Rock Systems in India: A Simple Guide to Geological History
Geology is the study of the Earth’s composition, structure, and history. This includes mineralogy for rock composition, structural geology for geological structures, The rock system in geology classifies rocks based on mineral content, age, and formation.
India’s geological history is divided into four primary systems: Archaean (2.5 billion years old), Purana (1400-600 million years old), Dravidian, and Aryan. These systems help reveal the rich diversity and complex history of India’s rock formations, while the geological structure of India plays a crucial role in understanding its geological history.
The Role of Geologists in Earth Sciences
Geologists play a vital role in various industries, with diverse work environments encompassing the field and office.
- Their core objective is to enhance our understanding of the Earth’s geological aspects.
Earth’s Dynamics: Minerals, Rock system and the role of Geological Survey of India
- Mineralogy and Earth’s Rock Composition: Vital for understanding rocks’ mineral makeup and chemical structure.
- Structural Geology and Deformation: Explains the formation of geological structures like folds and faults during mountain-building.
- Geophysics: Utilizes various techniques to explore Earth’s properties, including seismology for understanding earthquakes and gravimetry to determine underground structures.
- Geomorphology: Investigates how surface processes like weathering and erosion shape landscapes.
- Geologic History and Stratigraphy: Provides a framework for understanding Earth’s evolution, employing principles of younger beds overlying older ones.
- Paleontology: Analyzes fossils to study the evolution of life, with fossils dating back over 3.5 billion years.
- Geological Survey of India: Plays a pivotal role in comprehensive geological research and studies.
Understanding Rock Systems: Categorization and Significance
The term “rock system” generally denotes a geological idea encompassing the organization and categorization of rock varieties, considering aspects such as mineral content, age, and how they formed.
- Geologists use these systems to classify and gain insights into the history and composition of Earth’s rock formations.
- The exploration of rock systems significantly enriches our understanding of geological processes and Earth’s past.
The Geological Structure of India’s Rock System
Geological Structure:
- Geological structure primarily pertains to the arrangement and deposition of rocks in the Earth’s crust, influenced by earth movements or their absence.
- It also extends to the morphological features of rocks, such as the Gondwana structure.
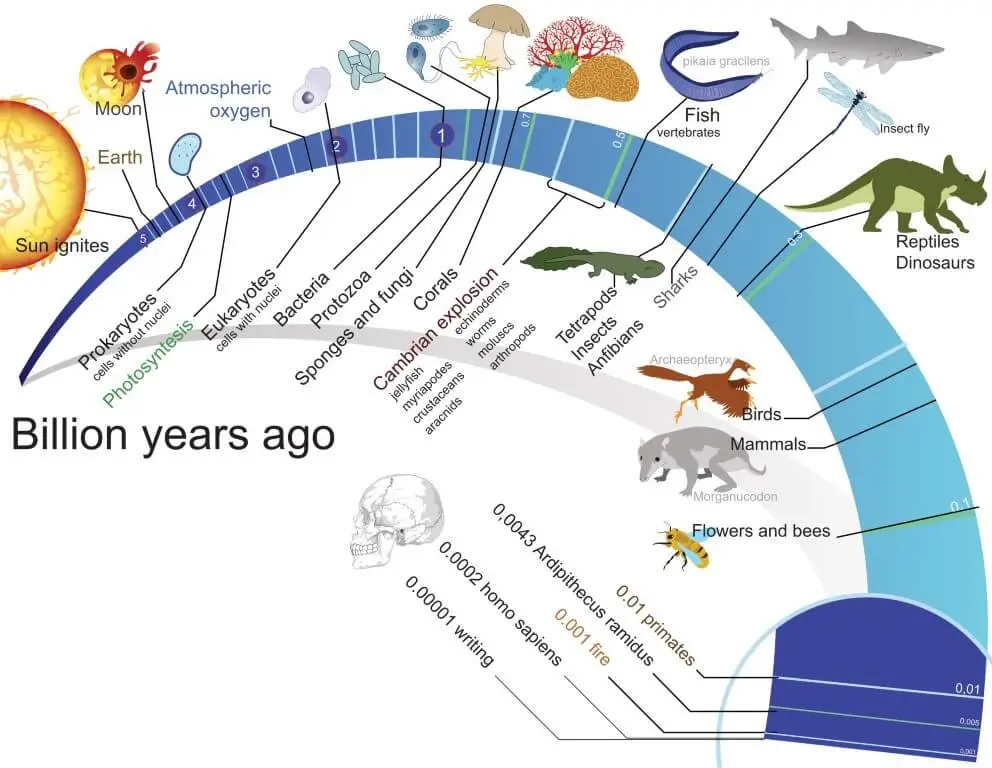
Chronicles of Earth: Geological Time Scale
The Geological Time Scale involves dating geological formations and the evolution and extinction of life based on their time and origin.
- Giovanni Ardunia introduced the Geological Time Scale in 1760, while the standardized version was developed during the 1881 International Geological Congress in Italy.
- India also has its own Geological Time Scale, advocated by T.S. Holland.
- Geological Survey of India: Plays a pivotal role in comprehensive geological research and studies.
Geological History of India:
- Physiographic divisions in India, like Peninsular India and Extra Peninsular India, serve as references for these geological formations.
Geological Evolution of India: Himalayas, plains and Indian Rock System:
- Peninsular India has been part of the Earth’s crust since its formation.
- The Himalayas were uplifted during the Tertiary period.
- The Indo-Gangetic plain began forming aggradational during the Pleistocene period, a process that continues through sedimentation in river floodplains and the lower part of the Gangetic plain.
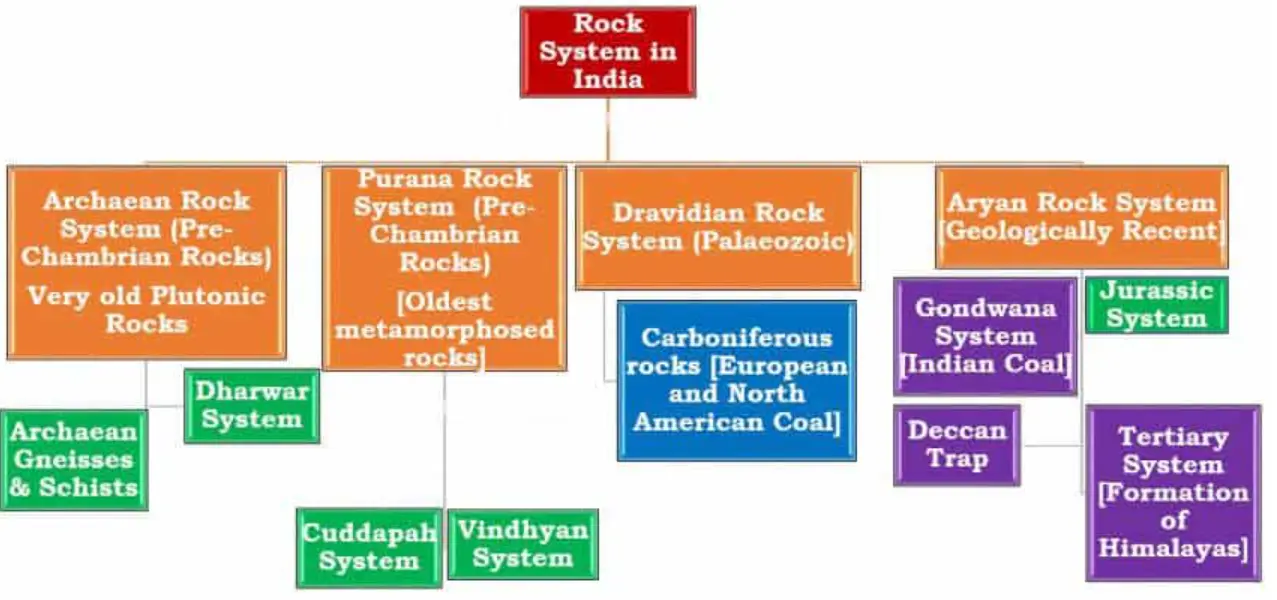
- Considering this intricate and diverse geological past, the Geological Survey of India has categorized the nation’s rock systems into four primary divisions.
- The Archaean Rock System
- The Purana Rock System
- The Dravidian Rock System
- The Aryan Rock System
| The Geological Survey of India: Role, History, and Significance |
|
Role of GSI:
|
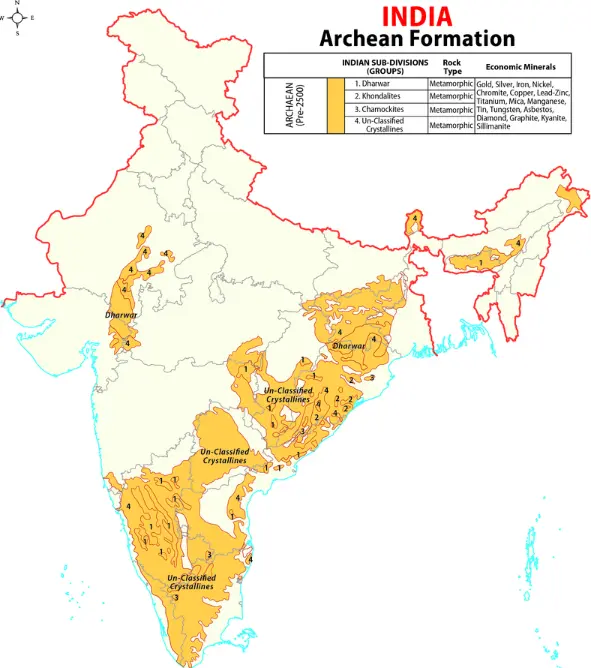
Archaean Rock System (Precambrian Rocks): Earth’s Ancient Foundation
-
- Early Tectonic Evolution: The initial phase of tectonic development involved the cooling and solidification of the Earth’s upper crust during the Archaean era, occurring more than 2.5 billion years ago, within the Precambrian Period.
- This period is characterized by the emergence of gneisses and granites, particularly in the Indian Peninsula.
- Early Tectonic Evolution: The initial phase of tectonic development involved the cooling and solidification of the Earth’s upper crust during the Archaean era, occurring more than 2.5 billion years ago, within the Precambrian Period.
- These rocks constitute the foundation of the Indian Craton, which is a block of the Indian Subcontinent from the ancient Gondwanaland.
- About: The term ‘Archaean’ was coined by J.D. Dana in 1782 to describe the Earth’s oldest rocks.
- The Archaean rock group comprises two systems:
- (a) Archaean System: Comprising granites and gneisses.
- (b) Dharwar System: Including the earliest sedimentary rocks.
- Gneiss exhibits varying mineral compositions from granite to gabbro.
- Schists are predominantly crystalline and may contain minerals like mica, talc, hornblende, and chlorite.
Archaean Gneisses and Schists: India’s Ancient Foundation
- Formation: Originated approximately 4 billion years ago.
- Resulted from the solidification of molten magma, occurring during a period when the Earth’s surface was intensely hot.
- Terminology:Often referred to as the ‘Basement Complex.’
- Serves as the foundational layer for subsequent rock deposits.
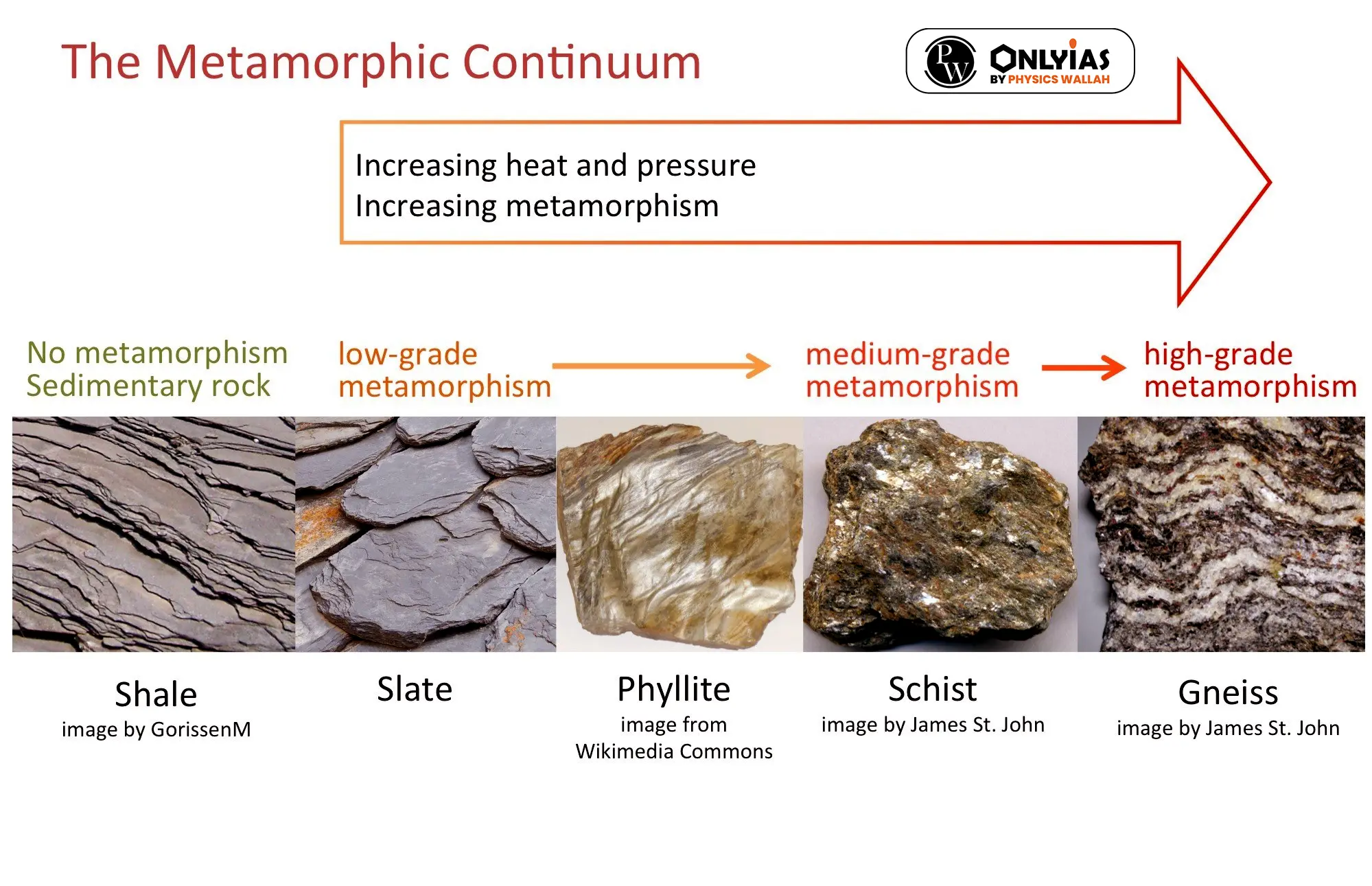
- Fossil Absence: Azoic or unfossiliferous, meaning they lack any evidence of ancient life forms.
- Composition: Foliated in structure, characterized by thin sheet-like layers.
-
- Highly crystalline due to their volcanic origins.
- Classified as plutonic intrusions, signifying their deep-seated location within the Earth’s crust.
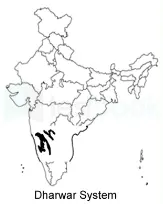
Dharwar Metamorphosed Rocks: Insights into India’s Rock System
- Formation Period: These rocks formed over an extensive time span, ranging from 4 billion years ago to approximately 1 billion years ago.
- Metamorphosed Sedimentary Rock System:
- This rock type is predominantly composed of highly metamorphosed sedimentary materials.
- They originated through the process of metamorphism, transforming sediments from Archaean gneisses and schists.
- Oldest Metamorphosed Rocks:These rocks stand out as the oldest known examples of metamorphosed rocks.
- Abundance in Dharwar District: They are notably abundant in the Dharwar district of Karnataka, India.
- Economic Significance:
-
- These rocks hold significant economic value due to their rich mineral content.
- They are a prime source of valuable minerals, including high-grade iron-ore, manganese, copper, lead, gold, and other important resources.
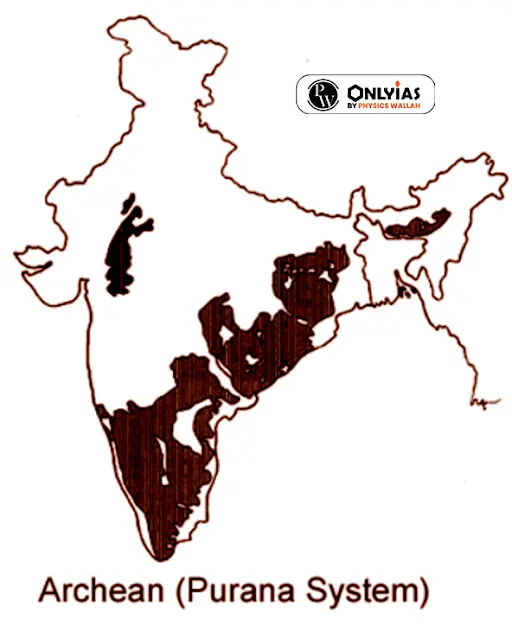
Purana Rock System: Formation and Significance
- Combined Nomenclature: The Purana rock system encompasses both the Cuddapah and Vindhyan rock systems.
- Formation Process: These rocks originated through the erosion and deposition of Archean and Dharwar rocks.
-
- This geological process is estimated to have occurred between 1400 and 600 million years ago.
- Predominantly Sedimentary: These rocks are primarily of a sedimentary nature, characterized by their formation from deposited sediments.
- Mineral Wealth: The Purana rock system frequently hosts precious mineral reserves, potentially encompassing iron, manganese, copper, and other vital metals indispensable for diverse industries.
- Building Resources: Specific geological formations within the Purana rock system offer access to top-quality construction materials such as sandstone, limestone, and granite, playing a pivotal role in construction and the development of infrastructure.
- Water Resources: Certain Purana rock strata have the capacity to function as excellent aquifers, effectively storing and supplying groundwater, which holds immense importance for agriculture and human consumption.
Cuddapah Rock System: Formation, Minerals, and Significance
Origin from Cuddapah District: The Cuddapah rock system derives its name from the Cuddapah district in Andhra Pradesh.
-
- This nomenclature is due to the extensive presence of Cuddapah rocks in the region.
- Formation Process: These rocks were created through the accumulation of sedimentary materials such as sandstone, limestone, clay, and other similar deposits.
-
- These sediments were laid down within synclinal folds, situated between two mountain ranges.
- Prominent Outcrops: The most prominent outcrops ( like groundnut, cotton, red gram, Bengal gram are grown) of Cuddapah rocks are observed.
- Rich in Minerals: Cuddapah rocks are notable for their mineral content, which includes ores of iron, manganese, copper, cobalt, nickel, and more.
Abundant Limestone: These rock formations also house substantial reserves of limestone suitable for cement production.

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Crash Course
Crash Course Combo
Combo Optional Courses
Optional Courses Degree Program
Degree Program










