Introduction: Insights into the Early Solar System and Cosmic Composition
Minor planets, also known as asteroids or planetoids, are celestial objects that orbit the Sun but are significantly smaller than the major planets. These rocky and metallic bodies vary in size from a few meters to hundreds of kilometers in diameter.
They primarily inhabit the asteroid belt, a region located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, but can also be found throughout the solar system. Minor planets are remnants from the early stages of solar system formation and provide valuable insights into the history and composition of our cosmic neighborhood.
Diverse World of Minor Planets: Characteristics, Categorization, and Exploratory Endeavors
Minor planets, also known as asteroids and dwarf planets, are small celestial objects that primarily reside in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
- Location: Most minor planets are found in the asteroid belt, a region between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
- However, some can be found in other parts of the solar system.
- Size: Minor planets vary in size from a few meters to hundreds of kilometers in diameter.
- The largest asteroids are often referred to as “dwarf planets.“
- Composition: They are composed of rock and metal and are remnants from the early solar system, representing material that can never be converted into full-fledged planets.
- Number: There are millions of minor planets in the solar system, but only a fraction of them have been discovered and cataloged.
- Categorization: They are categorized into different groups based on their characteristics.
- These groups include main belt asteroids, near-Earth asteroids, Trojans, and trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs).
- Main Belt Asteroids: The majority of minor planets reside in the asteroid belt and are known as main belt asteroids.
- Near-Earth Asteroids: Some minor planets have orbits that bring them close to Earth, and they are known as near-Earth asteroids.
- Trojans: Trojans are minor planets that share an orbit with a larger planet, such as Jupiter. They are located at stable points known as Lagrange points.
- Dwarf Planets: Certain larger minor planets, like Ceres, Pluto, Eris, Haumea, and Makemake, are classified as dwarf planets, a distinct category from traditional asteroids.
- Exploration: Space missions, such as NASA’s OSIRIS-REx and Japan’s Hayabusa2, have been launched to study and collect samples from minor planets to learn more about the solar system’s formation.
|
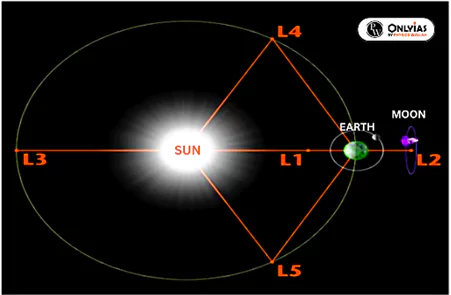
Understanding Lagrange Points: Stable Celestial Locations and Their Significance in Space Exploration
|
Asteroids: Relics of the Early Solar System and Their Role in Planetary Science
They are celestial objects that orbit the Sun.Asteroids are often referred to as minor planets.
- Planetary Remains: Asteroids are remnants from the early solar system that never coalesced into full-fledged planets.
- They are typically around 4.6 billion years old, similar to the age of the solar system.
- Orbit Between Mars & Jupiter: Most asteroids orbit the Sun in a region called the asteroid belt, which lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
- Composition: Asteroids are primarily composed of rocky materials.
- Some asteroids contain metallic minerals, and a few even have traces of ice.
- Examples: Ceres is the largest asteroid in the asteroid belt.
- It is also classified as a dwarf planet due to its size and characteristics.
Exploring the Solar System’s Debris Zones: Asteroid Belts, Kuiper Belt, and Their Scientific Significance
The solar system is not just a collection of planets. It also contains regions filled with smaller objects.
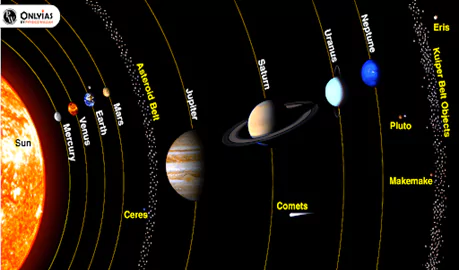
Asteroid Belts: Solar System Insights
- Location: The main asteroid belt is situated between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2.2 to 3.3 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun.
- (1 AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun.)
- Composition: This belt primarily consists of asteroids, which are rocky or metallic objects.
- Some of the largest asteroids within the main belt include Ceres, Vesta, and Pallas.
- Formation: The main asteroid belt is believed to be a region where planetesimals, early building blocks of planets, failed to coalesce into a planet due to the strong gravitational influence of Jupiter.
- Purpose: It provides a glimpse into the composition of the early solar system and is a subject of study for astronomers and space missions.
Kuiper Belt: Exploring Solar System’s Edge
- Location: The Kuiper Belt is located in the outer region of the solar system, beyond the orbit of Neptune, starting at about 30 AU from the Sun and extending much farther.
- It is considered the boundary of the solar system.
- Composition: The Kuiper Belt contains a diverse population of objects, primarily composed of icy bodies, including dwarf planets like Pluto, Haumea, Makemake, and Eris.
- These objects are sometimes referred to as “Kuiper Belt Objects” (KBOs).
- Formation: The Kuiper Belt is thought to be a remnant of the early solar system, containing objects that never coalesced into full-fledged planets or were scattered to the outer regions.
- Purpose: It is a critical region for studying objects beyond Neptune and understanding the processes that shaped the solar system’s outer reaches.
- It has also been a target for space missions, including the New Horizons mission to Pluto.
Conclusion:
- Minor planets such as asteroids and objects in the Kuiper Belt are key to understanding the early solar system and its composition. The exploration of these celestial bodies gives insight about complex dynamics of space, while the study of Lagrange points has facilitated stable conditions for space missions. Through continued research and exploration, we can deepen our knowledge of these essential components of our cosmic neighborhood.
Previous Year Question (Prelims)
Q. The group of small pieces of rock revolving round the sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter are called:(UPSC CSE 1997)
- Meteors
- comets
- meteorites
- Asteroids
Ans: d
Q. Consider the following statements regarding asteroids:(UPSC CSE 1998)
- Asteroids are rocky debris of varying size orbiting the sun
- Most of the asteroids are small, but some have diameters as large and 1000 km
- The orbit of asteroids lies between the orbits of Jupiter and Saturn
Choose the correct options :
- 1, 2 and 3 are correct
- 2 and 3 are correct
- 1 and 2 are correct
- 1 and 3 are correct
Ans: c
Q. What is difference between asteroids and comets?(UPSC CSE 2011)
- Asteroids are small rocky planetoids, while comets are formed of frozen gasses held together by rocky and metallic material.
- Asteroids are found mostly between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars, while comets are found mostly between Venus and Mercury.
- Comets show a perceptible glowing tail, while asteroids do not.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Ans: b