A research by HSBC shows that India needs to embrace hybrid vehicles over the next 5-10 years on the way to full electrification.
About Hybrid Vehicles
About Electric Vehicle
|
|---|
Also Read:
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Indian scientists claim to have discovered High Velocity Air Fuel (HVAF) Spray Technique as an alternative to hard chrome plating.
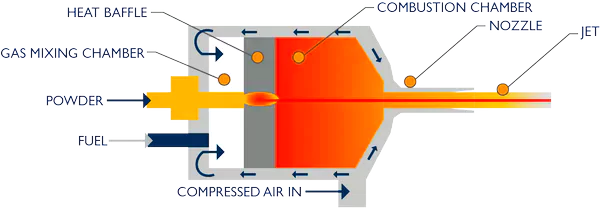
Chrome Plating
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Scientists have combined real human brain tissue with electronics to make a new kind of biocomputer.
Neuromorphic computing :
|
|---|
Stem cells:
|
|---|
These are networks formed by changing the function of self-organizing brain-like structures called organoids which are connected to microelectrode arrays (MEAs) to create networks that resemble real brains.
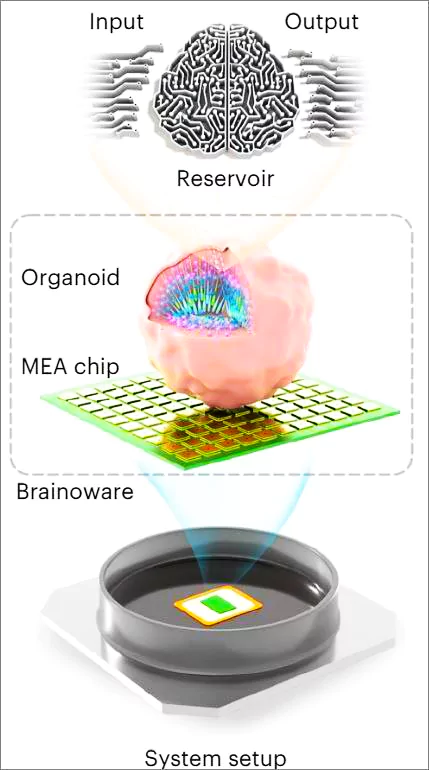
It linked a brain organoid to microelectrodes, forming an organoid neural network, a live component in an artificial neural network.
The research represents a groundbreaking and captivating proof-of-concept exploration into organoid intelligence, demonstrating the potential utilization of brain organoids for adaptive reservoir computing.
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A senior congress leader was prevented from visiting Assam’s Batadrava Than during his political campaign.
Batadrava Than, or Bordowa Than, is one of the most sacred sites for Assamese Vaishnavites.
The Ek Saran Naam Dharma:
|
|---|
News Source: Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
As per India Meteorological Department (IMD), January of 2024 has been the second driest since 1901.
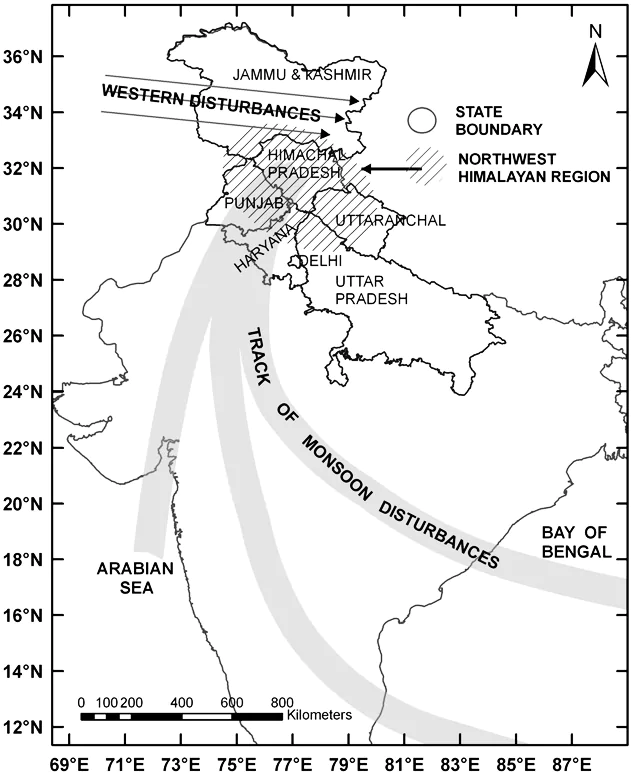 Literal Meaning of Western Disturbance: In term WD, the “Disturbance” means an area of “disturbed” or reduced air pressure while the “Western” implies that the disturbance travels from the west to the east direction.
Literal Meaning of Western Disturbance: In term WD, the “Disturbance” means an area of “disturbed” or reduced air pressure while the “Western” implies that the disturbance travels from the west to the east direction.News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Supreme Court questioned the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir about the non-publication of orders for the suspension of Internet services.
| Favor | Against |
|
|
|
|
Anuradha Bhasin vs Union of India Case, 2020:
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Reserve Bank of India barred Paytm Payments Bank ltd. from offering all its core services from March 2024.
| Feature | Payment bank | Commercial bank |
| Deposits | Maximum limit is set up to Rs 1 lakh | No restrictions. |
| Minimum capital: | A minimum capital of Rs 100 crore, with promoters contributing at least 40% of the capital. | Commercial banks, meanwhile, need to have Rs 500 crore as its paid-up voting equity capital. |
| Minimum balance:. | They are zero balance accounts there is no minimum balance required | Many commercial banks require you to have a minimum balance in your account. Failure to do so may result in a penalty |
| Loans and credit: | A payments bank is not allowed to give any form of loan or issue a credit card, which is also a form of unsecured personal loan. | No such Restrictions |
| Government securities | 75% of the total Demand Deposits needs to be invested in Government Securities | Maximum 22% needs to invest in Government securities |
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, India has increased its tally of Ramsar sites (Wetlands of International Importance) to 80 from existing 75 by designating five more wetlands, three from Karnataka and two from Tamil Nadu as Ramsar sites.
World Wetlands Day 2024 (WWD)
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Need a ‘mechanism’ to detect vendetta in ED-States cases: Supreme Court” which was published in the Hindu. The Supreme Court calls for a mechanism to detect political vendetta in the Enforcement Directorate (ED) probe.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Supreme Court, Enforcement Directorate (ED), Money Laundering Act, and Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
Relevancy for Mains: Enforcement Directorate: Role, Significance, Challenges and Way Forward. |
|---|

| On the Basis of | Enforcement Directorate (ED) | State Police |
| Jurisdiction | The Enforcement Directorate operates as a specialized law enforcement agency under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, GoI. | State police function under the administrative control of their respective state governments. |
| Function | The primary mandate of the Enforcement Directorate is to enforce economic laws, focusing on cases related to money laundering and foreign exchange violations under the (PMLA) and the (FEMA)
|
State police are tasked with maintaining law and order, preventing and detecting crimes & ensuring public safety, as Police and Public Order fall under State subjects as per the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution of India. |
| Investigation | The Enforcement Directorate examines cases related to economic crimes, financial scams, money laundering, and foreign exchange infractions, aiming to locate, identify, confiscate, and track down the proceeds of crime. | State police investigate a wide range of crimes such as theft, robbery, assault, murder, kidnapping, drug trafficking, and other offenses outlined in the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and relevant state legislation. |
Registration of case |
They initiate investigations through search procedures & issue summonses, but they cannot independently register a case. Instead, they rely on agencies like the CBI or state police to register an offense, based on which the Enforcement Directorate files a Case Information Report. | State police, on the other hand, are authorized to independently initiate investigations into cognizable cases without requiring court orders.
|
Admissibility of statement |
The provisions of the PMLA confer greater power to the Enforcement Directorate compared to the police. Under the PMLA, statements recorded before an investigating officer are admissible in court as evidence. | Statements made by an accused to the police are generally inadmissible as evidence in a court of law. |
The credibility of leading investigative institutions are under scrutiny. The fight against corruption is closely linked to overhauling investigative processes, requiring collaboration among adjudicating authorities for transparency and fairness. The Supreme Court’s intervention in the ED-states conflict, advocating for a screening mechanism to alleviate concerns of perceived or actual political vendettas, is a positive development.”
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
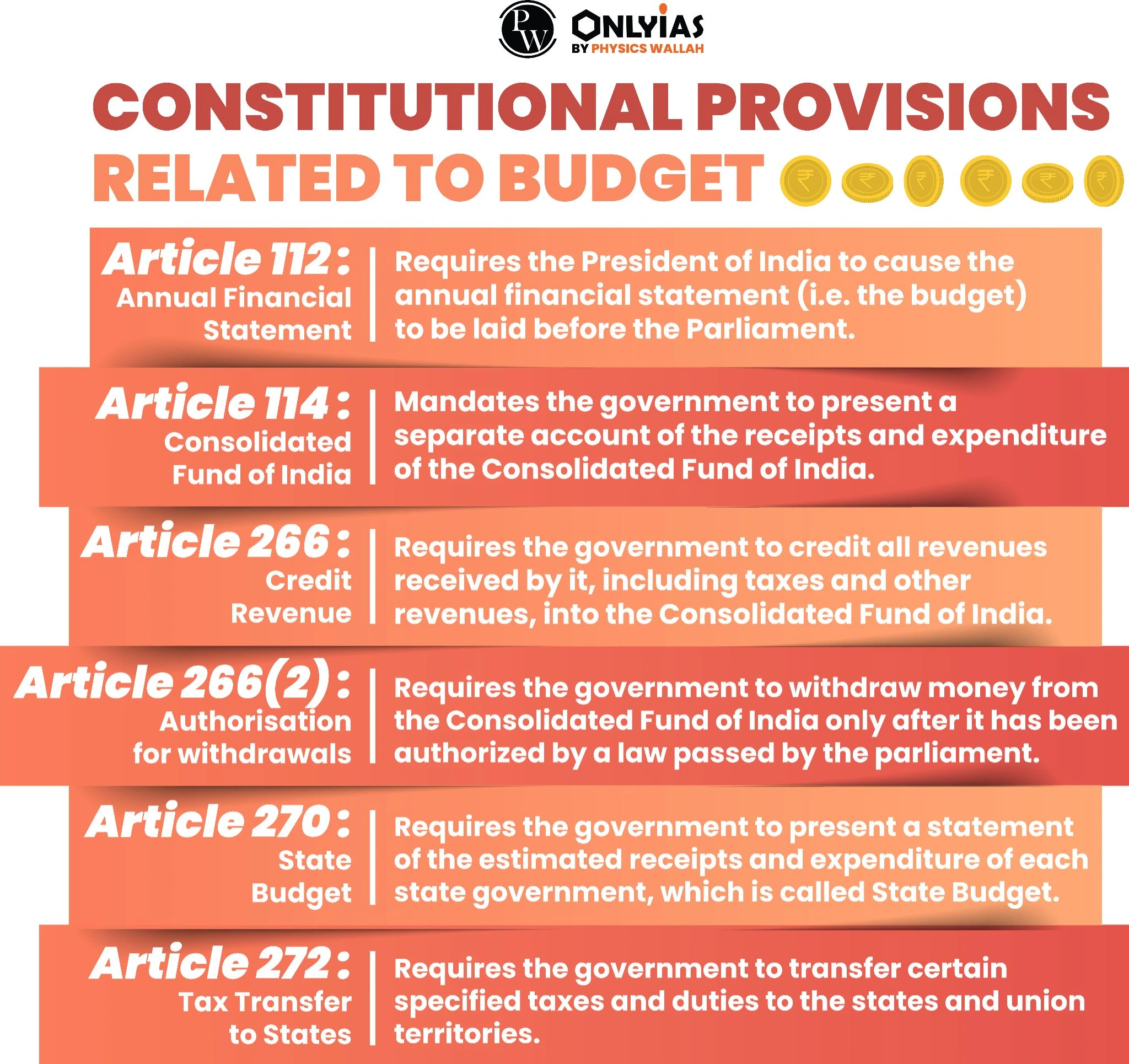
This article is based on the news “Parliament Budget Session Live Updates: Day after interim Budget, INDIA party leaders to chalk out joint strategy” which was published in the Indian Express.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Parliament Budget Session 2024 Live Updates, Union Budget 2024-25, $7-Trillion GDP: Indian Economy Review 2024, Foreign Flows, Ayushman Bharat, and Viksit Bharat @2047.
Relevancy for Mains: Interim Budget 2024: Key Highlights, Fund Allocation Related Data, & More. |
|---|
| Aspect | Interim Budget | Full Fledged Budget |
| Timing | Interim Budget Presented by the outgoing government before elections. | Full Fledged Budget Presented by the newly elected government. |
| Scope | Covers expenditures and receipts for a short period. | Encompasses all aspects of government finances for the fiscal year. |
| Purpose | Ensures continuity of essential functions temporarily. | Serves as a strategic guide for the entire fiscal year. |
| Policy Announcements | Limited major policy announcements. | Allows for comprehensive policy declarations. |
| Economic Survey | No presentation before the Interim Budget. | Usually presented a day before the Full Budget. |

 Revenue Budget: It includes the government’s revenue receipts and expenditure.
Revenue Budget: It includes the government’s revenue receipts and expenditure.
Interim Budget: Part A
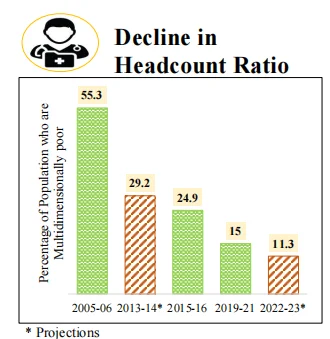
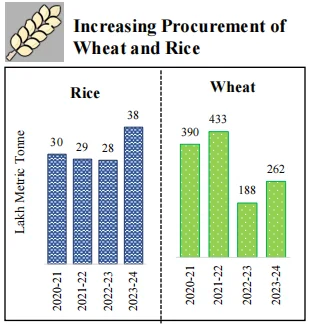
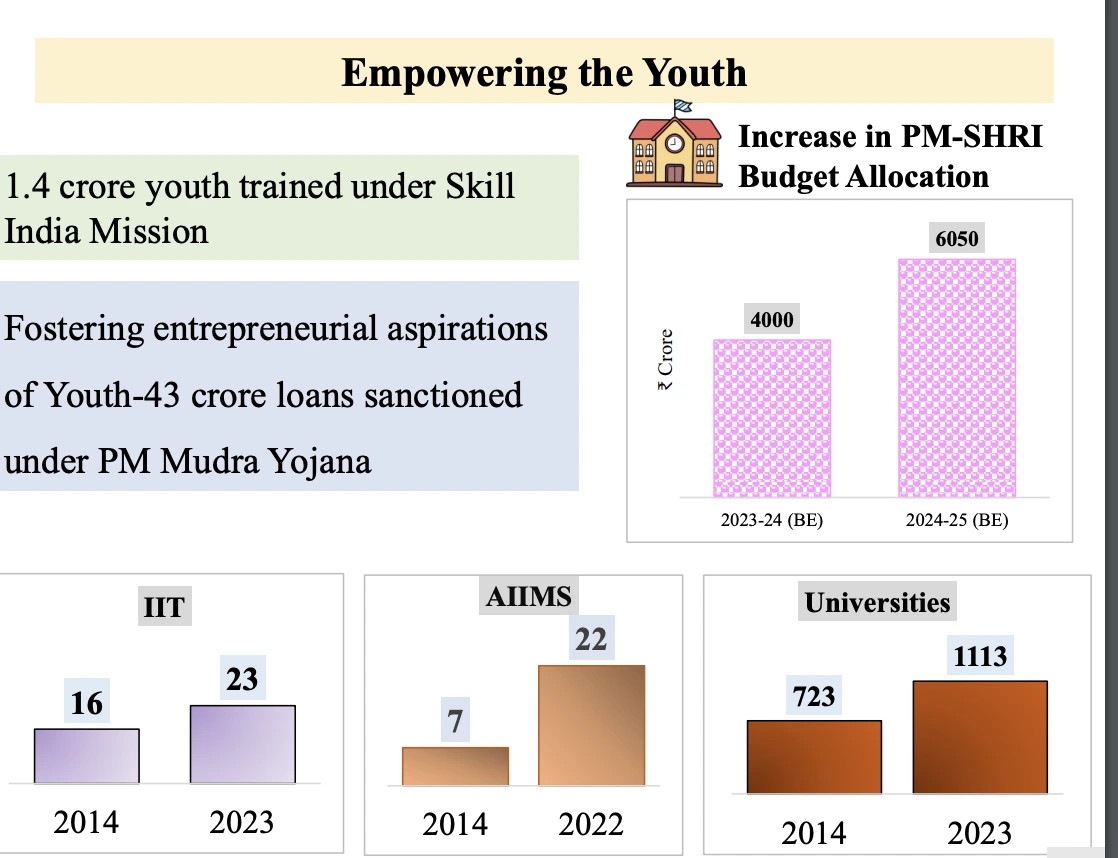
The government is focusing on four aspects of our society i.e., GYAN.
 PM-JANMAN Yojana: Aid the development of particularly vulnerable tribal groups (PVTG).
PM-JANMAN Yojana: Aid the development of particularly vulnerable tribal groups (PVTG).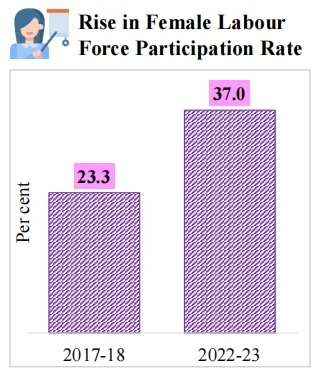
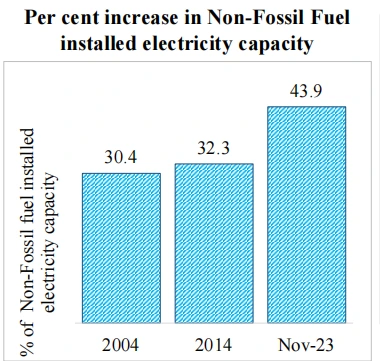 e-Mobility
e-Mobility
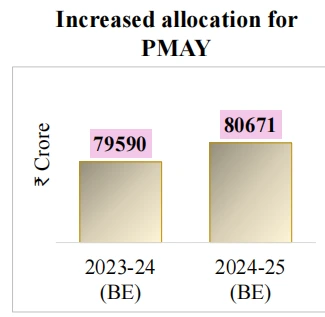 Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 to be expedited for improved nutrition delivery, early childhood care and development.
Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0 to be expedited for improved nutrition delivery, early childhood care and development.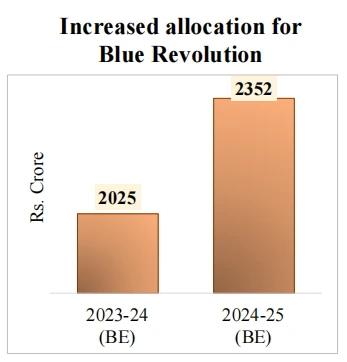
 5 Integrated Aquaparks to be set up.
5 Integrated Aquaparks to be set up.
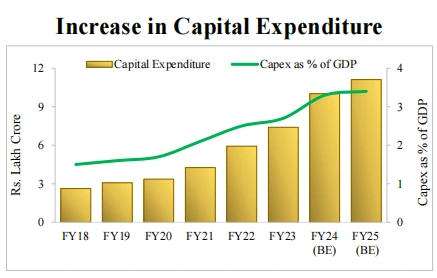
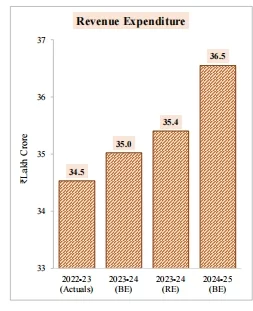
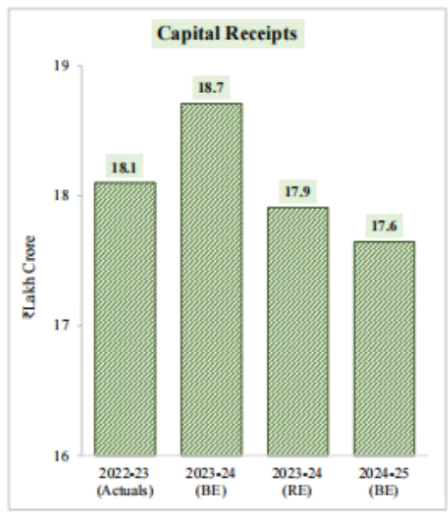 Fiscal Deficit: 5.1 percent of GDP.
Fiscal Deficit: 5.1 percent of GDP.Interim Budget: Part B
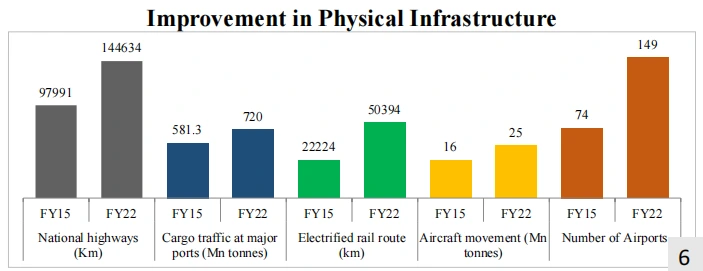
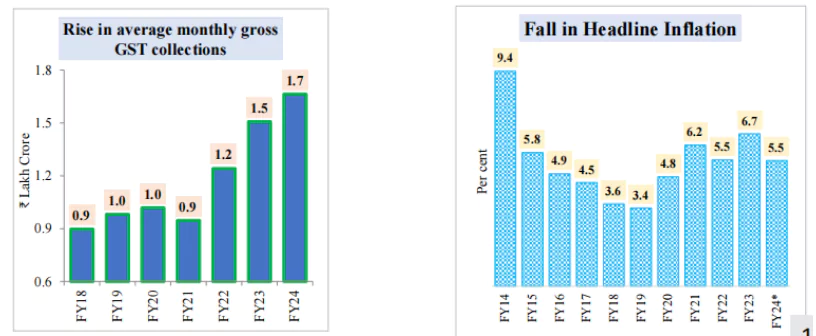
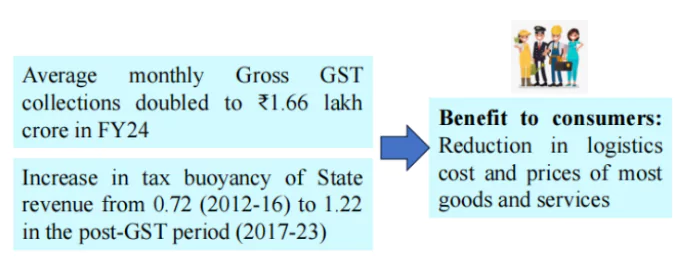 GST unified the highly fragmented indirect tax regime in India
GST unified the highly fragmented indirect tax regime in India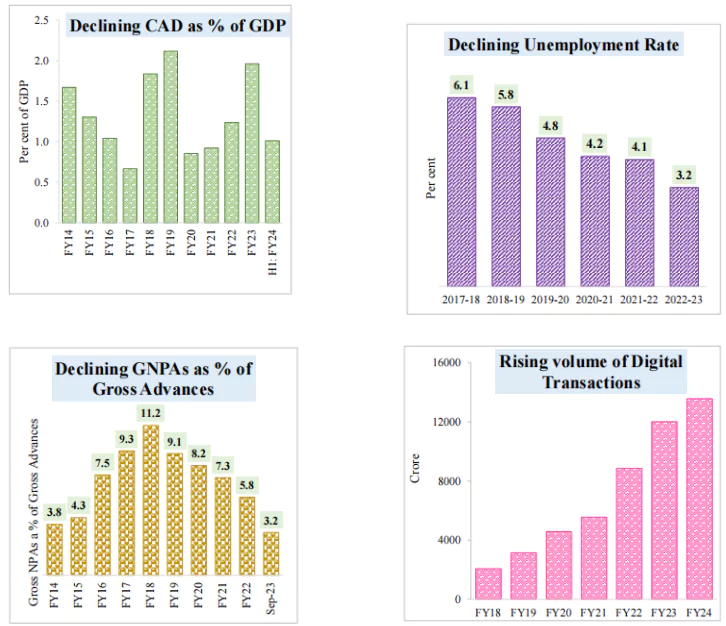
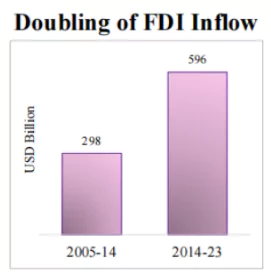
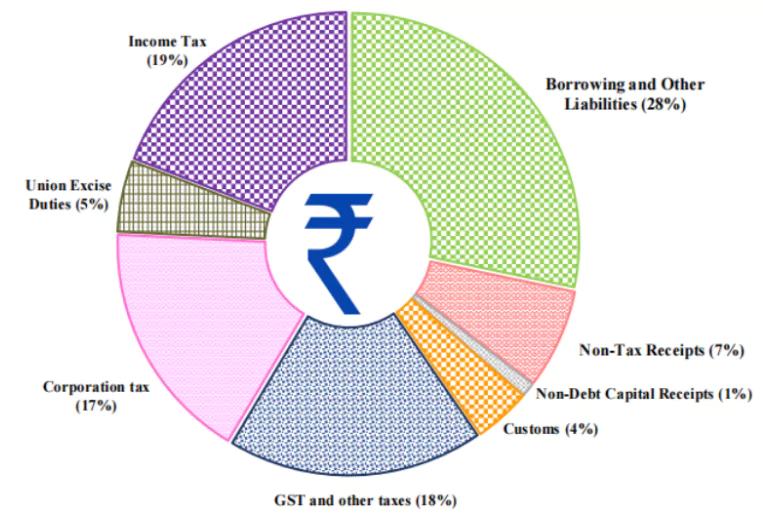
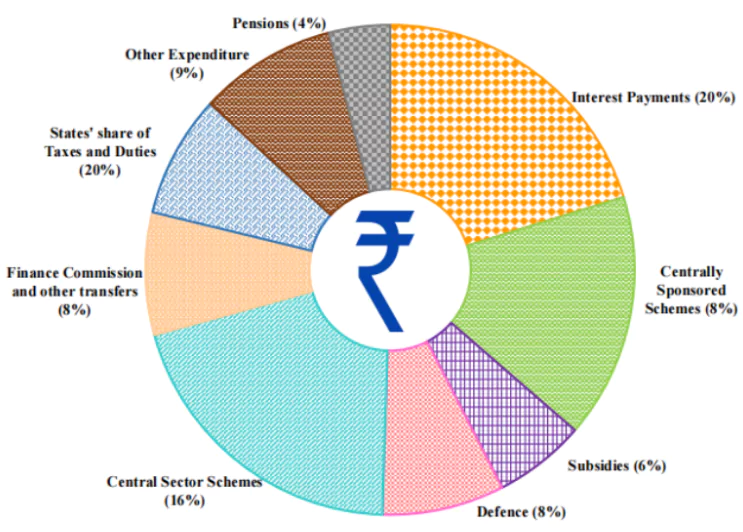
| Rupee Comes From: | Rupee Goes To: |
 |
 |
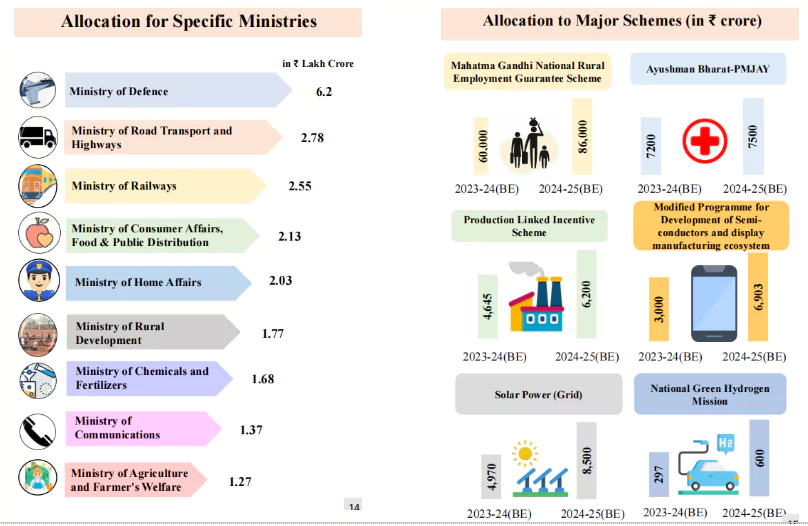
| Mains Question: What is the meaning of the term ‘tax expenditure’? Taking the housing sector as an example, discuss how it influences the budgetary policies of the government. (200 words, 10 marks) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
