Context:
In a major breakthrough for the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the field of medicine, scientists from the United States and Canada have found a new antibiotic – powerful enough to kill a superbug – using AI.
What is a Superbug?
What is Antimicrobial Resistance?
What is Acinetobacter Baumannii?
How did researchers use AI in this case?
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
Genetically modified food remains controversial, especially in Europe, but for some experts it is the best science-based method for a sustainable global food system amidst biodiversity loss and a rising population.
| Probable Question:
Q. By resisting genetically modified crops, India risks food security of its population and may fall behind the rest of the world where scientists are deploying gene editing tools to improve yields. Critically evaluate. |
What are genetically modified crops and organisms?
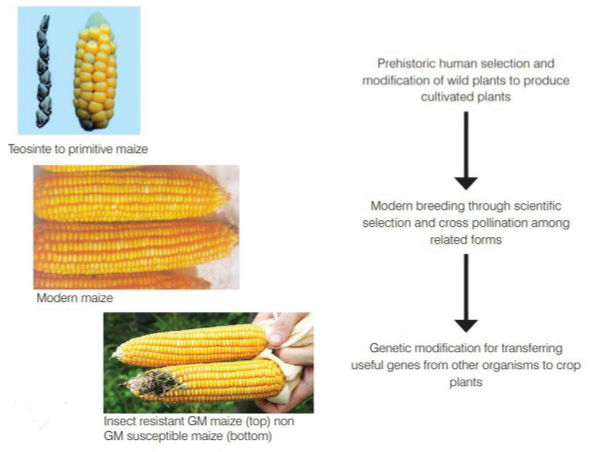
Image credit: GEAC
What is the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC)?
Regulatory framework in India:
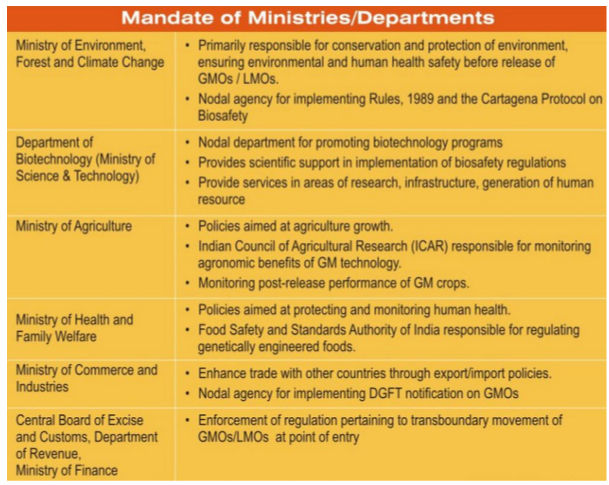
Image credit: GEAC
Acts and rules regulating the GM crops in India include:
Activities Covered:
GM crops in India:
Bt Cotton:
GM mustard:
Advantages of GM Crops:
Disadvantages of GM Crops
Way Forward
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
Punjab and Himachal Pradesh are set for a face-off as the 99-year lease on the Shanan hydropower project situated at Jogindernagar in Mandi district of Himachal Pradesh.
About Shanan Power Project:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
The death of over 288 passengers in train accident in the Balasore district of Odisha has brought into sharp focus the safety mechanisms needed to prevent such tragedies.
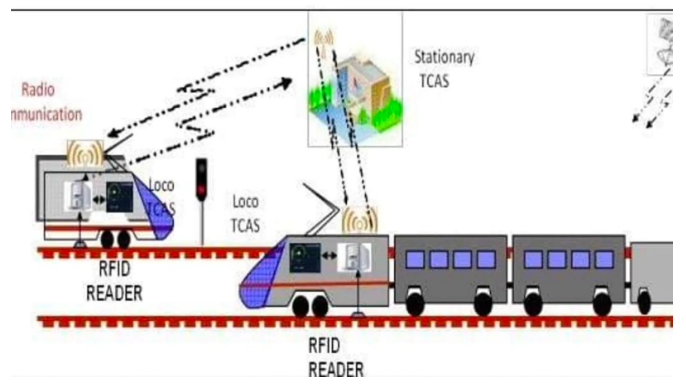
Image Source: Hindustan Times
What is Kavach?
How does Kavach work on Railway Systems?
Kavach deployment strategy?
Context:
The Karnataka HC recently ruled that having sexual intercourse with the dead body of a woman can’t fall under the ambit of rape or unnatural offences under the IPC.
Background:
What is necrophilia?
Ruling of the Karnataka High Court:
SC ruling in Parmanand Katara, Advocate vs Union of India:
Is necrophilia an offence in India?
Recommendations of the High Court:
News Source: Indian Express
Context:
The government’s fiscal deficit as of end December touched 59.8% of the full year Budget Estimate (BE) on subdued growth in revenue collections, according to Finance Ministry data released.
About the News:
About Fiscal Deficit:
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
Much ink has been spilled by now on the Budget’s hike in the tax-free ceiling under the new income tax system introduced in 2020, to ₹7 lakh from ₹5 lakh, with lower tax rates for those who give up existing tax exemptions.
Experts Concerns on take away of the old tax regime:
Why is the old tax regime required?
The old exemption-based regime helps guide families towards some level of prudent asset allocation to cope with life’s uncertainties, with a leg-up for building a critical asset over their working lives — a roof over their head.
Conclusion:
The nudge away from the old tax regime must be accompanied by greater financial literacy efforts from the government and regulators and a crackdown on unethical selling practices that could lead to people ending up in penury.
News Source: The Hindu
Context:
The first time an Egyptian President (Abdel Fattah El-Sisi) has been invited as chief guest for the Republic Day celebrations in India.
History of Relationships:
The Recent Engagements:
Bilateral Relations:
Areas of Cooperation
Geo-Strategic Concerns:
Conclusion:
Egypt is a major market for India and can act as a gateway to both Europe and Africa, can help in improving ties with Muslim-majority countries and together put a stronger voice in UNSC for developing nations.
Context:
The Prime Minister will inaugurate TRIFED’s Aadi Mahotsav festival in Delhi.
About Aadi Mahotsav:
Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India (TRIFED):
Some initiatives by TRIFED:
News Source: The Hindu
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
