The system of government outlines how authority is divided between the legislature and executive, indicating the specific type of governance embraced by a country. This arrangement is determined by the distribution of powers within the government. Different nations adopt diverse government systems, and in the case of India, the Constitution establishes a Parliamentary form of government.
Meaning and Mandate of Government
Meaning: Government is the system or group of individuals that exercise authority and control over a specific territory and its people.
- Functions: Governments are in charge of making and enforcing laws, rules, and regulations, managing public affairs, and providing essential services and infrastructure to its citizens.
- Role in Society: Governments play a central role in maintaining order, regulating societal interactions, and representing the interests of the state on the national and international stages.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Key Characteristics and Functions of Government
- Authority: Governments have the legitimate power to make and enforce laws within their jurisdiction, which can be derived from various sources, including Constitutions, elections, traditions, or force.
- Territorial Jurisdiction: Governments have defined geographical boundaries within which they enforce their laws and authority.
- These boundaries can range from local governments to national governments.
- Functions and Services: Governments provide essential services to their citizens, such as education, healthcare, transportation infrastructure, defense, etc.
- They also regulate various aspects of society, including the economy, public safety, and environmental protection.
- Law-making: Governments create and enact laws such as laws related to civil rights, taxation, criminal justice, and business regulations.
- Enforcement: They have the authority to enforce laws through law enforcement agencies, such as the police and judiciary.
- Foreign Relations: Governments engage in diplomacy and international relations, representing the state’s interests in interactions with other countries.
- They negotiate various treaties, engage in trade agreements, and participate in international organizations.
- Taxation: They collect taxes from individuals and businesses to fund public services and infrastructure projects.
- Defence and Security: They are responsible for national defense and security.
- Thus, they maintain armed forces and law enforcement agencies to protect the state from external threats and maintain internal order.
- Policy-making: Governments formulate policies and strategies to address the challenges of society and achieve specific goals.
- These policies can encompass areas like healthcare, education, economic development, and social welfare.
Types of Government
Government is classified into Unitary and Federal forms of government on the basis of the nature of relations between the union government and the regional governments.
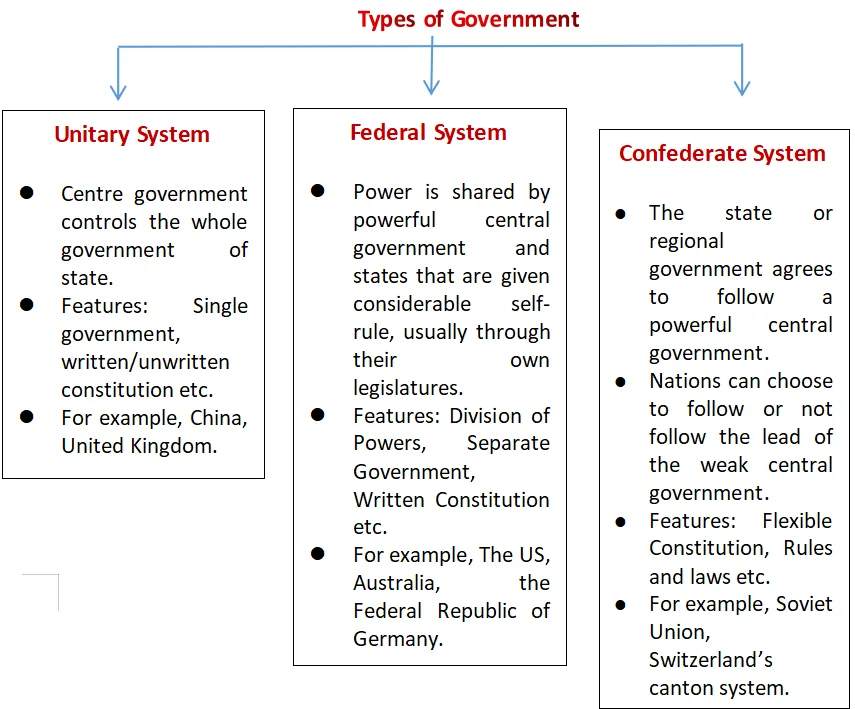
- Federal Government: In this form of government, powers are divided between the national government and the regional governments by the Constitution itself and both operate in their respective jurisdictions independently.
- Origin of the Term ‘Federation’: The word ‘Federation’ is derived from the Latin word “foedus” which means ‘treaty’ or ‘agreement.’
- Thus, a federation is a new state or political system formed through a treaty or an agreement between the various states or republics.
- Structure of a Federation: In this form of government, the national government is known as the Federal government or the Central government or the Union government and the regional government is known as the State Government or the Provincial government.
- Examples: Countries with a federal form of government include the USA, Switzerland, Canada, Russia, Brazil, Australia, Argentina, etc.
- Origin of the Term ‘Federation’: The word ‘Federation’ is derived from the Latin word “foedus” which means ‘treaty’ or ‘agreement.’
- Unitary Government: In this form of government, all the powers are vested in the national government, and the regional governments derive their authority from the national government.
- Example: Britain, France, China, Italy, Belgium, Japan, Norway, Spain, Sweden, etc.
Features of Federal and Unitary Governments
| Federal Government | Unitary Government |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
System of Government In India
Quasi-Federal System: The Indian Constitution provides for a quasi–federal system of government in the country.
- Reason: The framers of the Constitution adopted the federal system due to socio-cultural diversity and the large size of the country.
- Terminology in the Indian Constitution: The term ‘federation’ has nowhere been mentioned in the Constitution. In fact, Article 1 of the Constitution describes India as a ‘Union of States’.

India resembles the Canadian Federation in three ways, such as:
- Its formation (i.e., by way of disintegration);
- Its preference for the term ‘Union’ (the Canadian Federation is also called a ‘Union’); and
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Its centralising tendency (i.e. vesting residuary powers in the Centre (Example: Cyber Laws).
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
The system of government defines how power is divided between the legislature and executive, determining a country’s governance structure.
- Governments, tasked with managing public affairs, creating laws, and providing essential services, operate under various forms like federal and unitary systems.
- In India, the Constitution establishes a quasi-federal system to accommodate the nation’s socio-cultural diversity and vast geographical expanse, drawing elements from both federal and unitary frameworks.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Taxation in India: Systems, Evolution and Impact | Part – V (JUDICIARY) |
| Economic Development | Parliamentary System of Government |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









