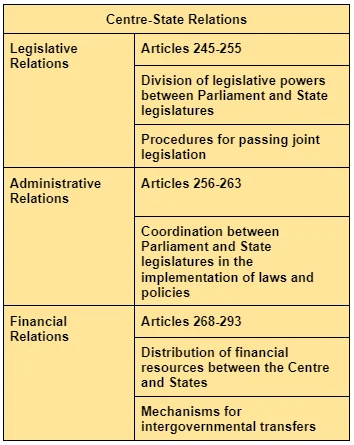
In India’s federal system, the doctrines of Pith and Substance, Colourable Legislation, and Territorial Nexus are essential for maintaining balanced Centre-State relations. These doctrines ensure that legislative powers are exercised appropriately and respect territorial boundaries. They help resolve disputes and uphold the division of powers between the Central and State governments.
Judicial Doctrines Governing Centre-State Relations
Doctrine of Pith and Substance
- Purpose: The doctrine of pith and substance helps prevent legal conflicts by providing a framework for determining legislative competence, reducing the likelihood of disputes, and contributing to a stable legal environment.
- In constitutional law, it delineates legislative boundaries in a federal system, focusing on the true nature of a law to determine its validity.
- Core Principles of the Doctrine: The doctrine of pith and substance rests on several core principles:
- Legislative Competence: It is a tool to ascertain if a law falls within the designated powers of the Centre or States, preventing encroachment.
- True Nature of Legislation: The assessment of a law’s validity focuses on its primary purpose, rather than its incidental effects.
- Intra Vires Legislation: It allows a law impacting another level’s jurisdiction to be valid if its primary purpose aligns with the enacting level’s competence, recognizing overlapping effects based on primary intent.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Applications of the Doctrine: The doctrine of pith and substance finds application in various scenarios within a federal system:
- Distinguishing Between Central and Regional Laws
-
- The doctrine distinguishes between Central and regional government laws, clarifying legislative authority on specific matters.
- Resolving Jurisdictional Disputes
- It helps resolve disputes over legislative authority by providing a systematic approach to determine the competence of each government level.
- Protecting the Rights of States
- The doctrine safeguards regional governments’ rights and powers in a federal system, preventing the Centre from encroaching on States’ legislative authority.
- Upholding the doctrine ensures courts protect regional autonomy and respect their legislative powers.
- Significance of the Doctrine: It plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of power between the Central and regional governments in a federal system:
- Maintaining Constitutional Balance
-
- The doctrine ensures that each government adheres to its designated powers, preventing overstepping constitutional boundaries and maintaining the balance of power in the federal structure.
- Ensuring Legislative Coherence
- The doctrine promotes coherence and consistency in lawmaking by delineating legislative spheres, preventing overlapping or conflicting claims of authority, and ensuring a streamlined and effective legislative process.
- Preventing Legal Conflicts
- The doctrine helps prevent legal conflicts by providing a framework for determining legislative competence, reducing the likelihood of disputes and contributing to a stable legal environment.
- Examples of the Application of the Doctrine of Pith and Substance
- State of West Bengal v. Union of India (1967)
-
- The Supreme Court of India held that the Central government’s law on the regulation of inter-State trade was intra vires under the doctrine of pith and substance.
- Fertilizer Corporation Ltd. v. Union of India (1981)
- The Supreme Court of India held that the Central government’s law on the acquisition of land for public purposes was intra vires under the doctrine of pith and substance.
- Minerva Mills Ltd. v. Union of India (1980)
- The Supreme Court of India held that the Central government’s law on the nationalisation of the textile industry was ultra vires under the doctrine of pith and substance.
Doctrine of Colourable Legislation
Definition: The doctrine of colourable legislation is a legal principle that prevents a legislature from indirectly enacting laws that it is not permitted to enact directly.
- Relevance in Federal Systems: This doctrine is particularly relevant in federal systems, where there is a division of power between the Central and the States.
- Key Aspects of the Doctrine of Colourable Legislation
- Prevention of Indirect Encroachment
- The doctrine of colourable legislation aims to prevent a legislature from indirectly encroaching upon the legislative domain of another level of government.
- Focus on True Purpose of Legislation
- The doctrine emphasises that the true purpose of a law, rather than its superficial appearance, should be considered when determining its validity.
- Ultra Vires Legislation
- If a law is found to be enacted solely for the purpose of indirectly enacting legislation that falls outside the legislative competence of the enacting level of government, it may be declared ultra vires under the doctrine of colourable legislation.
- Prevention of Indirect Encroachment
- Applications of the Doctrine of Colourable Legislation:
-
- Protecting State Rights
- The doctrine of colourable legislation serves as a safeguard for the rights and powers of State governments within a federal system.
- It helps to prevent the Central government from indirectly encroaching upon the legislative authority of the States.
- Judicial Review of Legislation
- Courts can apply the doctrine of colourable legislation to review the validity of laws enacted by legislatures.
- This helps to ensure that legislatures adhere to the constitutional boundaries of their legislative competence.
- Preventing Misuse of Legislative Power
- The doctrine of colourable legislation acts as a deterrent against legislatures attempting to circumvent constitutional limitations on their legislative powers.
- Protecting State Rights
- Examples of the Application of the Doctrine of Colourable Legislation
-
- K.C. Gajapati Narayan Deo v. State of Orissa (1953)
- The Supreme Court of India held that the State government’s law regulating land acquisition was ultra vires under the doctrine of colourable legislation.
- State of Bombay v. Bombay Education Society (1954)
- The Supreme Court of India held that the State government’s law regulating educational institutions was ultra vires under the doctrine of colourable legislation.
- State of Rajasthan v. Union of India (1977)
- The Supreme Court of India held that the Central government’s law regulating gambling was ultra vires under the doctrine of colourable legislation.
- K.C. Gajapati Narayan Deo v. State of Orissa (1953)
Doctrine of Territorial Nexus
Definition: The Doctrine of Territorial Nexus asserts that laws are applicable only within the territorial boundaries of the enacting legislature.
- Derived from Article 245 of the Indian Constitution, it grants exclusive power to State legislatures for making laws on State List matters, limiting their application to the respective State’s territory.
- Constitutional Basis and Scope: The Doctrine of Territorial Nexus ensures that States have the autonomy to make laws on matters that are of concern to their own citizens, and it prevents the Central government from encroaching on the legislative powers of the States.
- Judicial Affirmation of the Doctrine of Territorial Nexus: The Doctrine of Territorial Nexus has been affirmed by the Supreme Court of India in a number of cases:
- State of Bihar v. Kameshwar Singh: The Supreme Court held that a State law that imposed a tax on goods transported from one State to another was invalid because there was no sufficient connection between the law and the object to which it applied.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
These doctrines play a crucial role in preserving the balance of power within India’s federal structure.
- By preventing conflicts and ensuring that laws are within the proper jurisdiction, they contribute to a stable and effective legal system.
- Their application helps maintain harmony between the Centre and States, ensuring adherence to constitutional boundaries.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Supreme Court of India | Federalism |
| Legislative Procedure In State Legislature | Centre State Relations in India |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









