The Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers Department of Pharmaceuticals introduces the RPTUAS Scheme (Revamped Pharmaceuticals Technology Upgradation Assistance).
News Source: Business Standard
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The 96th Academy Awards ceremony took place in Hollywood, Los Angeles, California.
| Awards | Oscars 2024 Winners |
| Best Picture | Oppenheimer |
| Best Actor | Cillian Murphy (Oppenheimer). |
| Best Actress | Emma Stone (Poor Things). |
| Best Director | Christopher Nolan (Oppenheimer). |
| Best Supporting Actor | Robert Downey Jr (Oppenheimer). |
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Avaana Sustainability Fund (ASF)
|
|---|
News Source: Financial Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
According to the ‘Democracy Report 2024’ released by the Gothenburg-based V-Dem Institute, India, has failed on multiple metrics to emerge as “one of the worst autocratizers”.
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Madhya Pradesh High Court directed the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) to conduct a scientific survey of the Bhojshala Temple-Kamal Maula Mosque complex in Dhar district.

News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently the Prime Minister inaugurated Sabroom Land Port in Tripura located along the India-Bangladesh international border.
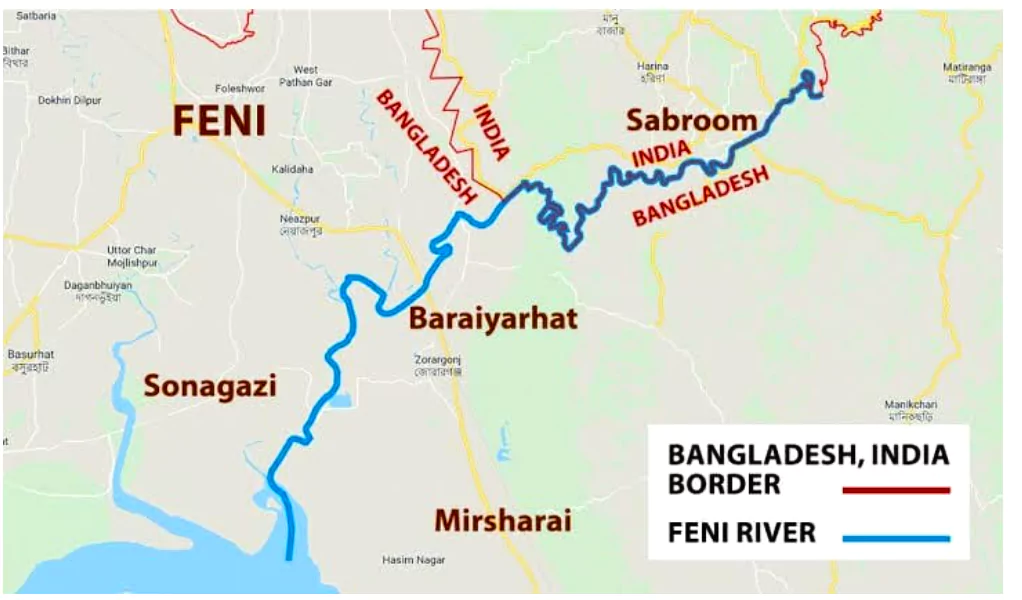
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

| Other Variants of Agni Missile: The other variants of the Agni missiles developed by DRDO include the 700-km range Agni-1, the 2,000-km Agni-2, the 3,000-km Agni-3, and 4,000-km range Agni-4. |
|---|
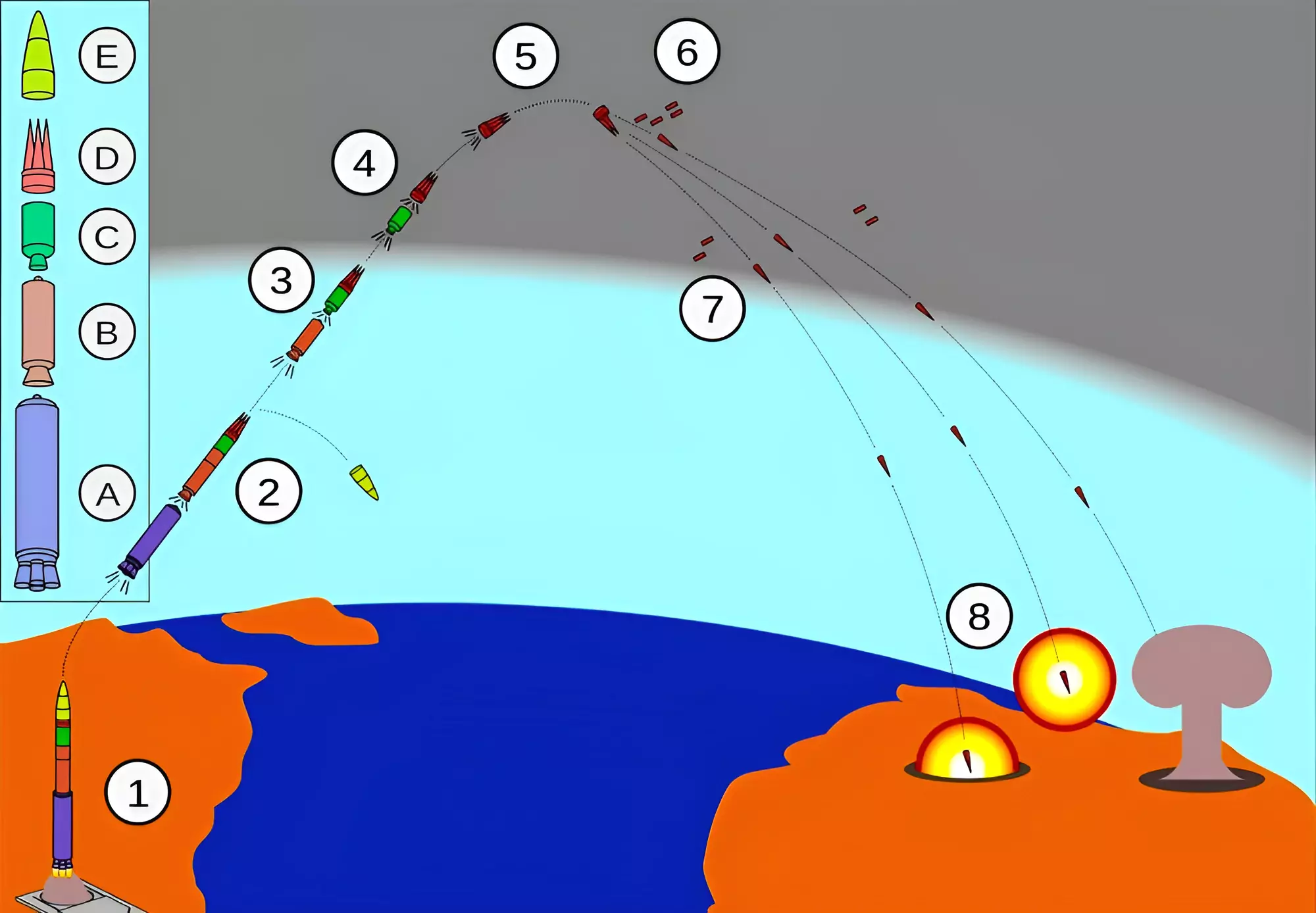
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Kerala Mumps Outbreak: Kerala is currently facing a surge in mumps cases.
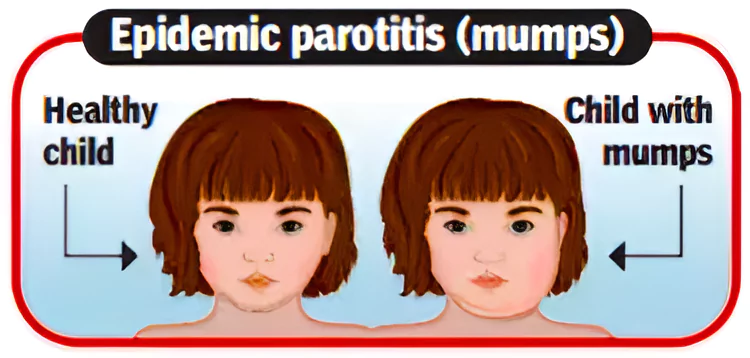
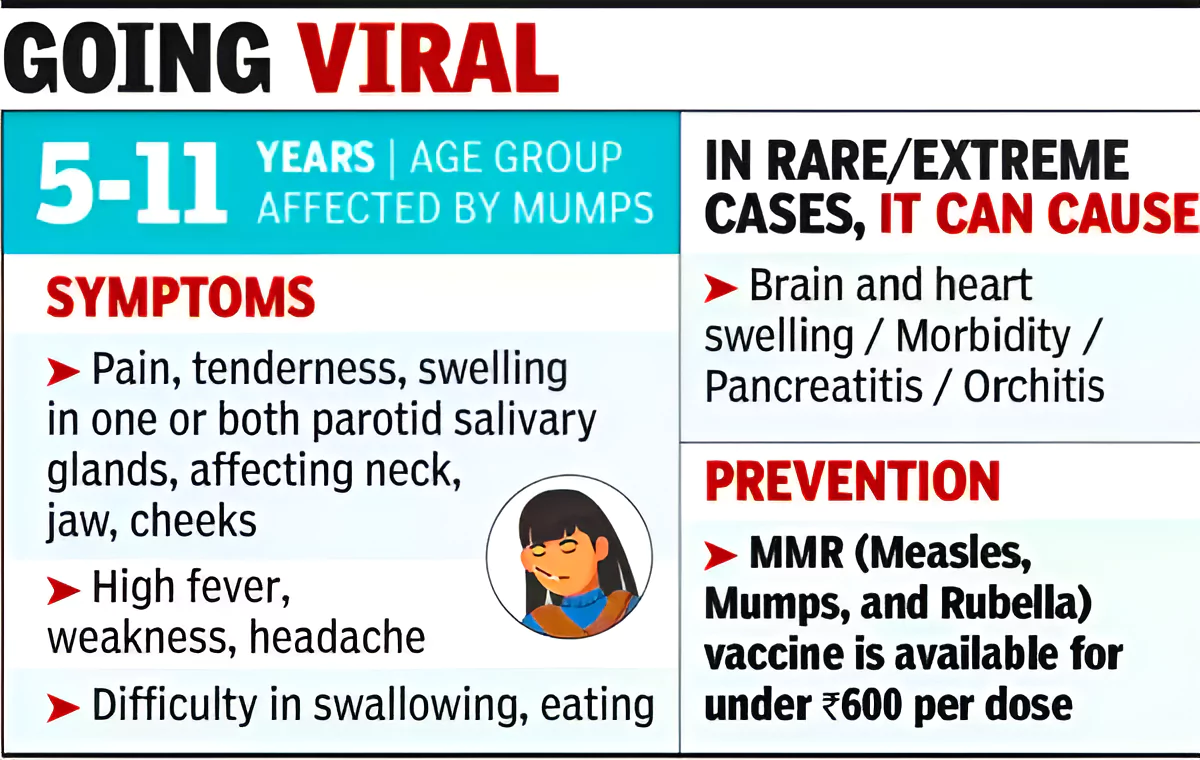 It is also known as parotitis.
It is also known as parotitis. 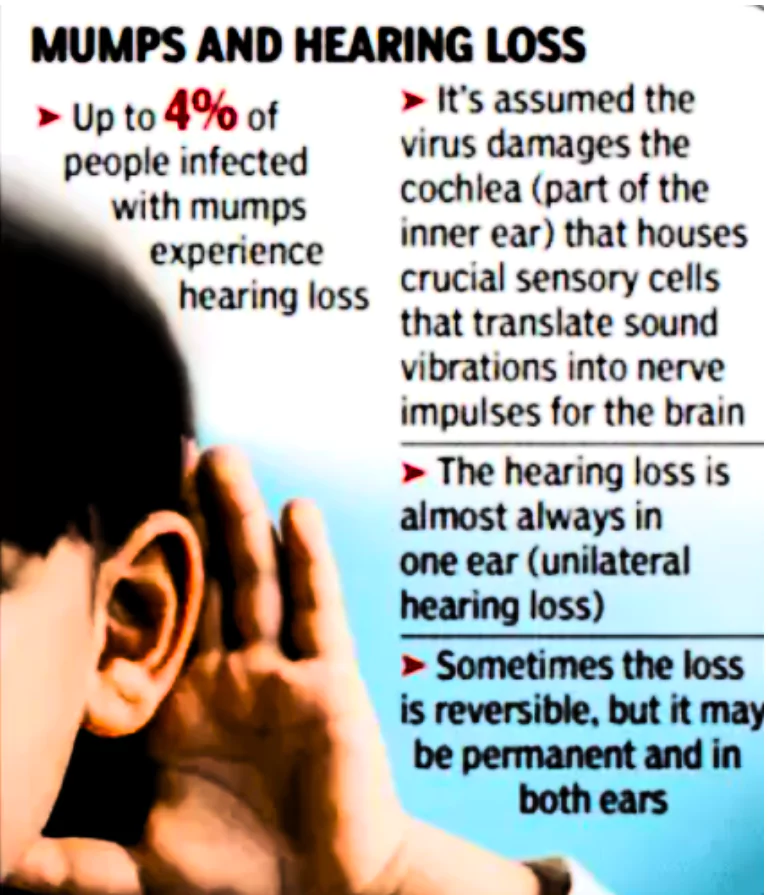
News Source: Indian-express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Minister of Communications Ashwini Vaishnaw has launched the Curtain Raiser of World Telecom Standardization Assembly Delhi 2024 (WTSA 2024).
International Telecommunications Union (ITU)
|
|---|
News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
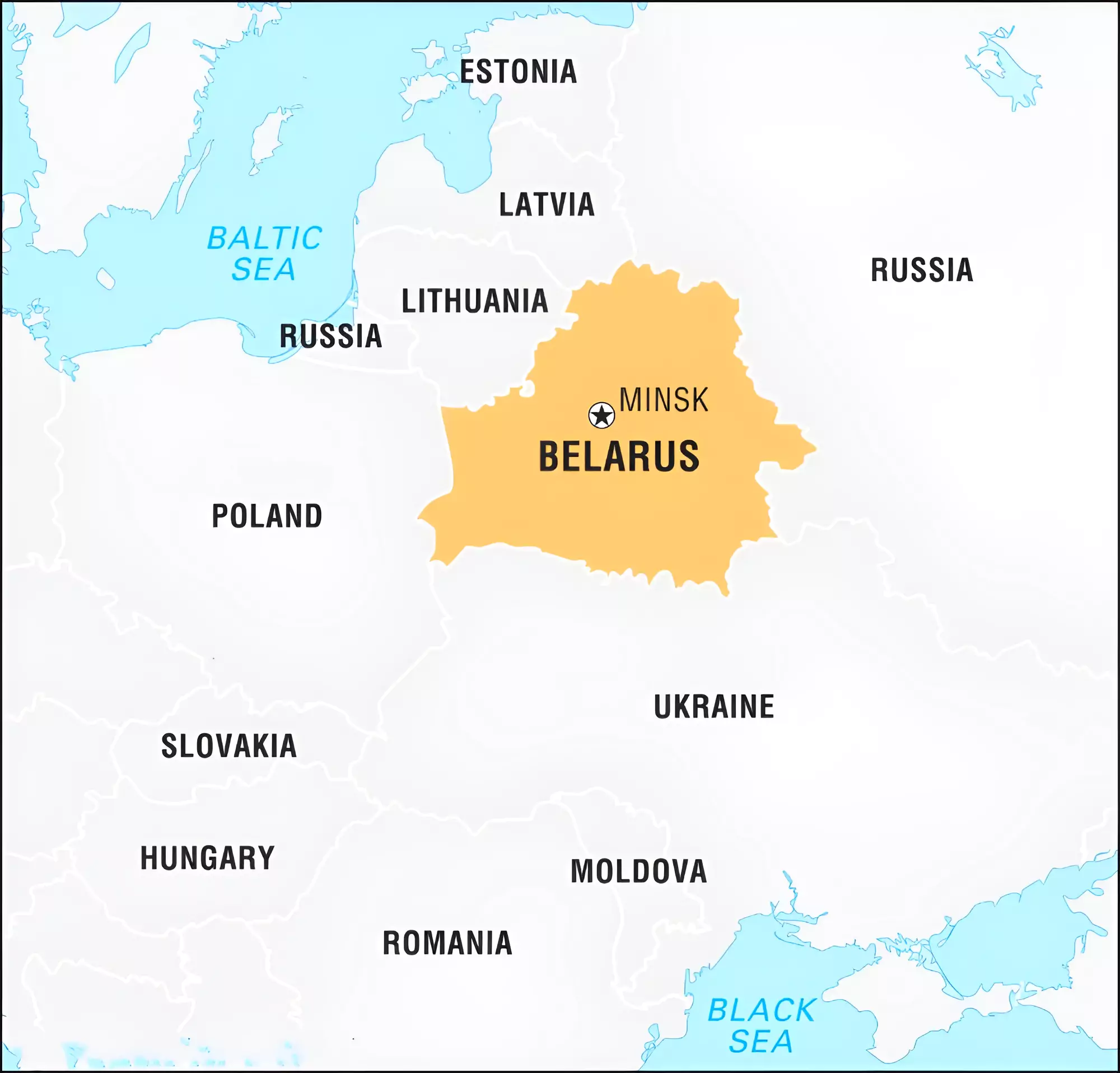
Recently, on a 3-day Visit to India, Foreign Minister of Belarus Sergei Aleinik discussed Bilateral cooperation with India’s External Affairs Minister Dr. S. Jaishankar.
News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This Article is based on the news “Centre notifies CAA 2024 rules ahead of Lok Sabha polls schedule announcement” which was published in the Indian Express. The Ministry of Home Affairs Monday notified the Citizenship Amendment Rules 2024.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Indian Citizenship, Indian Citizenship Act, and Citizenship Amendment Rules 2024.
Relevancy for Mains: Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA)- Provisions, Concerns and Way Forward. |
|---|
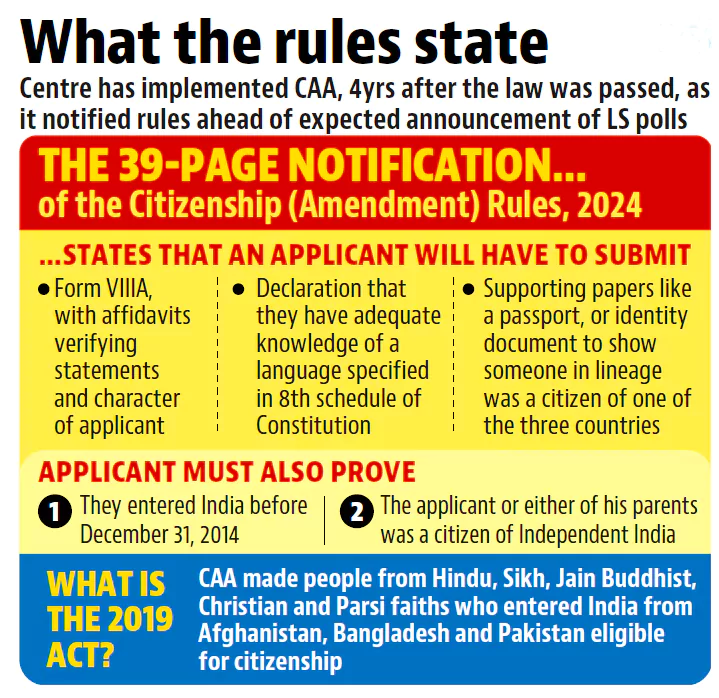
Who are ‘Citizens’?
Constitutional Provisions for Citizenship:
Citizenship by Naturalisation:
|
|---|
Citizenship Act of 1955: It provides for the acquisition and determination of Indian citizenship.
|
|---|
Assam Accord
|
|---|
National Register of Citizens (NRC):
National Population Register (NPR):
Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 (CAA):
|
|---|
| Intelligible Differentia: It refers to the reasonable and logical basis for classifying individuals into distinct groups for the purpose of legislation. |
|---|
Since the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) 2019 discriminates based on religion, it strikes at the root of the concept of secularism, which is the basic structure of the Constitution. Therefore, the CAA can be made religion-neutral by granting citizenship to all migrants irrespective of their religious status.
| Prelims PYQ (2021):
With reference to India, consider the following statements: 1. There is only one citizenship and one domicile. 2. A citizen by birth only can become the Head of State. 3. A foreigner once granted the citizenship cannot be deprived of it under any circumstances. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) 1 and 3 (d) 2 and 3 Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
