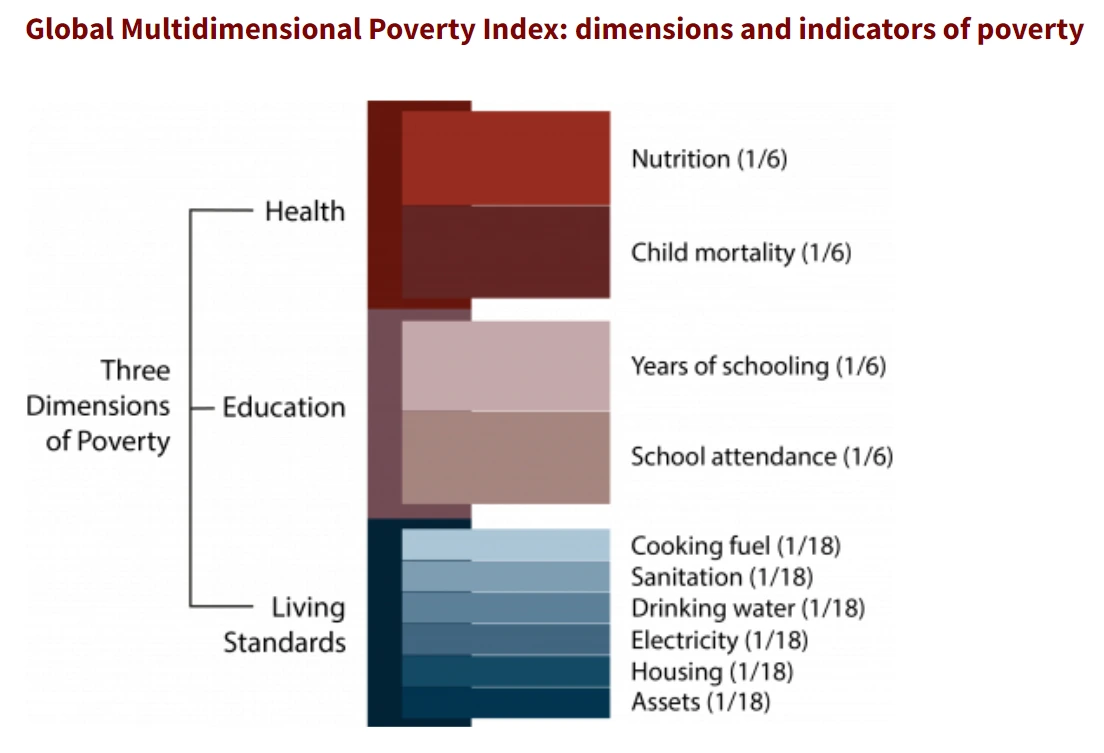 Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI): It is an international measure of acute multidimensional poverty that complements traditional monetary poverty measures by capturing the acute deprivations in health, education, and living standards that a person faces simultaneously.
Global Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI): It is an international measure of acute multidimensional poverty that complements traditional monetary poverty measures by capturing the acute deprivations in health, education, and living standards that a person faces simultaneously.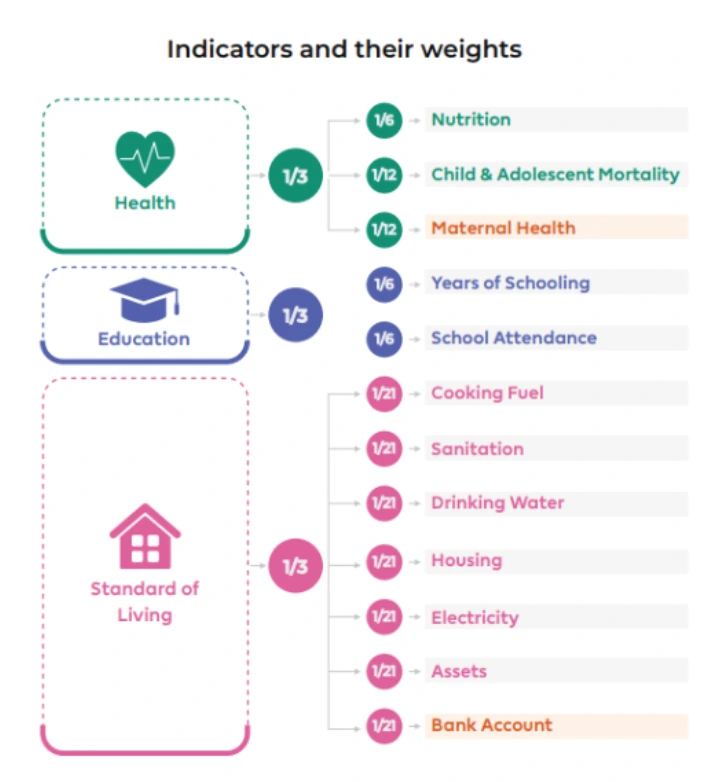 Multidimensional Poverty Index (MP) is considered a better measure to estimate poverty than conventional measures.
Multidimensional Poverty Index (MP) is considered a better measure to estimate poverty than conventional measures.Alkire and Foster (AF) Methodology
|
|---|
Also Refer: Consumption-based Poverty Estimates Have Relevance
The Government of India has made significant efforts to enhance the quality of life for millions of individuals, focusing on the SDG 1.2 target of halving poverty in all its dimensions.
Also Read: India Skills Report 2024 And Skill Development In India
Also Refer: Regional Income Disparities In India
| Mains Question: Critically examine whether growing population is the cause of poverty OR poverty is the main cause of population increase in India. (150 words, 10 Marks) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
