The Indian Constitution is a comprehensive and evolving document, designed to ensure the principles of democracy, unity, and justice. It encompasses a wide range of features, including the Parliamentary system, secularism, local self-government, and independent bodies. Despite criticisms regarding its length, complexity, and borrowed elements, the Constitution remains a robust framework aimed at addressing India’s diverse socio-political landscape.
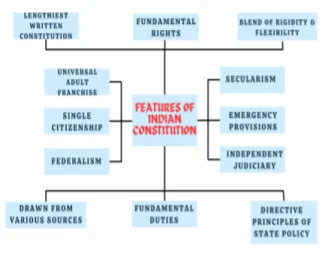
Salient Features of the Indian Constitution: An Overview
Lengthiest Written Constitution: Constitution of India holds the distinction of being the longest-written Constitution globally.
- Initially comprising a Preamble, 395 Articles distributed across 22 Parts, and 8 Schedules, it laid the foundation for our democratic republic (Currently, the Indian Constitution has expanded to encompass 448 articles spanning 25 parts, along with 12 schedules and 106 amendments).
- Foresight of the Framers: The framers’ foresight led them to incorporate intricate provisions, eliminating potential loopholes and defects.
- Global Constitutional Experiences: The framers of the Constitution drew on global constitutional experiences, addressing challenges faced by other nations.
- They carefully incorporated provisions to navigate these issues effectively.
- Addressing India’s Unique Challenges: The Constitution’s size is influenced by the country’s vastness and unique challenges related to language, scheduled castes, tribes, and minorities.
- Special Privileges for Certain States: Certain states like Nagaland(Article 371A), Mizoram(Article 371G), Assam(Article 371B), and Gujarat(Article 371), were granted unique privileges.
- Comprehensive Structure for Central and State Governments: It outlines the structure for both the Central Government and States, unlike the Australian and American Constitutions, which omitted specifics on state government machinery.
- Detailed Provisions for Governance and Administration: Unlike many Constitutions, the Indian Constitution not only establishes fundamental governance principles but also delves into administrative specifics, including detailed provisions on Centre-State relations and emergency situations.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course

Principles Enshrined in the Constitution
- In accordance with the Preamble, India is proclaimed a Sovereign Socialist Secular Democratic Republic, emphasizing its autonomy from external influences.
- Introduction of Socialism in the Preamble: The term Socialist was introduced into the Preamble by the 42nd Amendment Act 1976, denoting state participation in production.
- India is currently moving towards privatization in its mixed economy model.
- Equal Treatment of All Religions: In a Secular state, no religion is recognized as the state religion.
- All religions are treated equally, and the state is concerned with regulating human relations, not the relationship of man with God.
- Democratic Governance: The term Democratic signifies that the government derives its authority from the will of the people.
- Rulers are elected through democratic processes, ensuring a representative government.
- Fundamental Democratic Principles: In democratic principles, Justice, Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity are fundamental.
- Elected Head of State: A Republic signifies an elected, not hereditary, head of State. India’s President exemplifies this democratic essence.
Blend of flexibility and rigidity
- Amendment Methods: Constitutions incorporate different amendment methods, which are both flexible and rigid.
- India employs a special process, while the British, with its unwritten Constitution, follows standard law-making, embodying flexibility.
- The US Constitution, being rigid, presents challenges in amendments. In contrast, the Indian Constitution incorporates both procedures, offering flexibility and adaptability.
- Balancing Rigidity and Flexibility: The Indian Constitution incorporates diverse amendment procedures: simple majority, special majority, the requirement of half of the states to give their assent in cases that affect the federal provision of the Constitution.
- This nuanced approach blends rigidity and flexibility, fostering both continuity and change.
Federal Structure of Government
- Overview of India’s Federal Structure: India’s federal structure, outlined in our Constitution, harmonizes regional and central governance.
- Cornerstones of Indian Federalism: The written framework, power division, bicameral Legislature, and an independent Judiciary are the cornerstones of our federalism.
- Balancing Unity and Decentralization: Indian federalism upholds unity, decentralization, and Union dominance.
- Unitary Tendencies in Indian Federalism: Central powers like Governor appointments and Emergency provisions highlight the unitary tendency within the federal framework.
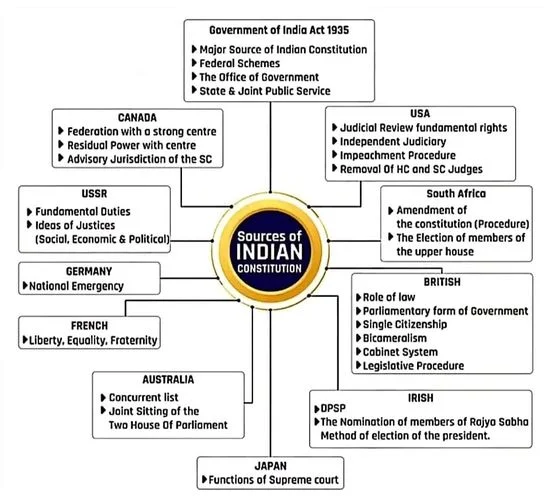
Drawn from various sources
- International Influences: India’s Constitution drew inspiration from various international sources, including the Government of India Act of 1935 for its structure, the United States Constitution for its emphasis on judicial independence and Fundamental Rights, and others.
- Borrowed Elements in India’s Constitutional Design: The architects of India’s Constitution adapted borrowed elements to fit India’s unique circumstances.
- Example: while India’s cabinet system draws inspiration from the United Kingdom, it functions differently and does not wield absolute authority like its British counterpart.
Fundamental Rights
- Key Difference: A fundamental distinction between the Indian Constitution and the Government of India Act of 1935 lies in the inclusion of Fundamental Rights in the former, underscoring India’s commitment to individual liberties.
- Part III: Part III of the Indian Constitution, often called the ‘conscience,’ contains Fundamental Rights.
- These rights protect citizens from State and individual power, emphasizing the delicate balance between individual liberty and societal interests.
Directive Principles of State Policy
- Positive Obligations of the State: A distinctive aspect of our Constitution is Directive Principles (Part IV) provide positive directives to the State, emphasizing its obligation to promote the welfare of the people.
- Importance Directive Principles in Governance: Directive Principles, while non-binding, hold paramount importance in governance, striving to fulfil the ideals of social and economic justice outlined in the Preamble.
- They address income disparities, equal opportunities, and wealth distribution.
- Social Justice and Equity: Social justice directives encompass facilities for marginalized groups like Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, women, children, and workers, ensuring equal justice,education, and healthcare.
- The Conscience of the Constitution: DPSPs, alongside Fundamental Rights, form the conscience of the Constitution.
Fundamental Duties
- Introduction of Fundamental Duties: The 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act in 1976 incorporated “Fundamental Duties” (Part IVA, Article 51A) for citizens.
- Significance of Fundamental Duties: These duties serve as a constant reminder, aligning citizens’ Fundamental Rights with essential democratic norms and conduct.
- Comparison with Directive Principles: Similar to Directive Principles, these duties lack judicial enforcement but serve as reminders, integrating citizen responsibilities into India’s basic law—a distinctive constitutional feature.
Independent Judiciary
- Role of an Independent Judiciary: An independent Judiciary serves as the bedrock of the rule of law and democracy.
- Separation of Powers: The Constitution meticulously separated the Judiciary from the Legislature and Executive, empowering it with the crucial tool of judicial review.
- Balancing Government Branches: This authority enables the Judiciary to maintain the delicate balance between government branches, preventing unwarranted intrusion.
- Independence and Security of Tenure for Judges: The Constitution grants complete financial independence and security of tenure to Judges, ensuring their impartiality and autonomy in administering justice.
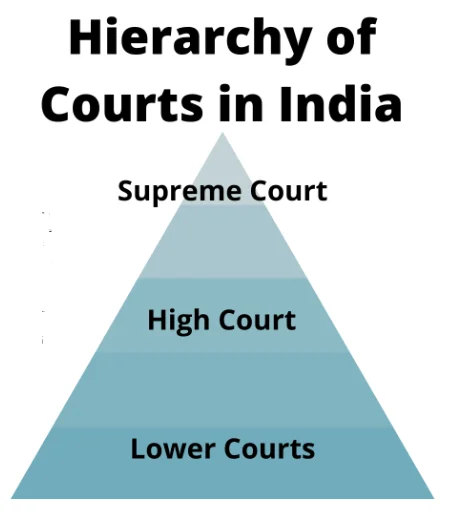
Integrated Judiciary
- Unified vs. Decentralized Judicial Systems: India’s judicial framework differs significantly from federal nations like the USA.
- While they follow a decentralized system, India has established an integrated and unified approach to justice.
- Integrated Judicial Structure: In India’s judicial structure, a single hierarchy prevails.
- The Supreme Court stands at the national level, overseeing High Courts at the state level and, further down, the subordinate courts at the district and lower levels.
- Enforcing Both Centre and State Laws: Unlike the USA, where federal laws are enforced by the federal judiciary and state laws by state judiciary, India follows a single system of judiciary where courts from lowest to highest level enforce both Centre and State laws.
- Consistent and Equitable Justice: This unified approach ensures justice for all citizens in a consistent and equitable manner.
Single Citizenship
- Dual Polity and Single Citizenship: The Indian Constitution embodies a dual polity, distinguishing between the Centre and States. Despite this division, it establishes a unique concept of single citizenship.
- Unified Citizenship: This means that every Indian, regardless of their residence or birthplace within the country, holds the same citizenship, i.e., Indian, fostering a cohesive national identity.
- Comparison with Dual Citizenship: Unlike the USA, where dual citizenship (national and state) exists, every Indian enjoys unified citizenship with equal rights across the country.
- Commitment to Equality, Unity, and Integrity: This provision in our Constitution stands as a testament to our commitment to equality, unity, and integrity.
Emergency Provisions
- Federal Nature with a Unitary Twist: One of the distinctive features of the Indian Constitution is its federal nature, which transforms it into a unitary character during times of emergency.
- This shift in power dynamics during a state of emergency underscores the Constitution’s ability to adapt and address critical situations, ensuring the nation’s stability and security.
- Centralization of Powers During Emergencies: During emergencies, the Indian Parliament gains authority to legislate on State list subjects and direct State executive powers, centralizing all powers within the Union government.
- This transformation results in a unitary character, emphasizing the Constitution’s adaptability in ensuring a unified response to critical situations.
Universal Adult Franchise
- Foundation of Democratic Participation in India: In India, the democratic essence thrives in the universal adult suffrage granted to every citizen not below the age of 18 years (Article 326)
- The Constitution (Sixty-first Amendment) Act, 1989, lowered the voting age of elections to the Lok Sabha and to the Legislative Assemblies of States from 21 years to 18 years.
- Ensuring Equal Participation: This fundamental right ensures equal participation in electing representatives without any prejudice, emphasizing the democratic spirit ingrained in our Constitution.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Bedrock of Indian Democracy: Universal adult franchise stands as the bedrock of our democracy, embodying the essence of popular sovereignty.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
The Constitution of India stands as a beacon of democratic principles, balancing flexibility with rigidity to adapt to changing times while preserving core values. Its provisions for Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles, and a federal structure reflect a deep commitment to justice, equality, and the well-being of all citizens.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Part – V (JUDICIARY) | FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS (UDAAN) |
| Preamble of the Indian Constitution | Directive Principles of State Policy |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program










