Prime Minister inaugurates the Hindustan Urvarak & Rasayan Ltd (HURL) Sindri Fertilizer Plant at Sindri, Dhanbad, Jharkhand.
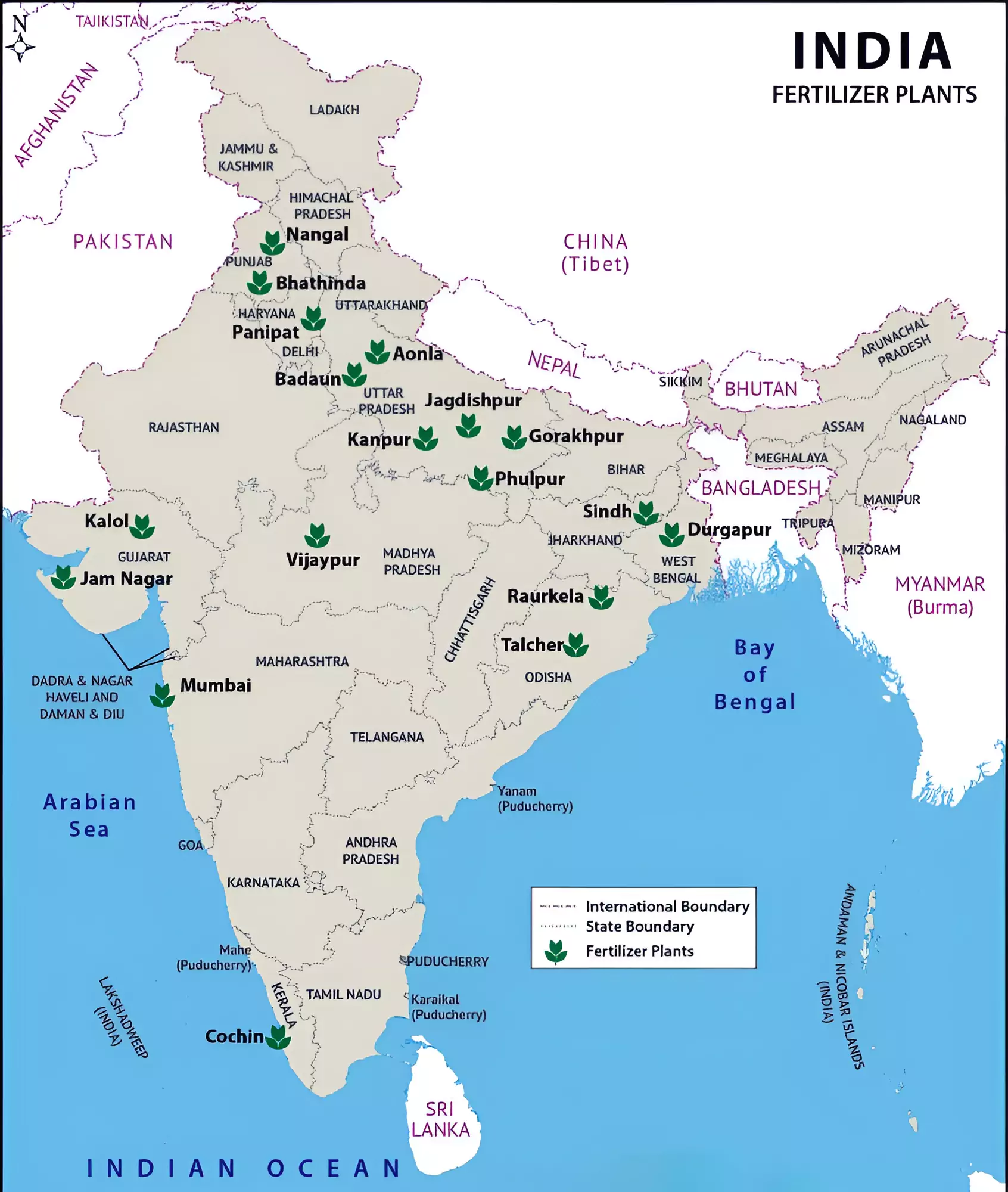
Fertilizer Sector in India
|
|---|
News source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Financial Intelligence Unit-India (FIU-IND) imposed a penalty on Paytm Payments Bank Ltd concerning the violations of its obligations under the PMLA.
Issued by: The order was issued by the Director FIU-IND under Section 13(2)(d) of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002 read with the Prevention of Money Laundering (Maintenance of Records) Rules, 2005
The Prevention of Money Laundering Act 2002
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, the Union Home and Cooperation Minister, started the National Urban Cooperative Finance and Development Corporation Limited in New Delhi.
News Source: AIR
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
During its Sixth Session in Nairobi, Kenya, the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA) adopted a resolution on sustainable lifestyles submitted by India.
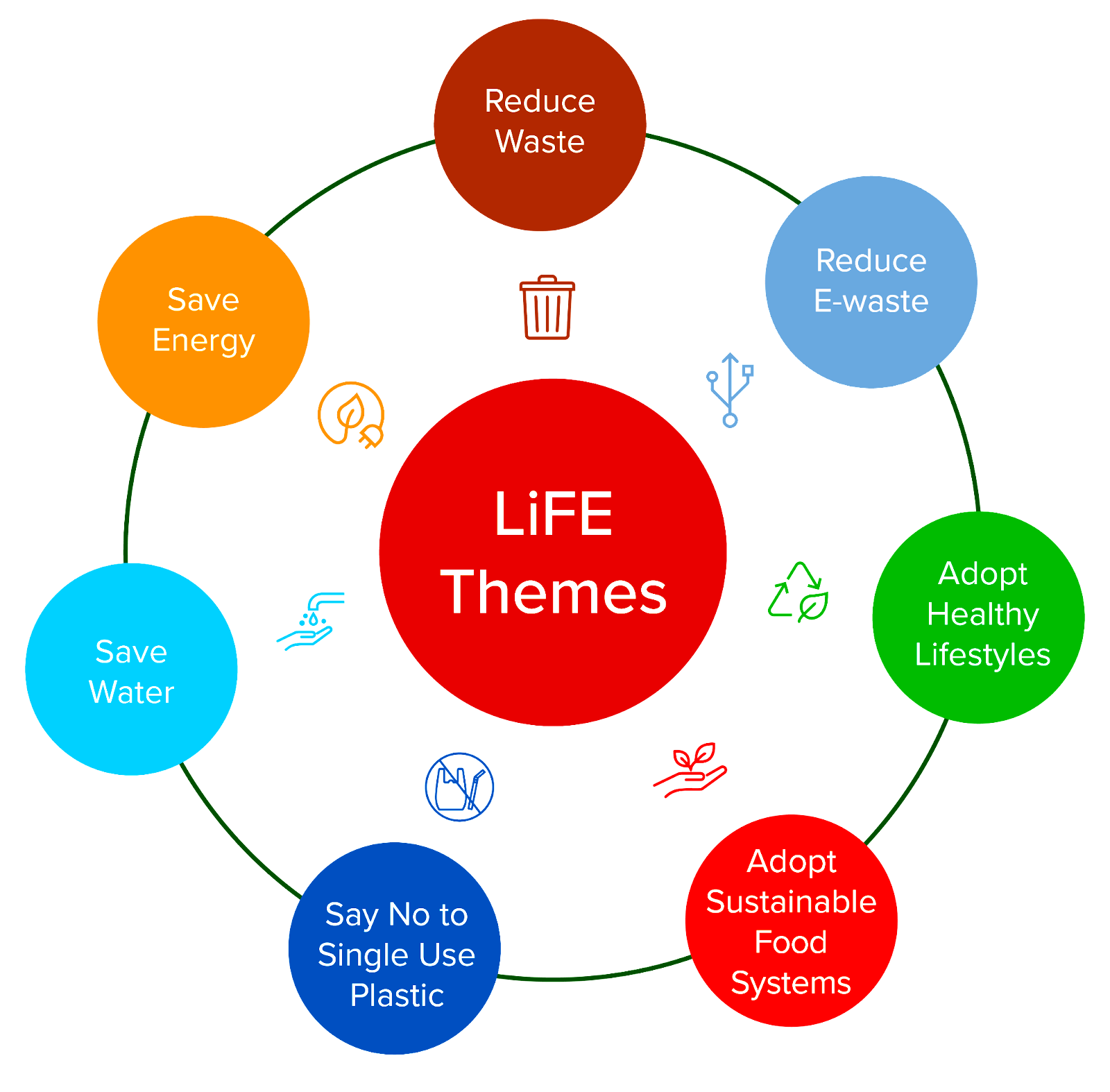 Promotion of Education and Skill: This resolution promotes education and skill because education and skill accelerate collective efforts towards sustainable consumption and production.
Promotion of Education and Skill: This resolution promotes education and skill because education and skill accelerate collective efforts towards sustainable consumption and production.
Sustainable Development
2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, an article was published in the State of India’s Environment 2024 by the Centre for Science & Environment on the ‘Rise of Invasive Alien Species’.
Invasive Species:
|
|---|
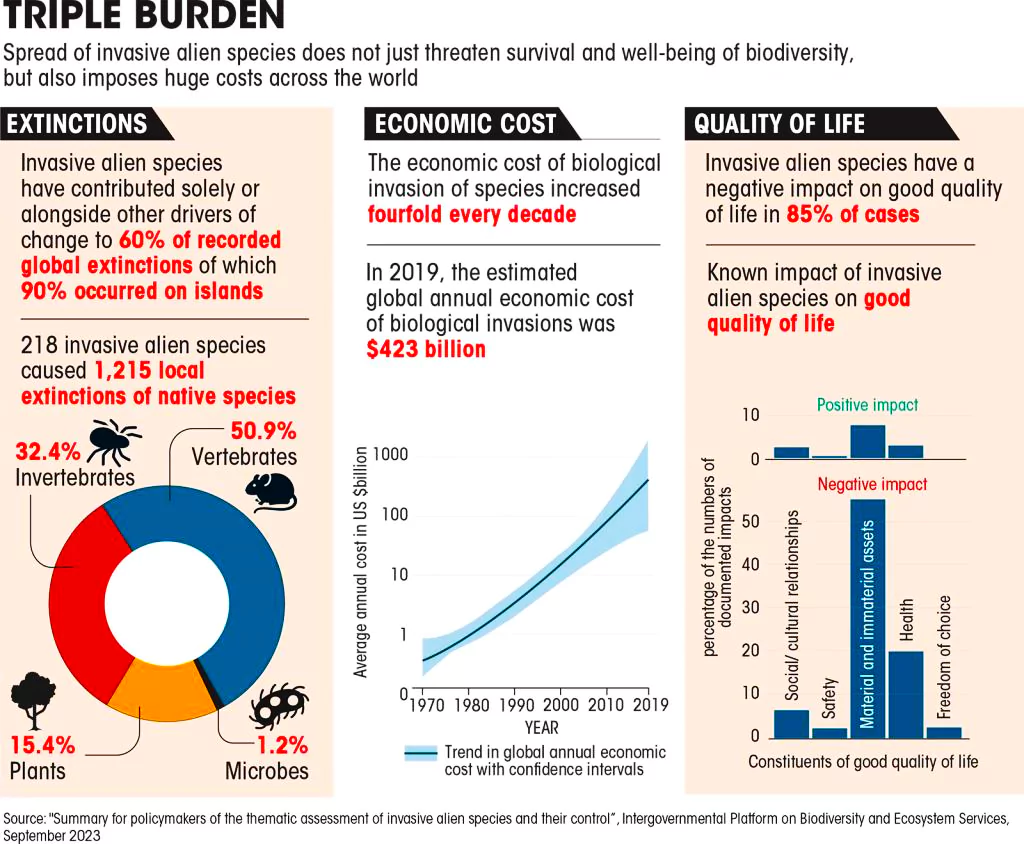
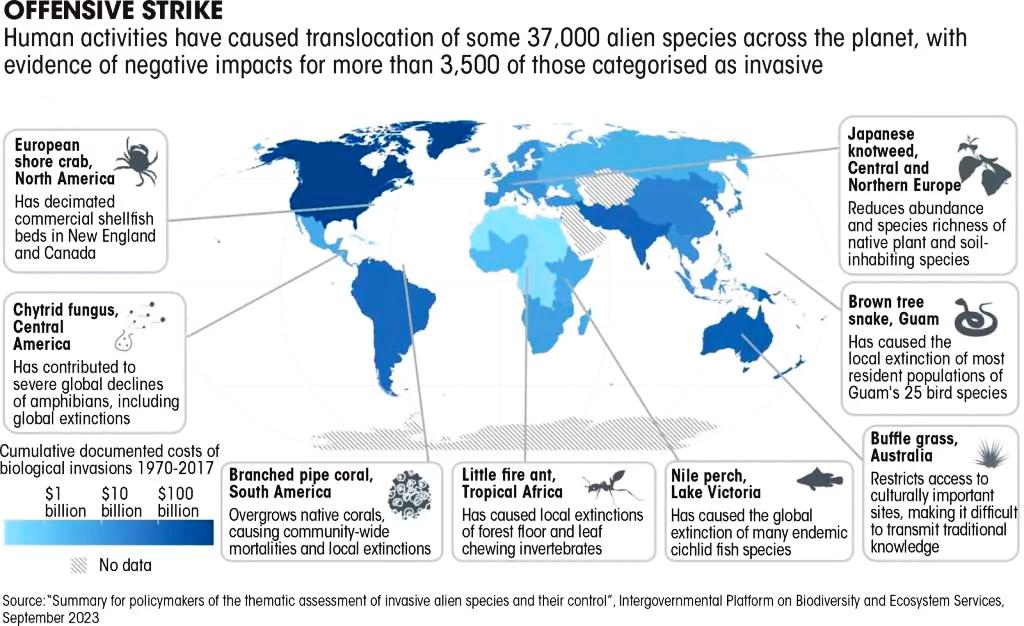
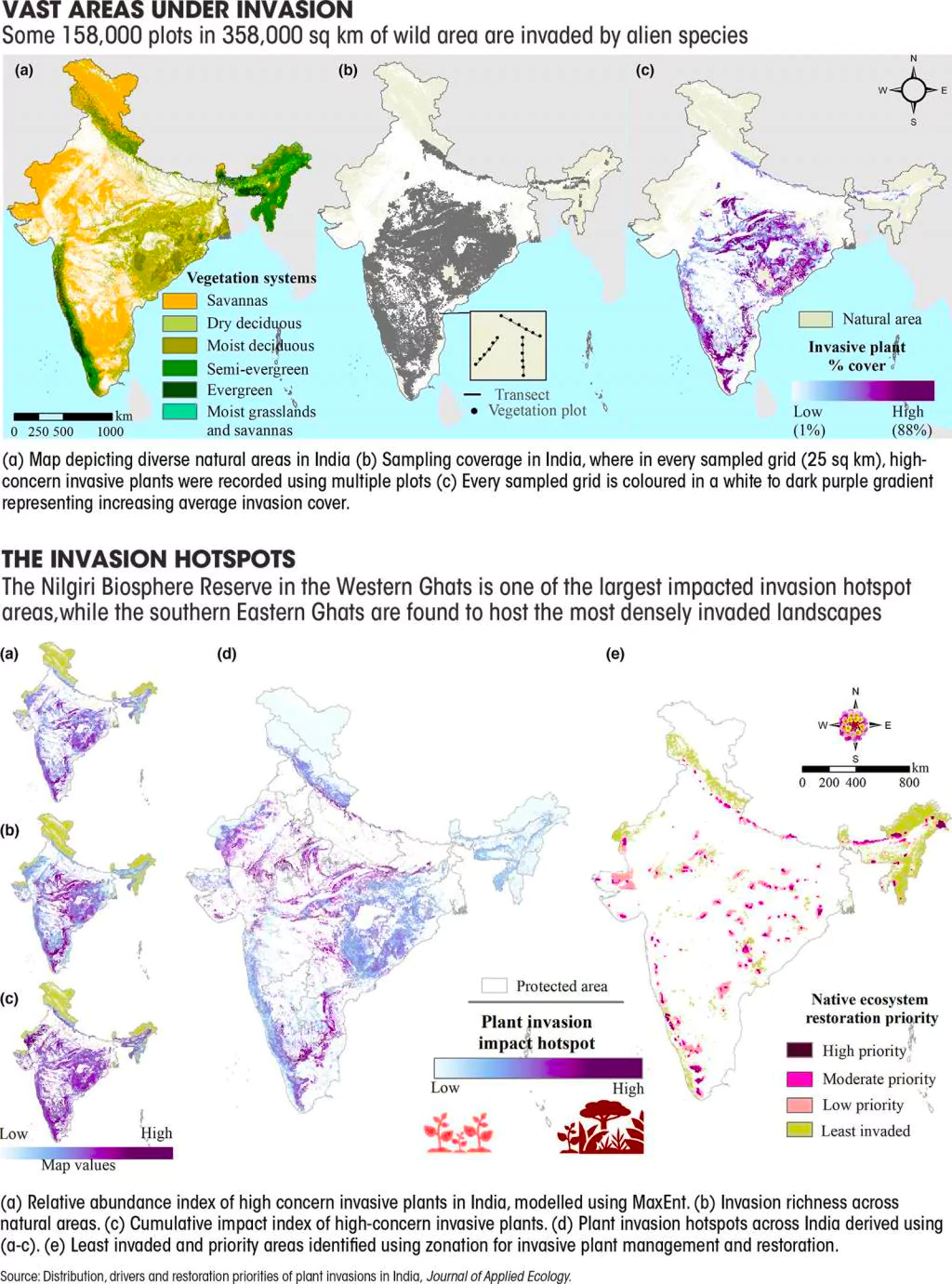
News Source: DTE
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
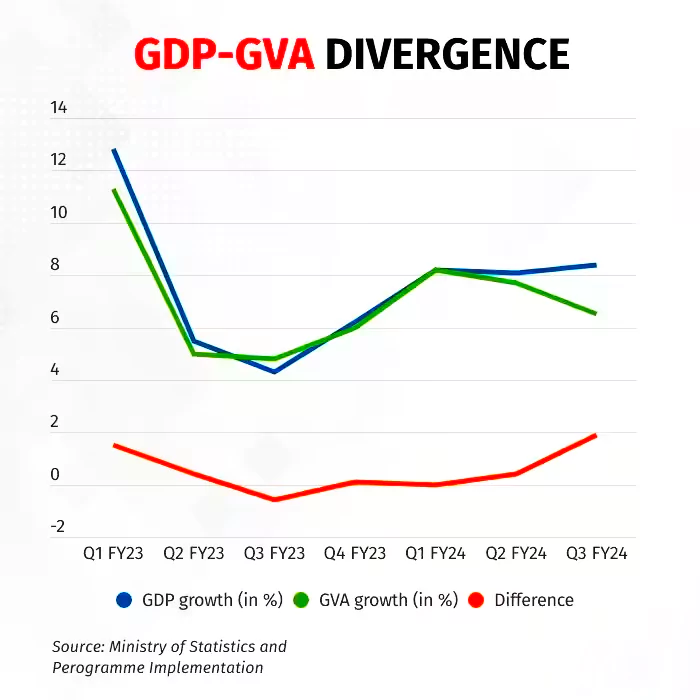
Recently, Data released by the National Statistical Office (NSO) showed that the difference between the two sets of growth rates widened to a 10 Year high in Q3 (Oct-Dec 2023-24).
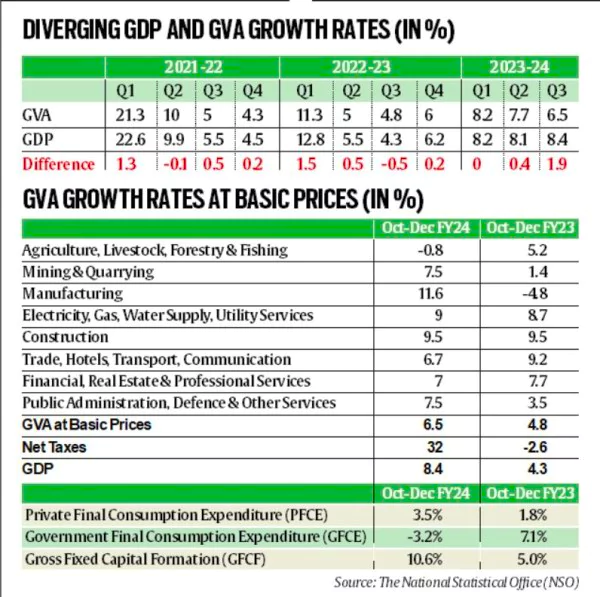
During Q3 of FY24 in India, the deviation in GDP and GVA shows how economic recovery is complicated. Although overall GDP looks strong, looking at GVA and specific sectors gives a more detailed picture. Dependence on public spending highlights the need for balanced and sustainable growth for India’s economy.
News Source: The Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Exercise Samudra Laksamana is conducted at the coast of Visakhapatnam.
INS Kiltan:
|
|---|
News Source: PIB
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Recently, Sri Lanka and India signed the contract for building Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems in Delft (Neduntheevu), Nainativu and Analaitivu islands off Jaffna peninsula in the island’s north.
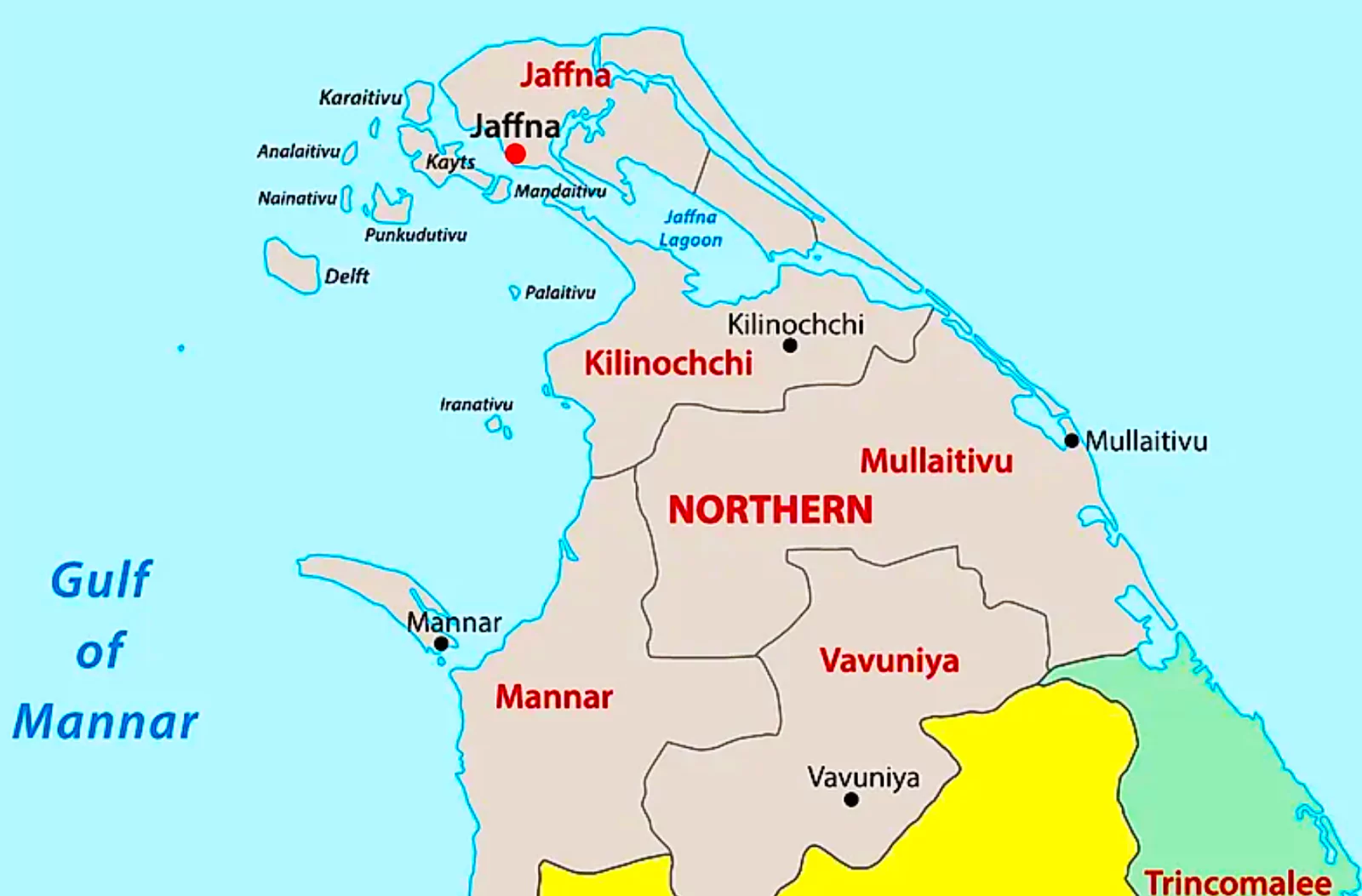
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This Article is based on the news “Another major boost to Atmanirbharta in defence: Ministry of Defence signs five major capital acquisition contracts worth Rs 39,125.39 crore” which was published in the Pib. Recently, the Ministry of Defence signed five major capital acquisition contracts worth Rs 39,125.39 crore marking a significant boost to the Make in India initiative and indigenous capabilities in defence.
| Relevancy for Prelims: India Defence Exports, Industrial Policy, FDI, Interim Budget 2024-2025, Defence Technology, DRDO, and Vijay Raghavan Panel.
Relevancy for Mains: Atmanirbharta in Defence Sector: Need, Challenges, Steps Taken by the Government, and Way Forward. |
|---|
Present Legal Framework for Defence Policies
|
|---|
Here are the some major challenges in achieving atmanirbharta in defence sector;
Steps taken by the Government to Achieve Atmanirbharta in Defence Sector
|
|---|
The Defence Minister emphasised the need for atmanirbharta in defence for the country not an option but a necessity in the fast-changing global scenario.
| Prelims PYQ (2018):
What is “Terminal High Altitude Area Defence (THAAD)”, sometimes seen in the news? (a) An Israeli radar system (b) India’s indigenous anti – missile programme (c) An American anti -missile system (d) A defence collaboration between Japan and South Korea Ans: (c) |
|---|
| Mains Question: What is the significance of Indo- US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo- Pacific region. [250 Words, 15 Marks] |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This Article is based on the news “Shri Narayan Rane says in last 10 years under transformative leadership of the Prime Minister there has been an unprecedented increase in the number of women entrepreneurs in India” which was published in the Pib. Recently, the 9th Annual Shakti International Women Entrepreneurs Summit was held in New Delhi.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Status Of Women In India, Women Empowerment Schemes, Women In STEM, MSMEs, Self Help Groups (SHGs), and Ima Keithel Or Mothers Market.
Relevancy for Mains: Women Entrepreneurs In India: Status, Need, Challenges, Schemes, and Way Forward. |
|---|
India’s First Female Entrepreneur:
|
|---|
The promotion and encouragement of women entrepreneurs in India carry numerous benefits for both individuals and the overall economic and societal landscape. Here are many reasons why there is a need for more women entrepreneurs in India:
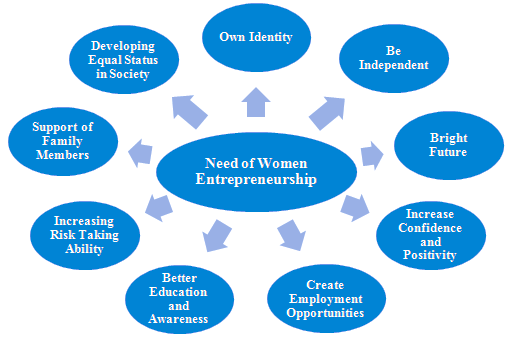
|
|---|

Schemes For Women Entrepreneurs in India
|
|---|
About Self Help Groups (SHGs)
Women Led Enterprises
About WomenStartup Programme
|
|---|

Major problems of women entrepreneurs in India are as follows;
Women entrepreneurship is an essential source not only for the economic growth of a country but can also act as a powerful tool to break off the shackles that existed owing to the extremely pervasive gender inequalities. Women’s entrepreneurship will shift the narrative from women’s development to women-led development.
| Prelims PYQ (2017):
Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (a) World Economic Forum (b) UN Human Rights Council (c) UN Women (d) World Health Organization Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
