Religious Policies of the Portuguese in India # |
Trade Routes and Forced Conversions in India #
In 1497-99 Vasco da Gama sailed around the Cape of Good Hope and crossed the Indian Ocean to arrive at Calicut (now Kozhikode) on the south-west coast of India. With this discovery, Portuguese in India were driven by their desire to establish trade routes and spread Christianity. Their religious policies became the most potent weapon of Imperial expansion.
Portuguese Zeal: Forced Conversions and Imperial Control in India #
- Propagation of Christianity: The Portuguese in India were zealous about spreading the Christian religion.
- Religious Fundamentalism: Most Initial Missionaries were fundamentalists who were ready to use violent means against non-Christians.
- Anti-Muslim Sentiment: They aimed to fight against Muslim infidels. This was a continuation of their battles in Europe and West Asia.
- Political Control: The Portuguese in India used their religious policies as a means to establish and maintain political control.
- Racist Attitudes: The Portuguese in India thought themselves to be racially superior to ‘native heathens’ and had to civilise them including bringing them towards the light of Christianity.
| Also Read: Alfonso de Albuquerque: Architect of the Portuguese Empire in Asia |
Portuguese Coercion: Forced Conversions and Cultural Suppression in India #
The Portuguese in India pursued aggressive conversion policies, aiming to convert the local population to Catholicism.
- Conversion Policies: Forced Conversions through Churches, Matrimony, and Restrictions in India
- Establishment of Churches: They aimed at aggressive propagation of the christian faith.
- These missions were often accompanied by forced conversions, with the local population coerced into adopting Christianity.
- Matrimony: The Portuguese in India commander, Afonso de Albuquerque, advocated for his soldiers to wed the captured Muslim and Hindu females, which necessitated a change of faith to Christianity.
- A number of these women chose death over such unions, while others saw it as an opportunity for a less grim existence.
- Adoption and Conversion: Directives were given for Hindu orphans to be immediately taken to the College of St. Paul for baptism, education, and indoctrination.
- Religious Restrictions: Legislation was enacted prohibiting Christians from employing Hindus, and Hindu public worship was declared illegal.
Conversion Policies Reflected from the Words of Bishop Duarte Nunez (member of Delegation of Clergy): #“It would be to the service of God to destroy in this island alone these temples and to raise in their stead churches with saints. And whoever wants to live in this island let him become a Christian and he shall possess his lands and houses as he has till now done; if he does not want to do so, let him leave the island.” |
- Destruction of Hindu Temples: Temple Destruction and Forced Conversions
- Around 300-1000 Hindu temples were destroyed by the Portuguese in India.
- This was part of their policy to eradicate Hinduism and promote Christianity.
- It was a significant source of resentment among the local population.
- Inquisitions: Forced Conversions and Religious Brutality
- Its primary aim was to enforce Catholic orthodoxy.
- It was a powerful office set up within the Catholic Church to root out and punish heresy.
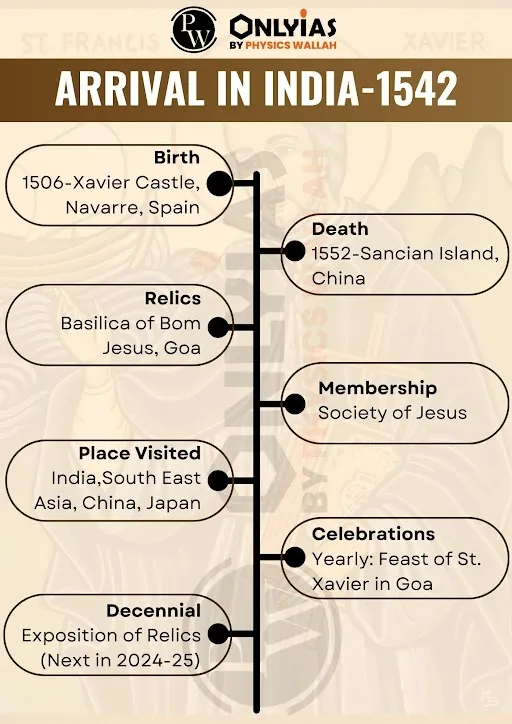
- In 1546, Francis Xavier proposed the establishment of the Goan Inquisition in a letter addressed to the Portuguese King, John III.
- It was established in 1560, briefly suppressed from 1774 to 1778, and continued thereafter until it was finally abolished in 1812.
- It targeted not only Hindus but also Jews, Muslims, and even converted Christians who were suspected of heresy.
- The Inquisition was known for its brutality, with numerous instances of torture and execution.
| Also Read: History of the French in India: Colonial Ventures, Rivalries, and Cultural Imprints |
Consequences of Portuguese in India: Forced Conversions and Social, Economic Strife #
- Creation of Social Hierarchy: Forced Conversions and Social Stratification
- A loose three tiered social structure came into existence based mainly on religion.
- This was the result of discriminatory treatment against the non-converted population in social-economic and political fields.
- This reduced social mobility with the non-christians.
- Three tiered social structure
| 1 | Original Christians | European Born |
| Indian Born | ||
| Mixed Race | ||
| 2 | Converted Christians | Hierarchy based on previous Status |
| 3 | Non-Christians | Mostly Konkani speaking Hindus |
- Discrimination in Economic Life: Forced Conversions Impacting Opportunities.
- Exclusion from Public Office: Non-Christians were forbidden from occupying any public office, and only a Christian could hold such an office.
- This policy limited the economic opportunities available to non-Christians and consolidated power within the Christian community.
- Restrictions on Production of Christian Devotional Objects: Hindus were forbidden from producing any Christian devotional objects or symbols.
- This policy restricted the economic activities of non-Christian artisans and craftsmen.
- Cultural Subjugation: Forced Conversions Spark Local Revolts
- Books in Konkani and Sanskrit were Banned.
- Restrictions were put on many traditional dances, foods and clothing.
- Religious ceremonies observed at various stages of life like birth, adolescence and death were prohibited.
- These discriminatory policies further alienated the local population and led to numerous revolts against Portuguese in India.
| Also Read: The Advent of Europeans in India: Reasons, Contributions, Impact and Rivalries. |
Impact of Portuguese in India: Forced Conversions and Cultural #
- Early Triumphs: The fervor to propagate Christianity served as a powerful impetus for the initial settlers, who pursued all missions with religious zeal.
- Establishing Stability: The conversion of people and their subsequent association with the Portuguese in India aided in solidifying the empire.
- It also gave people a reason to settle in new areas.
- Demographic Shift: Many of those who were converted to Christianity, either forcibly or through enticements, remain Christians today.
- Those who resisted were either killed or forced to abandon their homeland.
- Social Discord: The Portuguese in India exploited and benefited from the discord between newly converted Christians and Hindus, causing a rift in the social fabric of society.
- Destruction of Sacred Sites: They desecrated ancient Hindu shrines and replaced them with Churches, leading to the loss of many religiously significant structures and sites.
- Cultural Impact: Most native social and religious practices associated with public observance of non-Catholic religious rites associated with birth, marriage, and death were banned, forcing people to adopt the practices of the colonisers.
- As a result, local folk practices were gradually replaced.
- Political Impact: The Portuguese in India religious policies played a crucial role in their downfall in India.
These policies sparked political anxieties and led to conflicts with other powers, including the Deccan Sultans and Marathas, contributing to the decline of Portuguese in India.
St. Francis Xavier:
Known For:
|
| Also Read: Unravelling the Factors Behind the Portuguese in India |
Conclusion #
- The religious policies of the Portuguese in India were marked by intolerance and discrimination.
- While they did lead to the spread of Christianity in some regions, they also caused significant harm to the local population and led to widespread resentment against Portuguese rule.
Q. Consider the Following Statements: (UPSC 2021)
Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer (B) |
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Crash Course
Crash Course Combo
Combo Optional Courses
Optional Courses Degree Program
Degree Program