Recently Rajasthan State governments issued a notification declaring ‘orans’ as deemed forests raised fear in community dwellers about losing access to forest produce and livelihood.
What is a Deemed Forest?
|
|---|
Different Names for Sacred Groves
|
|---|
News Source: Down to Earth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
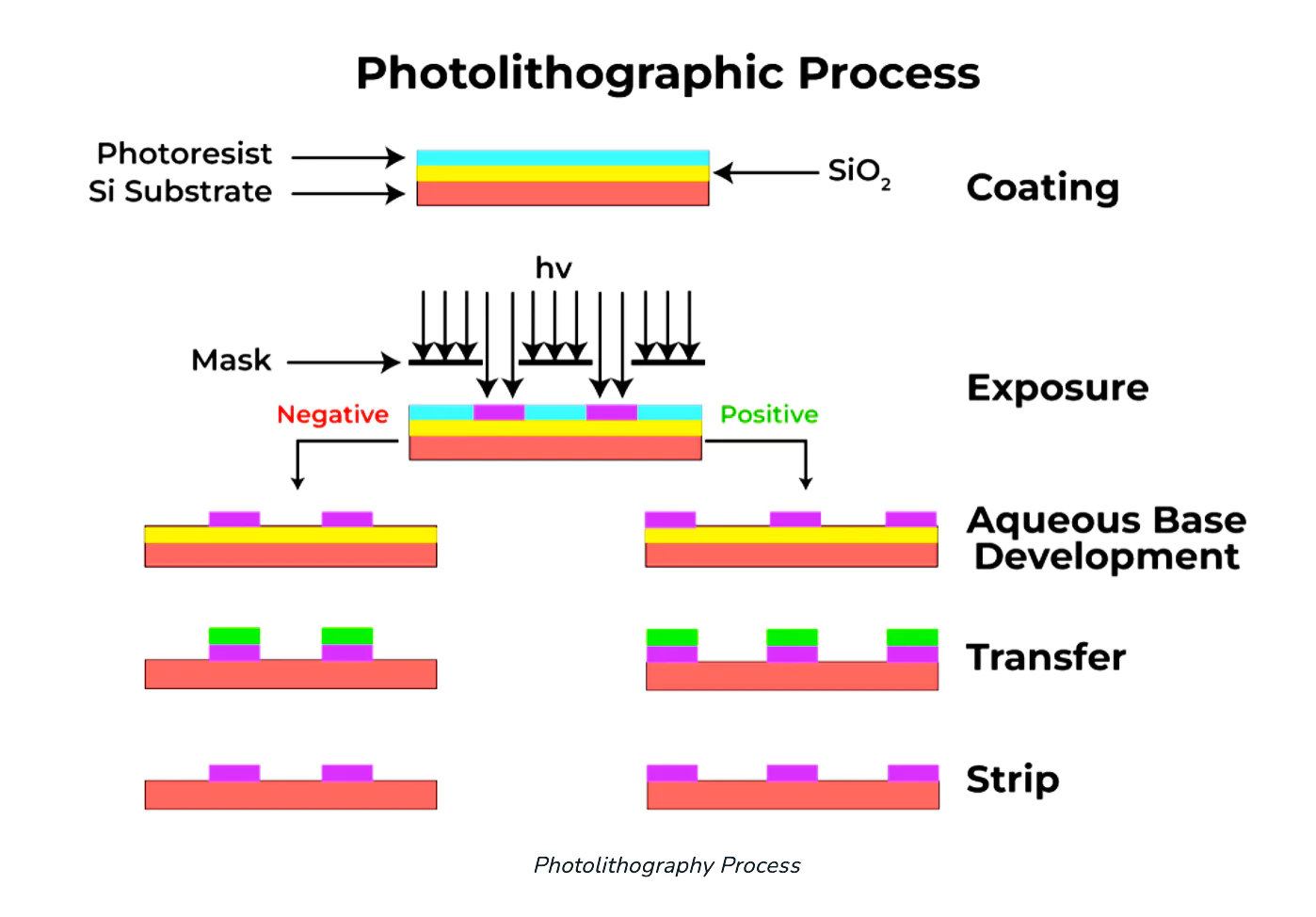 Soft Bake: The coated substrate is gently heated to eliminate solvent and guarantee uniformity.
Soft Bake: The coated substrate is gently heated to eliminate solvent and guarantee uniformity.| Photoresists Photoresists are essentially hydrocarbon polymers composed of a novol-ack resin, a photoactive compound and an organic solvent. |
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The Supreme Court slammed the former Uttarakhand forest minister for illegal construction and felling of trees inside Jim Corbett National Park, part of the Corbett Tiger Reserve.

| Type | Examples |
| Trees | Sal, Haldu, Sissoo, Rohini, Khair, over 110 varieties |
| Shrubs | 51 species including Ber, Karaunda |
| Flowering Trees | Kachnar, Semal, Dhak and Amaltas |
| Species Type | Examples |
| Mammals | Royal Bengal Tiger, Asiatic Elephant, Leopards, Sloth Bears, Deers (Sambar, Chital, Hog Deer), Otters, King Cobra. |
| Birds | Over 580 species including great pied hornbill, white-backed vulture, Hodgson’s bushchat. |
| Reptiles | Gharials, Mugger Crocodiles, King Cobra. |
News Source: Down to Earth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Guidelines for Prevention of Misleading Advertisements and Endorsements for Misleading Advertisements 2022
|
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
The 2023-24 El Nino event has peaked as one of the five strongest on record according to WMO.
El Niño:
|
|---|
News source: The hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
Maldives has signed a defense agreement with China for obtaining non-lethal weapons and training.
News Source: Indianexpress
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
As per World Health Organization’s (WHO) latest HIV Drug Resistance (HIVDR) Report, resistance to the antiretroviral drug dolutegravir (DTG) is increasing among HIV patients.
About Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
|
|---|
News Source: Down to Earth
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This Article is based on the news “Law Commission recommends new law to protect trade secrets” which was published in the Indian Express. Recently, the Law Commission Of India in its 289th Report ‘Trade Secrets and Economic Espionage’ recommended a new law to protect ‘Trade Secrets’.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Law Commission Of India, TRIPS, World Intellectual Property Organisation (WIPO), Global Innovation Index 2023 (GII), and India Leads Global Rise In Patent Applications.
Relevancy for Mains: What law commission recommends to safeguard trade secrets? |
|---|
| S.NO. | Patent | Trade Secret |
| Scope | Protects new and useful inventions | Protects any secret information that provides economic value to the business |
| Example | Alexander Graham Bell’s Telephone 📞 | Coca-Cola’ secret Formula |
| Duration | 20 Years | Indefinitely, until the trade secret is leaked (intentionally or accidentally) |
| Rights | Gives the patent holder the right to exclude others from making, selling, using,importing the invention | Protects only against misappropriation |
| Territory | patent rights are territorial, i.e. protection only exists in countries where the patent is granted | No restricted to territory |
Law Commission of India
|
|---|
Intellectual Property Rights Policy Management (IPRPM) framework
|
|---|
Trade Secret law in India is mostly governed via common law such as:
The Department of Legal Affairs and the Legislative Department examined the issue of enacting the Economic Espionage Act and Trade Secrets Protection Act and prepared a concept paper along with a draft cabinet note and a draft Bill.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
This Article is based on the news “Women, Business and the Law 2024” which was published in the World Bank Group. Recently, the World Bank Group released the “Women, Business and the Law 2024” report.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Status Of Women In India, Women Entrepreneurs In India, Gender Equity And Equality, Rights Of Women, Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Status Of Women In India, and Social Empowerment.
Relevancy for Mains: Women, Business and the Law 2024: Key Highlights, and Challenges Related to Women in India. |
|---|
International Women’s Day
|
|---|
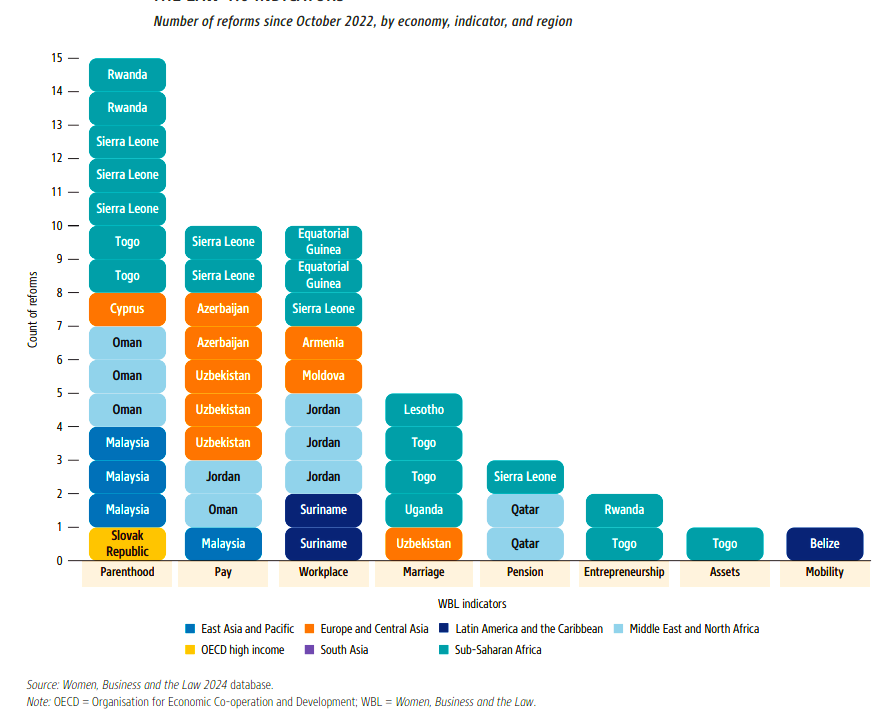
Need to Learn from Other Countries’ Practices:
|
|---|
The new Women, Business and the Law 2.0 three-tiered approach, reveals important gaps and demonstrates that the perceptions of experts on the status of women’s rights are not always in line with what is needed to implement those rights in practice. Effective implementation of equal-opportunity laws necessitates a robust supporting framework and accessible healthcare services.
| Prelims PYQ (2017):
Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (a) World Economic Forum (b) UN Human Rights Council (c) UN Women (d) World Health Organization Ans: (a) |
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
SC Verdict on Newsclick Shows Adherence to Due Pro...
Stay Invested: On Chabahar and India-Iran Relation...
Credit Rating Agencies, Impact on India’s De...
Catapulting Indian Biopharma Industry
Globalisation Under Threat, US Import Tariffs Have...
Global Report on Hypertension, Global Insights and...
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
