The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi today penned his thoughts on Sant Shiromani Acharya Shri 108 Vidhyasagar Maharaj Ji.

Doctrine of Essentiality:
|
|---|
Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved the Fair and Remunerative Price (FRP) of sugarcane for Sugar Season 2024-25.
About Sugarcane Crop:
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
An alternative route for trade to bypass the Red Sea was announced by the Israeli transport minister.
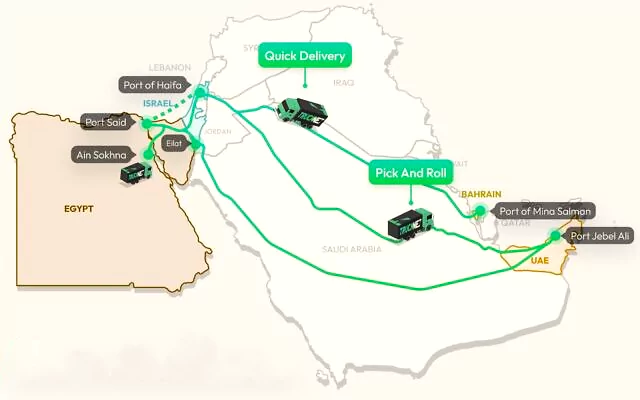
The Red Sea Crisis:
|
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
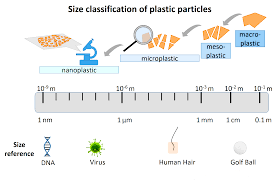
A recent study conducted by scientists at Columbia University in New York has found that a litre of bottled water may contain over one hundred thousand particles of micro and nano plastics.
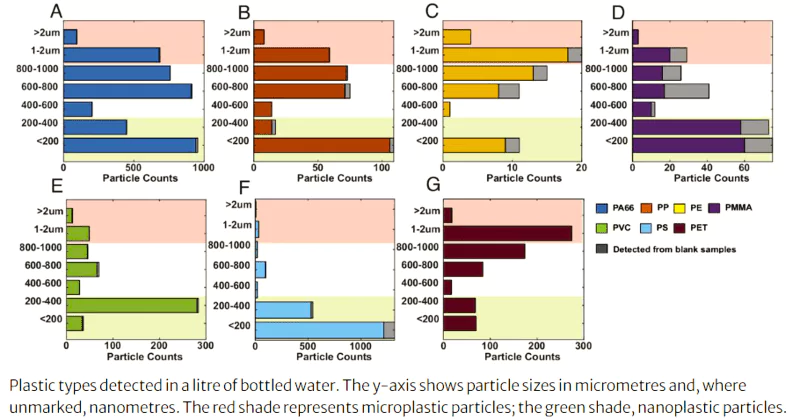 Presence of Unmatched Particles: The study also detected particles in the sample that didn’t correspond to existing standards.
Presence of Unmatched Particles: The study also detected particles in the sample that didn’t correspond to existing standards.News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
ISRO achieves human rating of CE20 cryogenic engine CE20 for Gaganyaan mission.
Gaganyaan Mission
|
|---|
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Union Cabinet has approved the amendment in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy on the space sector.
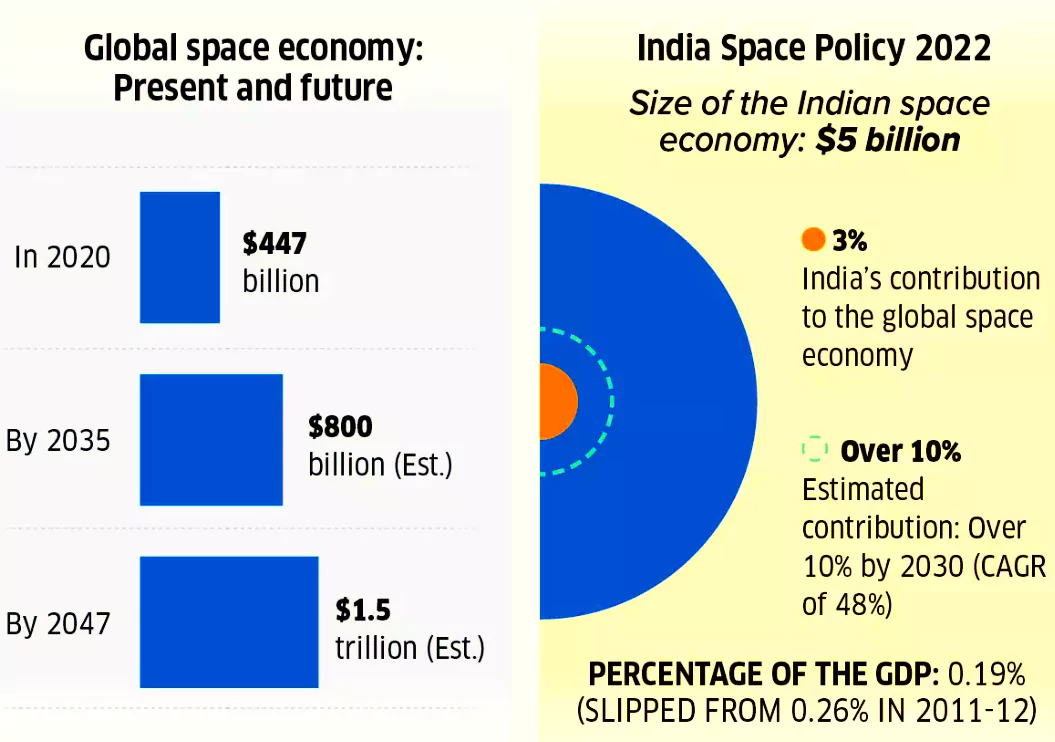
Indian Space Policy 2023
|
|---|
Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Union Cabinet approves the Flood Management and Border Areas Programme (FMBAP) for a period of additional five years.
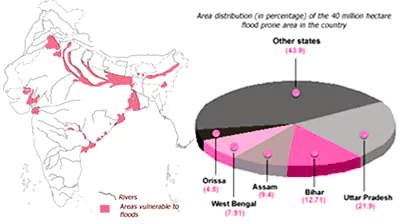
The Flood Management and Border Areas Programme has two components –
News source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

Recently, the 9th Edition of Raisina Dialogue 2024 began in New Delhi.
ORF (Observer Research Foundation)
|
|---|
News Source: IE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Astronomers have discovered a rare class of stars, called helium-covered hot stars.
Binary Star
|
|---|
Class O or B Star
|
|---|
News Source: ILF Science and The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Cabinet approves Proposal for Implementation of Umbrella Scheme on “Women Safety” which was published in the Pib. The Union Cabinet approved the proposal of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) of continuation of the implementation of Umbrella Scheme on ‘Women Safety in India’ at a total cost of Rs.1179.72 crore during the period from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Women Safety In India, Cyber Security, NCRB Report 2022 On Crime In India, and Cyber Kidnapping.
Relevancy for Mains: Women Safety in India: Concerns, Challenges, Laws, and Government Initiatives. |
|---|

Laws For Women Safety in India
|
Other Initiatives for the Empowerment of Women in India
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “When can a bill be designated as a ‘money bill’: SC to hear challenge” which was published in the Indian Express. In the backdrop of the recent judgement of the Supreme Court on the Electoral bond scheme, Money bills have recently become subject to a constitutional challenge.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Indian Parliament, Indian Judiciary, Supreme Court, Indian Constitution, Money Laundering Act, and Enforcement Directorate (ED).
Relevancy for Mains: Money Bill (Article 110): Definition, Constitutional Provisions, Significance, Recent Controversies, and Way Forward. |
|---|

A bill is not to be deemed to be a money bill by reason only that it provides for

The Supreme Court should clarify the constituents of the money bill for the legislative efficiency and proper functioning of the democracy.
| Prelims PYQ (2023):
With reference to Finance Bill and Money Bill in the Indian Parliament consider the following statements: 1. When the Lok Sabha transmits Finance Bill to the Rajya Sabha, it can amend or reject the Bill. 2. When the Lok Sabha transmits Money Bill to the Rajya Sabha, it cannot amend or reject the Bill, it can only make recommendations. 3. In the case of disagreement between the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha, there is no joint sitting for Money Bill, but a joint sitting becomes necessary for Finance Bill. How many of the above statements are correct? (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) All three (d) None Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
