The Prime Minister of the Cooperative Republic of Guyana recently arrived on an official visit to India.
Caribbean Community (CARICOM)
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has kept the repo rates unchanged for the sixth time in a row at 6.5 per cent.
| The repo rate is the interest rate at which the RBI lends to commercial banks. |
|---|
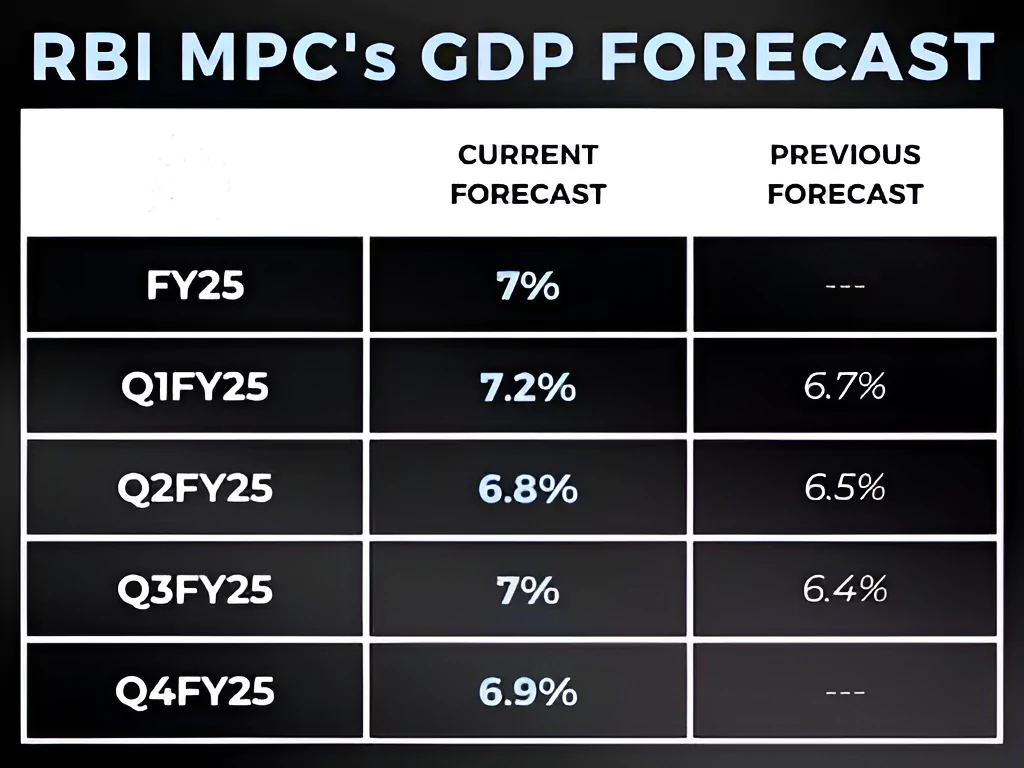 Taking into account this growth-inflation dynamics and the fact that transmission of the cumulative 250 bps policy rate hike is still underway,
Taking into account this growth-inflation dynamics and the fact that transmission of the cumulative 250 bps policy rate hike is still underway,
What is the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)?
Function: The MPC determines the policy interest rate (repo rate) required to achieve the inflation target. The Decision-Making Monetary Policy Committee
Members of Monetary Policy Committee
|
|---|
News Source: All India Radio
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
NITI Aayog and the Netherlands embassy released a report titled ‘LNG as a Transportation Fuel in Medium and Heavy Commercial Vehicle’ at the India Energy Week 2024.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
IRDAI recently released its draft Rural, Social Sector and Motor Third Party Obligations Regulations, 2024.
Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI)
|
|---|
News source: The Indian express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A committed investment of 6766 crores has been approved under the Production Linked Incentive Scheme (PLI) for White Goods containing Air Conditioners and LED lights.
What Are White Goods?
|
Production Linked Incentive Scheme
|
|---|
News Source: News on AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Prime Minister addressed the programme marking the 150th anniversary of Srila Prabhupada at Bharat Mandapam and released a commemorative stamp and a coin in his honour.

About Chaitanya Mahaprabhu
|
|---|
News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Union Cabinet has given its approval for the PRITHvi VIgyan scheme, a research scheme worth Rs 4,797 crore.
Sub-Schemes Under Prithvi VIgyan Scheme
|
|---|
News Source: Indianexpress
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Finance Minister has announced the launch of a new scheme to strengthen deep tech capabilities in the defence sector.
News Source: Indianexpress
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A recent study reported that Deep learning approaches are important for drug discovery.
What is Deep Learning?
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu and MIT News
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
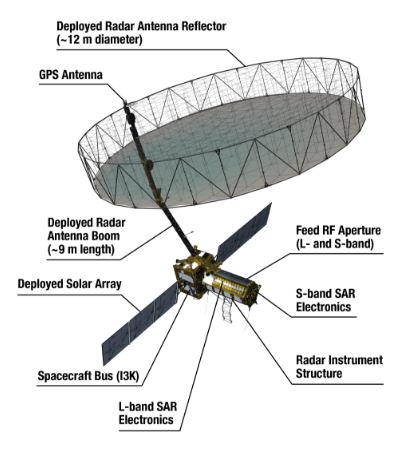
Kerala University of Fisheries and Ocean Studies (Kufos) will be part of an advanced NISAR phase 2 research project on forest biomass and carbon monitoring using radar data.
Kerala University of Fisheries and Ocean Studies (KUFOS)
|
|---|
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The European Union proposed a new goal for 2040 through its commission, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas net emissions by 90% compared to 1990 levels.
This proposal is an interim step required by the EU Climate Law (2021), which outlines a process to develop a 2040 target within six months of the first Global Stocktake (GST), which concluded at the 28th Conference of Parties to the UNFCCC in Dubai in December 2023.
What is Global Stocktake?
|
|---|
The EU has introduced several climate-focused policies alongside the 2040 proposal.
News Source: DownToEarth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “lon Musk’s Neuralink is a minefield of scientific and ethical concerns” which was published in the Indian Express. Neuralink has placed an experimental brain device (called Telepathy Chip) in a person in the first human test of the technology.
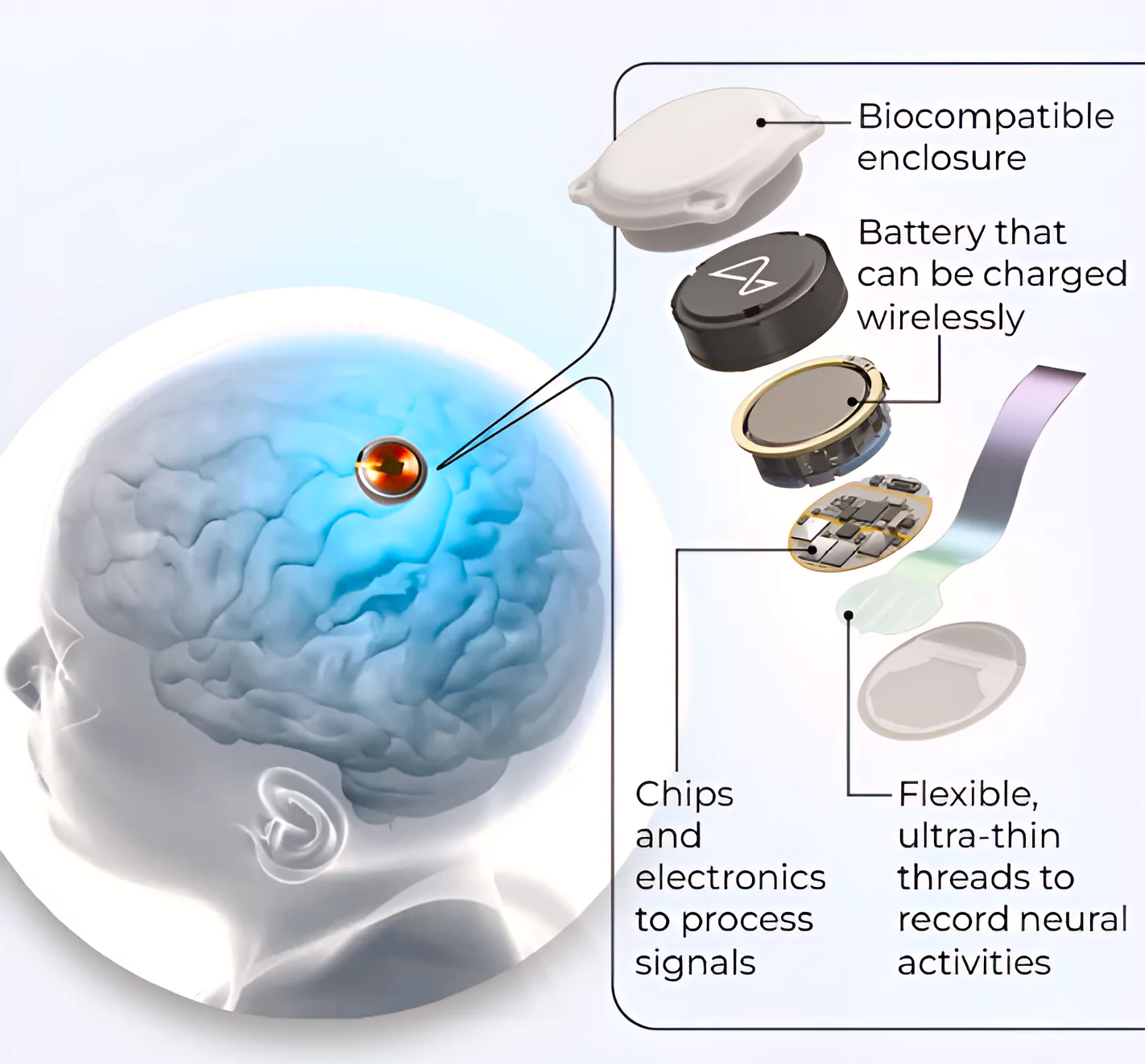 Telepathy Chip: It is a surgically implantable chip that records data from individual neurons, transmitting it to a computer for task execution.
Telepathy Chip: It is a surgically implantable chip that records data from individual neurons, transmitting it to a computer for task execution.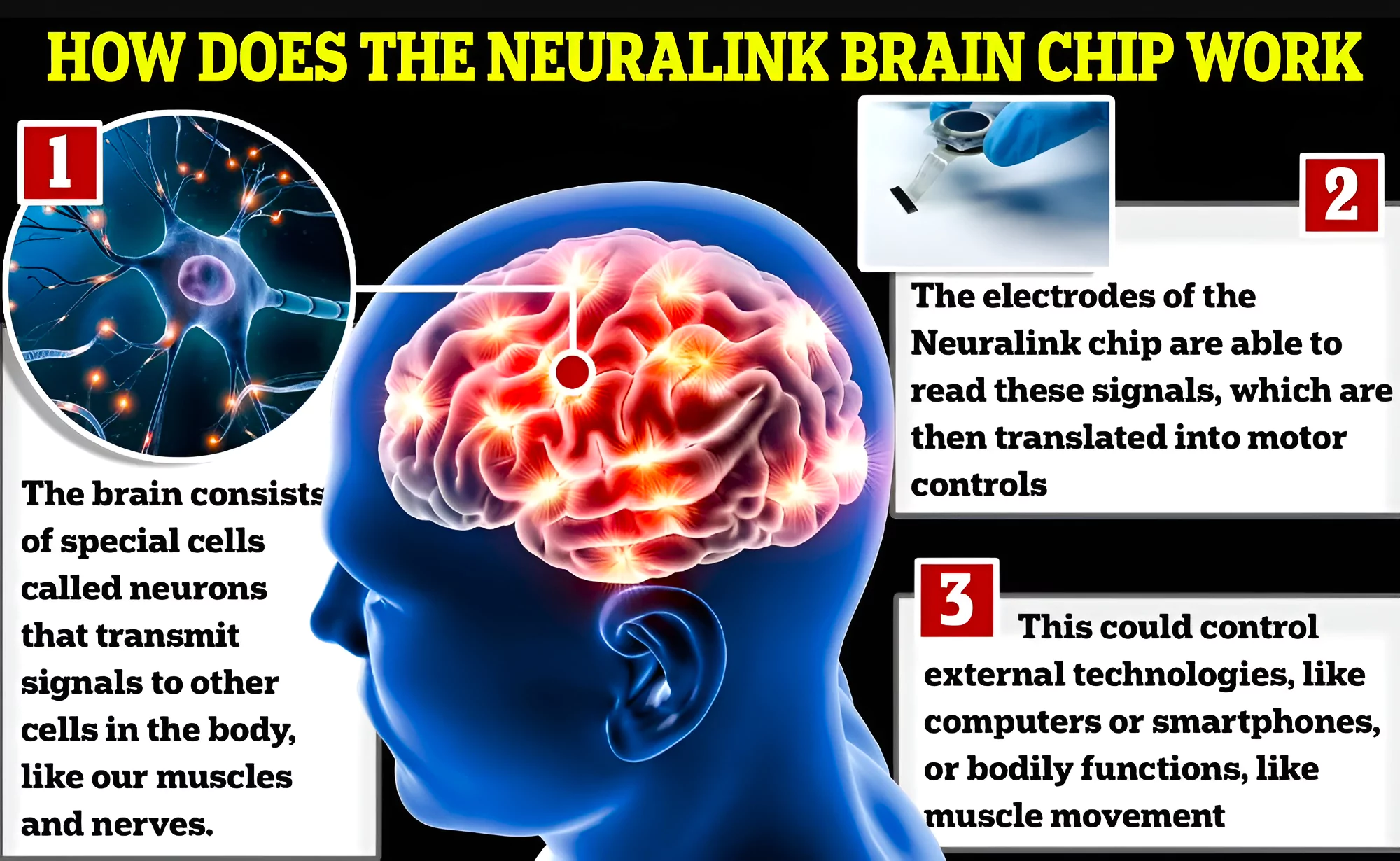
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “4 takeaways from Uttarakhand’s Uniform Civil Code Bill: on live-in relationships, bigamy and more” which was published in the All India Radio. Recently, the Uttarakhand government tabled the Uniform Civil Code (UCC) 2024 Bill in the Assembly which makes important changes in areas such as marriage, divorce, and succession.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Uniform Civil Code Bill 2024, Uniform Civil Code in India, Triple talaq, and Directive Principles Of State Policy.
Relevancy for Mains: Uttarakhand UCC Bill 2024: Provisions, and Concerns, Way Forward. |
|---|
Uniform Civil Code
|
|---|
|
|---|
Exception- Provisions of the UCC Bill do not apply to Tribal Communities:
|
|---|
2Ist Law Commission’s Stand on UCC
|
|---|
Uttarakhand’s initiative aligns with the words of K.M. Munshi, who contended that a Uttarakhand UCC bill would not defeat the freedom of religion since the state is empowered to make laws related to religious practices if intended for social reform.
News Source: The Indian Express
To Read more on the Uniform Civil Code (UCC), click here
| Mains Question: Discuss the possible factors that inhibit India from enacting for its citizens a uniform civil code as provided for in the Directive Principles of State Policy. (200 words, 12.5 marks) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
