Context: The government has recently approved the “Prithvi Vigyan” initiative at a cost of Rs 4,797 crore over a five-year period from 2021 to 26.
Must Read: Watsonx.AI: An AI Tool For Weather Forecasting
News Source: Pioneer
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The Jallikattu 2024 event in Madurai will be held for three days, beginning on January 15.
 A seal from the Indus Valley civilization depicting the practice is preserved in the National Museum, New Delhi.
A seal from the Indus Valley civilization depicting the practice is preserved in the National Museum, New Delhi.News source: The Economic Times
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Researchers have identified a new class of antibiotics with the potential to tackle a drug-resistant bacterium, Acinetobacter baumannii.
About Acinetobacter baumannii
|
|---|
To Read More: Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: At the Airports, the security personnel are enrolling passengers into Digi Yatra without their consent, by collecting the facial biometrics during check in.
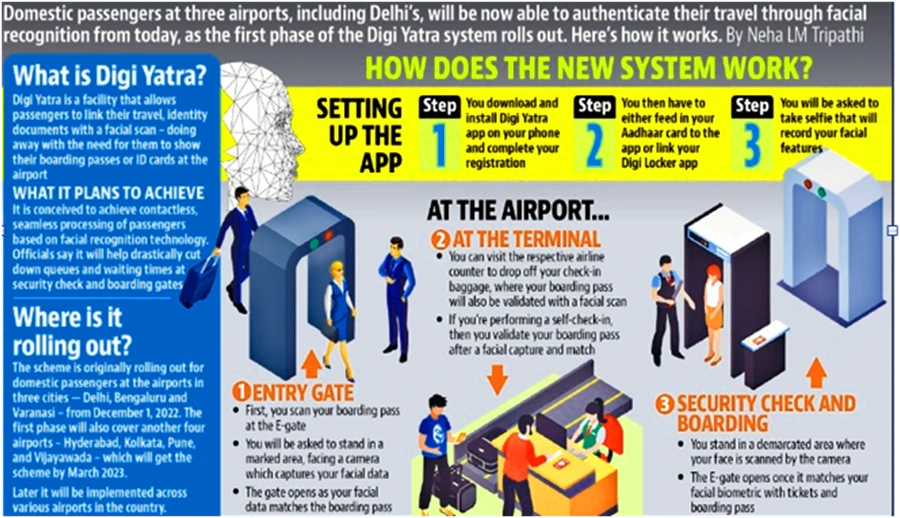
About Digi Yatra Foundation
About Facial Recognition Technology
|
|---|
Must Read: RCS UDAN: Transforming Air Connectivity
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways announced a greenfield corridor project for road connectivity in Kerala.
Must Read: India’s First Solar Expressway In Uttar Pradesh
News Source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: A note on a new ‘deep tech’ policy for India will be sent for Union Cabinet approval in the coming weeks.
What is Deep Tech?
|
|---|
Must Read: What Is Deepfake Technology?
News source: The Hindu
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: The marine commandos (MARCOS) of the Indian Navy safely evacuated the Indian crew from the bulk carrier, after a UK organization indicated pirate hijacking.
Must Read: How Are Houthi Attacks On Ships In The Red Sea Affecting Global Economy?
Read More about: Houthi Attacks, here.
News Source: Hindustan Times
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: International Braille Day has been observed on January 4 every year since 2019.

Disability in India
|
|---|
Must Read: Disability Inclusion: What Is It? And ILO’s SPARK Project
News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: Recently, the Ministry of Education has launched ‘Prerana: An Experiential Learning program’ for students in Classes 9 to 12 in line with the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Must Read: APAAR: One Nation One Student ID Registration Scheme
News Source: PIB
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Context: This article is based on the news “NITI Aayog hosted National Workshop on “Harnessing the Potential of Fisheries in Marine States” which was published in the PIB. NITI Aayog has recently hosted a National Workshop on “Harnessing Potential of Fisheries in the Marine States” in collaboration with the Government of Kerala and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) – Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) in Kochi, Kerala.
| Relevancy for Prelims: NITI Aayog,Ocean Resources And Its Potential Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI), Marine States in India, Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), Blue Economy, and Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Scheme (PMMSY).
Relevancy for Mains: Marine States in India and Addressing Challenges and Promoting Sustainability in the Fisheries Sector of India. |
|---|
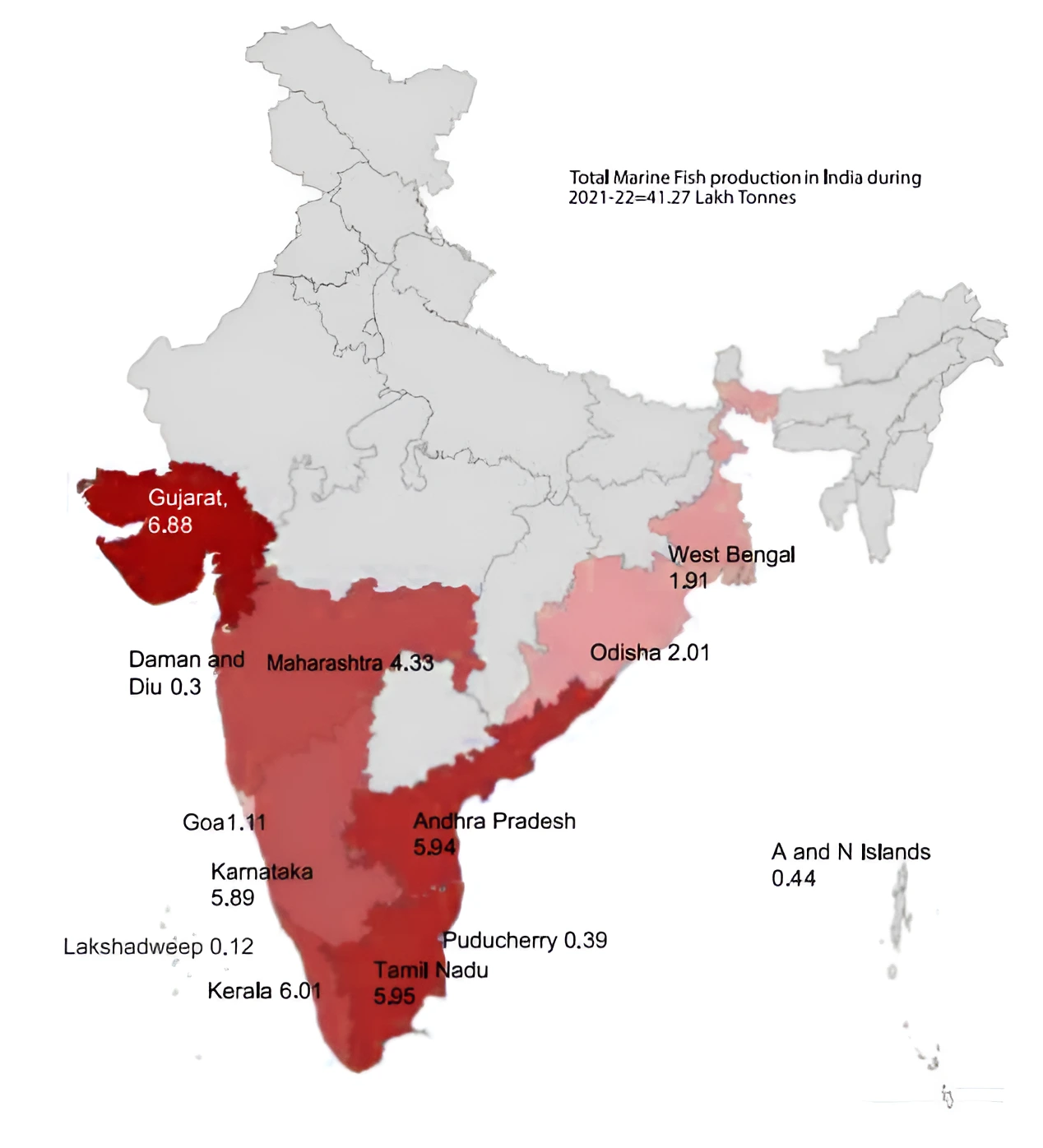
About Inland Fisheries
|
|---|
Continue To Read: National Scheme of Welfare of Fishermen, Eligibility, Benefits, Objective And More
About Integrated Multi-Trophic Aquaculture Fishing (IMTA)
|
|---|
| Mains Question: Defining Blue Revolution. Explain the problem and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (UPSC 2013) |
|---|
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
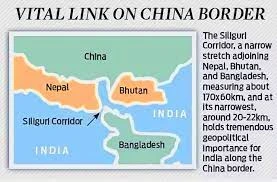
Context: This article is based on the news “Bangladesh elections today: The significance for India, explained” which was published in Indian Express. As elections in Bangladesh are scheduled to take place on 7 January, India is closely observing the process.
| Relevancy for Prelims: India Vs Bangladesh, Ruling and Opposition Party in Bangladesh: Awami League (AL),and Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) Alliance, India’s Neighbourhood First policy, and United Liberation Front of Asom (ULFA).
Relevancy for Mains: Bangladesh Elections 2024 and Its Impact on India Bangladesh Relations. |
|---|
 Ganga Water Treaty: In 1996, during Hasina’s first term in office as prime minister, the two countries signed the Ganga Water Treaty on sharing waters of the river Ganges.
Ganga Water Treaty: In 1996, during Hasina’s first term in office as prime minister, the two countries signed the Ganga Water Treaty on sharing waters of the river Ganges.
About India Bangladesh RelationsThe current state of affairs between the two neighboring nations is coined as the ‘Sonali Adhyaya’ or a ‘golden chapter,’ symbolizing the success story of India’s Neighbourhood First policy. The dimensions of the India Bangladesh relations are as follows:
|
|---|
 Drug Trafficking: Bangladesh is increasingly being used as a transit point by drug dealers and the drug mafia, which dispatches heroin and opium from Burma, and other countries of the golden triangle, to different destinations.
Drug Trafficking: Bangladesh is increasingly being used as a transit point by drug dealers and the drug mafia, which dispatches heroin and opium from Burma, and other countries of the golden triangle, to different destinations.Must Read: Drug Trafficking In India
The results of the 2024 Bangladesh elections are crucial for India Bangladesh relations, as the re-election of Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina and her Awami League would likely contribute to the maintenance of robust cooperation between the two nations.
| Mains Question: Critically examine the compulsions which prompted India to play decisive roles in the emergence of Bangladesh. (UPSC 2013) |
|---|
|
Must Read |
|
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
