The Prime Minister inaugurated a new statue of Sant Ravidas at Ravidas Park near Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, on his 647th birth anniversary.
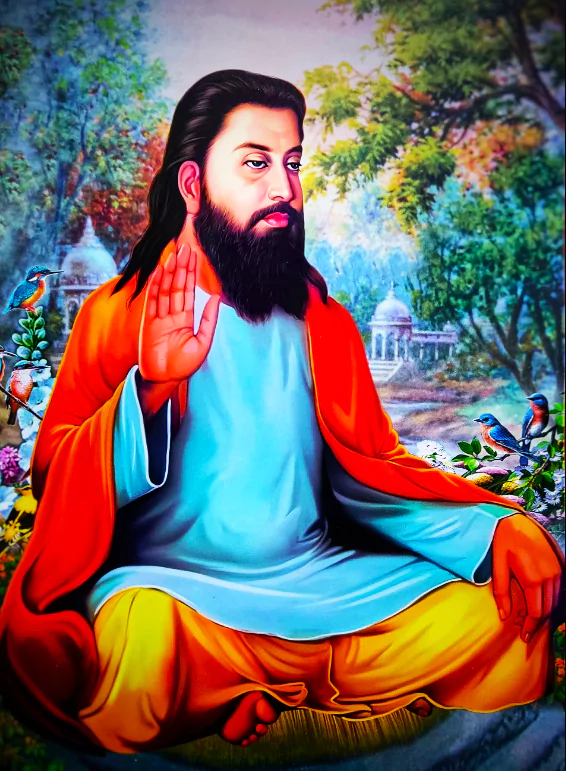

Sant Ravidas Ji’s teachings continue to inspire and guide millions towards a life of equality, compassion, and devotion. His emphasis on social justice, spiritual freedom, and the unity of humanity remains relevant, resonating with followers across different generations and communities.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Prime Minister inaugurated one of the largest-ever global textile events Bharat Tex 2024 on 26th February.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A 1,300-year-old temple belonging to the Badami Chalukyan period was discovered in Telangana recently.

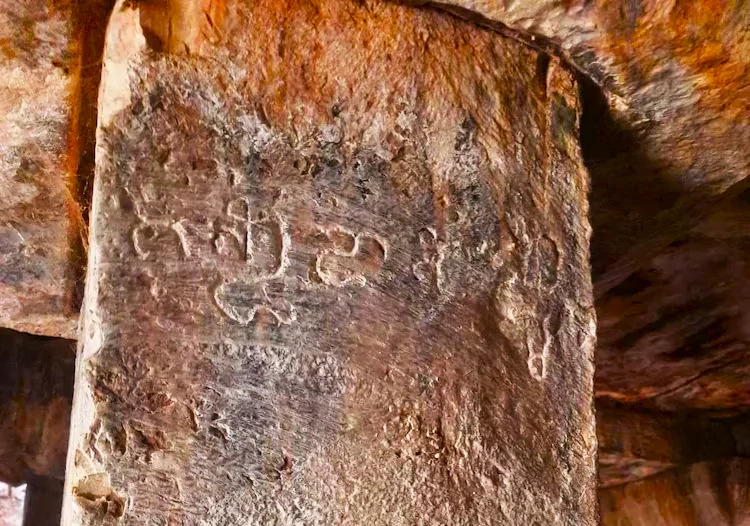
News Source: India Today
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The BharatGPT group, headed by IIT Bombay and seven other prestigious Indian engineering institutes, revealed plans to introduce its own ChatGPT-like service.
What are LLMs?
|
|---|
Hanooman is a series of large language models (LLMs).

| Benefits | Challenges |
|
|
News Source: Indianexpress
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
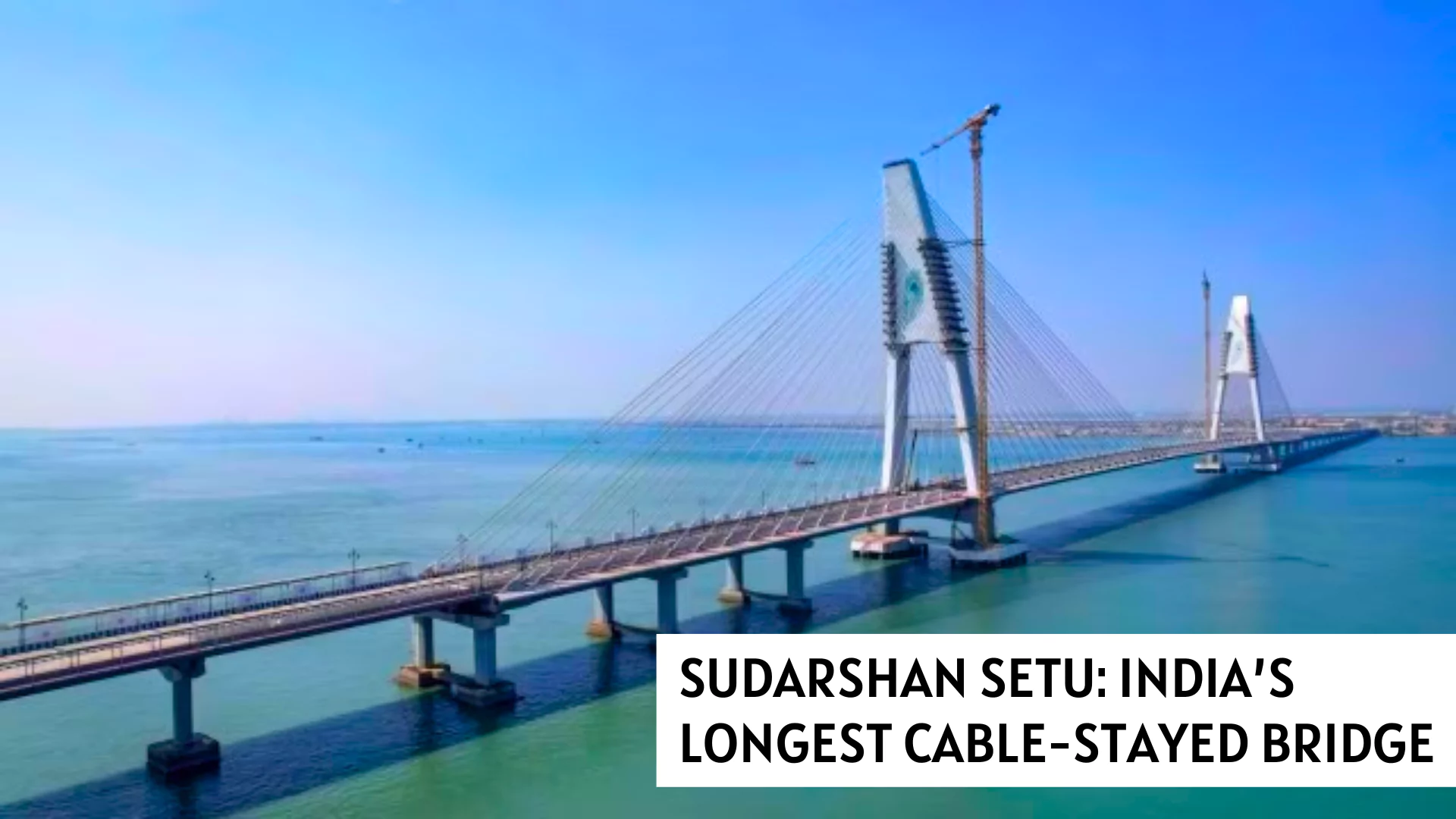

Recently, PM Narendra Modi inaugurated Sudarshan Setu connecting Okha mainland and Beyt Dwarka island in Gujarat.
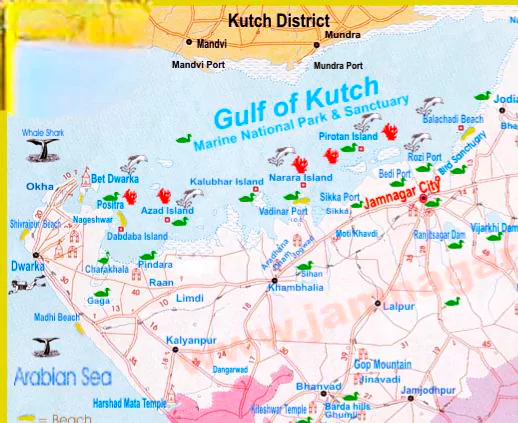 Geographical Location: Located off Gujarat, situated in the Gulf of Kutch, the okha town of devbhumi Dwarka district of mainland Gujarat to bet Dwarka. ( After the Union Territory of Diu (40sqKm), located at Una coast in Gir Somnath, Bet Dwarka(36sqKm) is the second largest island off Gujarat coast.)
Geographical Location: Located off Gujarat, situated in the Gulf of Kutch, the okha town of devbhumi Dwarka district of mainland Gujarat to bet Dwarka. ( After the Union Territory of Diu (40sqKm), located at Una coast in Gir Somnath, Bet Dwarka(36sqKm) is the second largest island off Gujarat coast.)News Source: IE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has asked the National Payment Council of India (NPCI) to become a Third-Party Application Provider (TPAP) for continued Unified Payments Interface (UPI) operation of the Paytm application.

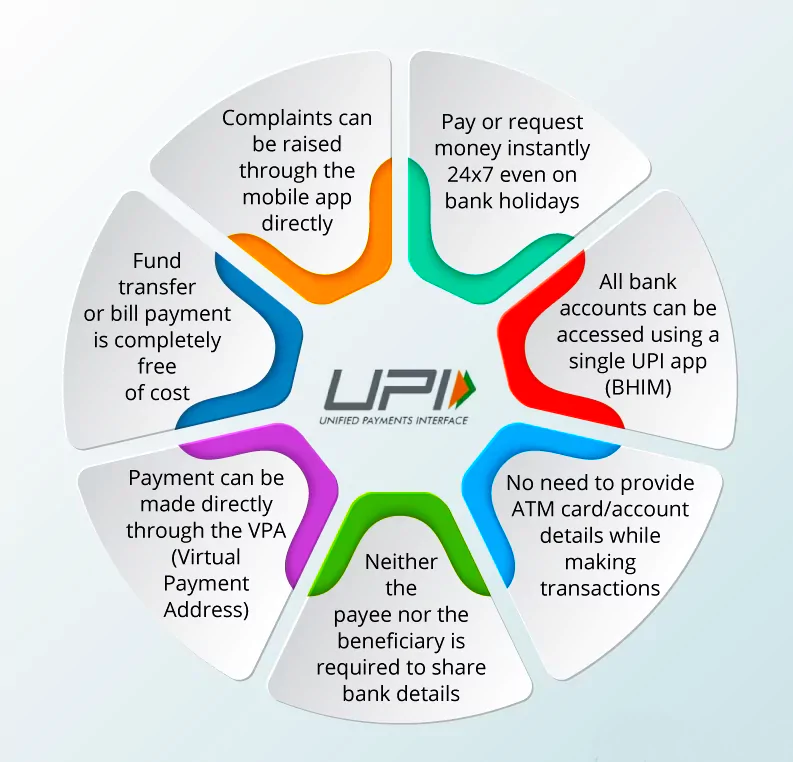 Existing Paytm UPI transactions were routed through PPBL which will be ceased now.
Existing Paytm UPI transactions were routed through PPBL which will be ceased now.
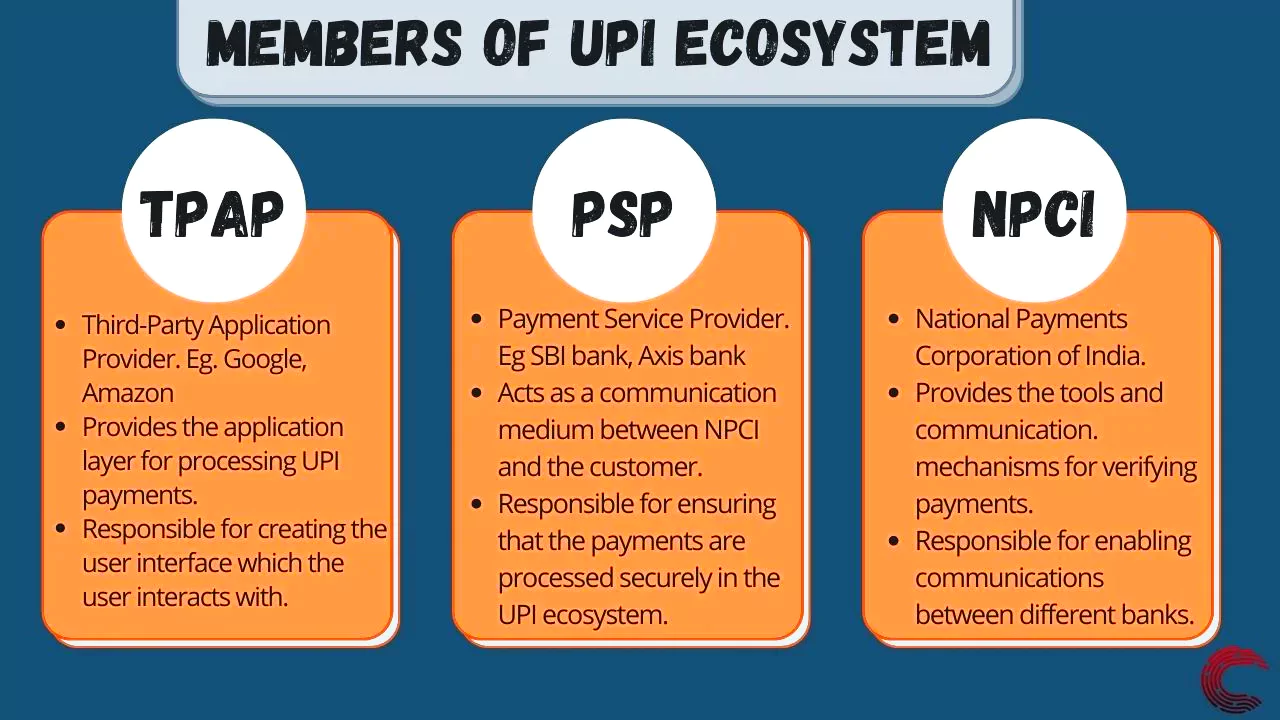 The new banks must have the capability to process high-volume UPI transactions.
The new banks must have the capability to process high-volume UPI transactions.News Source: Indianexpress
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Government has announced a plan to set up the “world’s largest grain storage plan in cooperative sector”.
Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS):
|
|---|
Data Statistics: India holds 11% (16 Crore Hectare) of World’s total Cultivable Area (138 Crore Hectare)
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Greek PM Kyriakos Mitsotak is on a 2-day State visit to India.




| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the 5th edition of Joint Military Exercise ‘DHARMA GUARDIAN’ between the Indian Army and the Japan Ground Self Defence Force commenced at Mahajan Field Firing Ranges in Rajasthan.
An Annual Exercise: It is an annual exercise and has been conducted alternatively in India and Japan since 2018.
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
A 2019 study by a Japanese scientist theorised that planets could also be formed in the massive dust and gas clouds found near supermassive black holes.
Formation of Planets
|
|---|
Active Galactic Nuclei
Other Defence Interaction Stage of India & Japan
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This article is based on the news “Per Capita Monthly Household Consumption Expenditure more than doubled during 2011-12 to 2022-23” which was published in the PIB. Recently, the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO), under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation released the Household Consumer Expenditure Survey (HCES) conducted from August 2022 to July 2023.
| Relevancy for Prelims: All India Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2022-23, National Sample Survey Office, and NITI Aayog.
Relevancy for Mains: Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2022-23: Highlights, Significance, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|

Why the Delay in the Survey?
|
|---|
Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE):
|
|---|
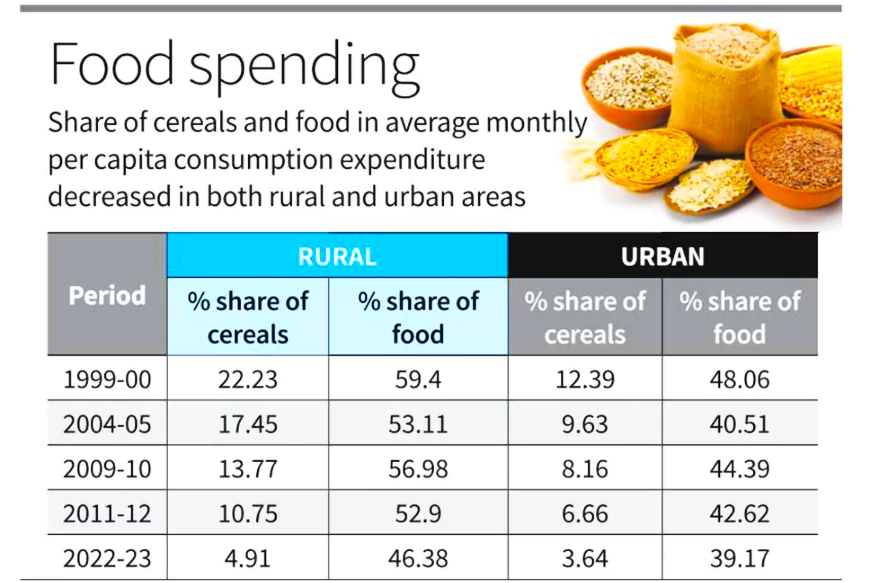
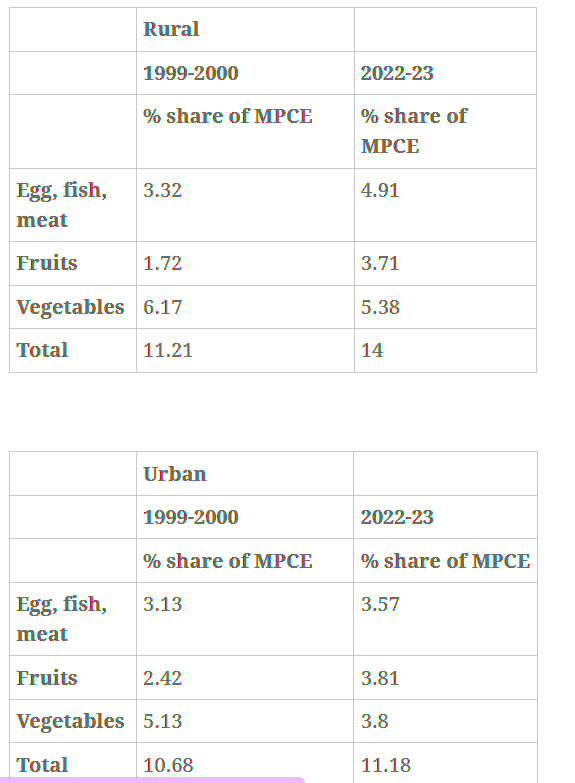
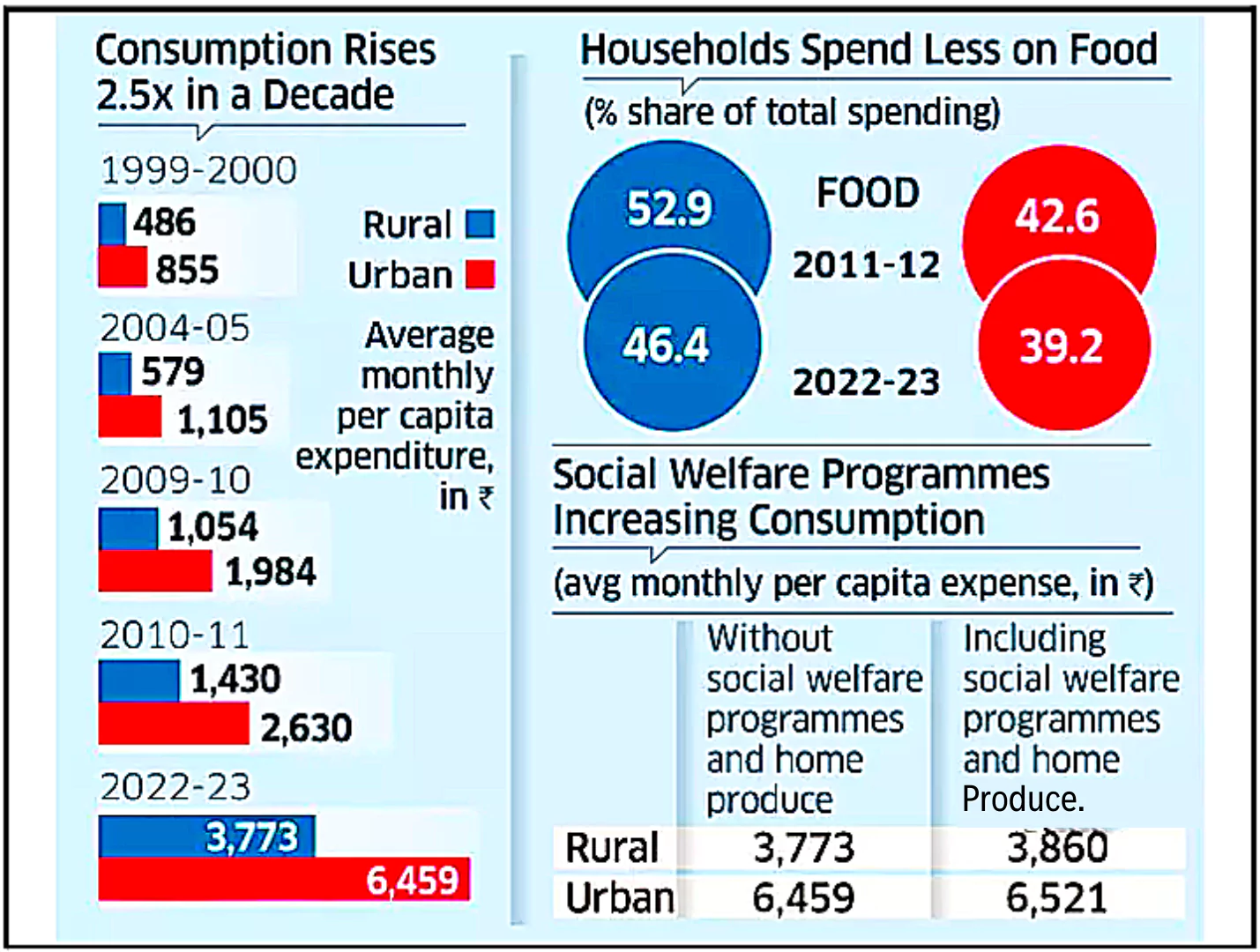
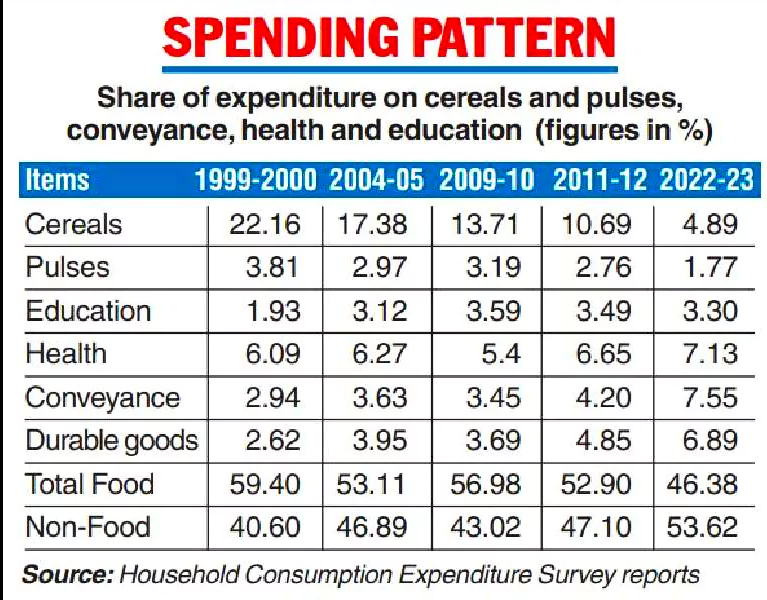
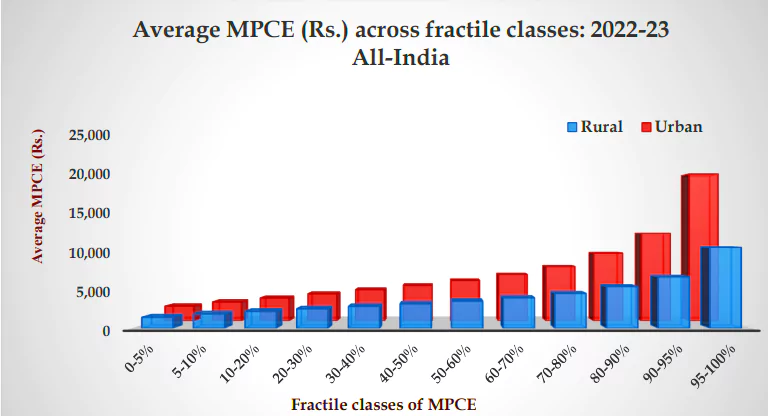
About Household Consumer Expenditure Survey (CES):
New Changes in the Methodology of Survey:
About National Sample Survey Office (NSSO):
|
|---|
On Consumer Price Inflation (CPI) Revision:
|
|---|
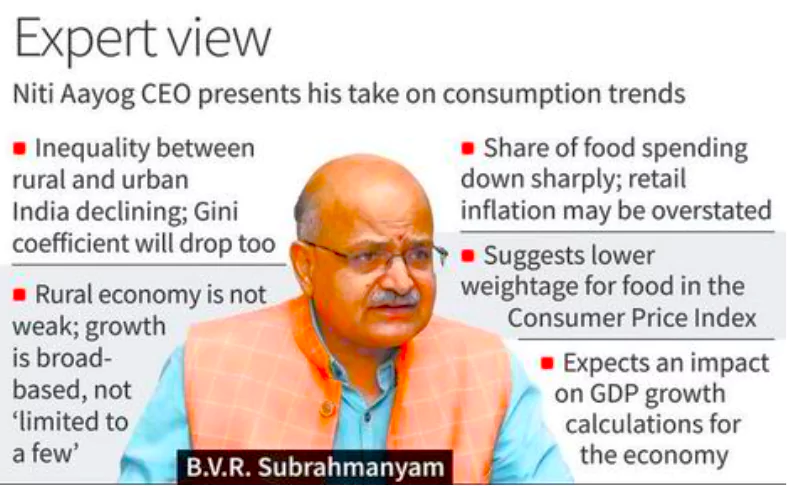
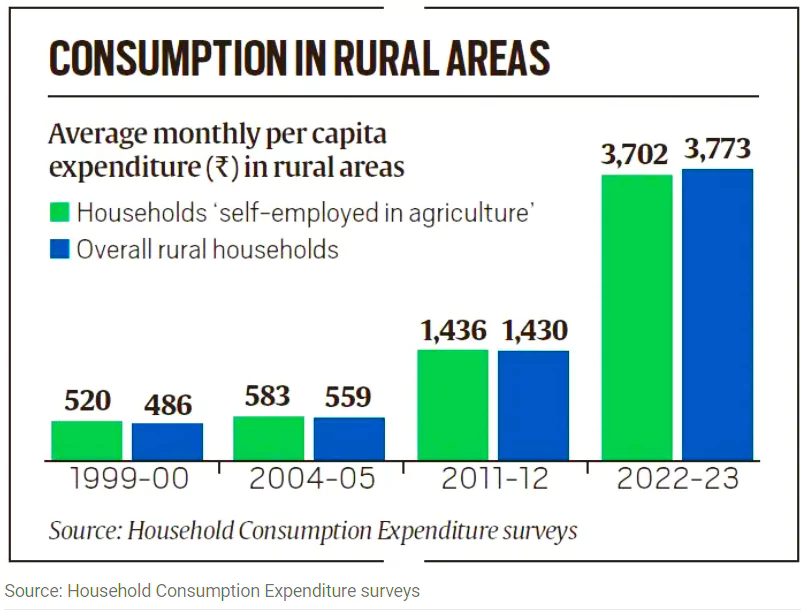 Fall in the Average MPCE of Agricultural Households: Compared to overall rural households, the average MPCE of agricultural households is decreased.
Fall in the Average MPCE of Agricultural Households: Compared to overall rural households, the average MPCE of agricultural households is decreased. The release of this survey marks an important step towards filling the data vacuum in the country. The next government should take this forward, initiate the much-delayed census exercise and take steps to strengthen the country’s statistical system.
News Source: PIB
To read more on NSSO, click here
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
