|
Importance Of Forest: Guardians Of Biodiversity And Life’s Essentials |
Importance of Forest: Earth’s Lifeline and Biodiversity Haven
- Forests are vast ecosystems characterized by dense collections of trees, shrubs, plants, and a rich variety of wildlife. Importance of Forest – covering one third of the earth’s land mass, they perform vital functions and support the livelihoods of 1.6 billion people. They are home to more than half of the world’s land-based species of animals, plants, and insects.
Importance of Forest: Nature’s Complex Ecosystems
- A forest is a large and complex ecosystem characterized by a dense collection of trees, shrubs, plants, and various organisms within a particular geographic area.
- Forests can vary widely in terms of tree species, climate, and ecological conditions.
Importance of Forest: Functions – Production, Protection, and Regulation for a Balanced Environment
- Productive Functions: Production of various types of wood, fruits and a wide range of compounds such as resins, alkaloids, essential oil, latex and pharmaceutical substances.
- Protective Functions: Importance of Forest lies in providing habitats for various organisms, conservation of soil and water, prevention of drought, shelter against wind, cold, radiation, noise, sounds, smells, and sights.
- Regulative Functions: Importance of Forest involves the regulation of absorption, storage, and release of gases, water, minerals, elements, and radiant energy.
- These underscore the Importance of Forest by improving atmospheric and temperature conditions and enhance the economic and environmental value of the land.
- Forests also effectively regulate floods and drought, emphasize the Importance of Forest in maintaining biogeochemical cycles..
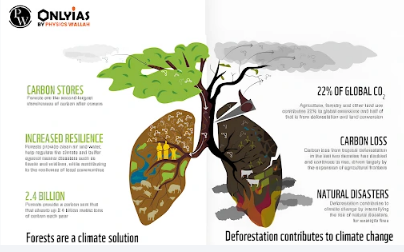
Importance of Forest: Biodiversity Preservation, Climate Regulation, and Economic Contributions
- Preserving Biodiversity:
- Forests serve as habitats for diverse wildlife, many of which are endemic and endangered, highlighting the Importance of Forest in preserving biodiversity.
- Forests help in preserving biodiversity are essential for the survival of numerous species.
- Forests provide habitats for plants and animals, including some of our planet’s most iconic species like the tiger, giant panda, gorilla and orangutan.
- Forests are home to over 80% of terrestrial biodiversity, including 80% of amphibians, 75% of birds, and 68% of mammals, underscoring the Importance of Forest in preserving diverse ecosystems.
- Carbon Sink:
- Forests are the largest storehouses of carbon after the oceans, as they absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis.
- They help mitigate climate change by storing carbon and releasing oxygen, thereby reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Forests provide habitat, and food as well as protection to wildlife species against extremes of climate and help in balancing carbon dioxide and oxygen of the atmosphere.
- Water Cycle:
- Forests play a critical role in the water cycle.
- They absorb rainwater and release it gradually, reducing the risk of floods and ensuring a constant supply of freshwater to rivers and streams.
- Forests also help recharge groundwater aquifers.
- Local Weather:
- Forests enhance local precipitation and improve water holding capacity of soil, regulate water cycle, maintain soil fertility by returning the nutrients to the soil through litter.
- Forests check soil-erosion, landslides and reduce intensity of flood and droughts.
- Ecosystem Services:
- Forests provide a wide range of ecosystem services, including pollination of crops by forest-dwelling insects, regulation of microclimates, and habitat for pollinators and predators that benefit agriculture.
- Reservoirs of Genetic Diversity:
- Forests have great biological importance as reservoirs of genetic diversity apart from playing an important role in regulating earth’s climate.
- Crucial Buffer:
- As the impacts of climate change, including floods and storms from rising sea levels and increased precipitation, become more frequent and severe, forests can provide a crucial buffer for our communities, emphasizing the Importance of Forest in climate resilience and disaster mitigation.
- Non-carbon Services:
- Forests also provide non-carbon services that are essential for human societies to thrive.
- Example: Its role in sustaining livelihoods to providing water and food security, and regulating global rainfall patterns.
- They provide raw materials to various wood industries like pulp and paper, composite wood, rayon and other man-made fibers, matches, furniture, shuttles and sport goods.
- Forests also provide many other minor products such as essential oils, medicinal plants, resins and turpentines , lac and shellac, katha and catechu, bidi wrappers and tasser silk.
- Medicine:
- About 40% of all the drugs used throughout the world have active ingredients extracted from plants and animals.
- Example: Quinine is used to treat malaria (from the cinchona tree), drug for leukemia from Vinca rosea, taxol from Taxus brevifolia etc.
- Economic Benefits:
- Forests provide numerous economic benefits, including timber and non-timber forest products such as fruits, nuts, resins, and medicinal plants.
- The forestry industry also creates jobs and generates revenue for many communities.
Threats from Deforestation, Illegal Logging, Climate Change, and Invasive Species
- Deforestation: The clearing of forests for agriculture, urbanization, and logging is a significant threat.
- Illegal Logging: Unregulated and illegal logging can lead to forest degradation.
- Climate Change: Changing climate patterns can affect the health and distribution of forests.
- Invasive Species: Non-native species can disrupt forest ecosystems.
Preserving the Forest: A Call for Continued Protection and Management
Forests are a precious natural resource that requires continued protection and management to safeguard their Importance of Forest, preserving their ecological, economic, and cultural significance for the nation.

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Crash Course
Crash Course Combo
Combo Optional Courses
Optional Courses Degree Program
Degree Program










