Judicial infrastructure is crucial for an efficient and effective justice system. Proper facilities and resources are essential for judges, lawyers, and court staff to perform their duties fairly and promptly. Since 1993-94, the Central Government has implemented a Centrally Sponsored Scheme to support State Governments in developing infrastructure for district and subordinate courts. This scheme aims to improve physical infrastructure and housing for Judicial Officers, enhancing the overall justice delivery system.
Enhancing Judicial Infrastructure for Effective Justice Delivery
Judicial Infrastructure in India
- Components of Judicial Infrastructure: It includes physical premises of courts, tribunals, lawyers’ chambers, digital and human resources etc.
- Definition of Efficient Judicial Infrastructure: The term “efficient judicial infrastructure” denotes providing equal and free access to justice which can be realised through a “barrier free and citizen friendly environment”.
- Responsibility for Development: Currently, the primary responsibility of development of infrastructure facilities for the judiciary rests with the state governments, but the Central Government regularly provides financial assistance under the Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: The Union Government has been implementing a Centrally Sponsored Scheme for Development of Infrastructure Facilities since 1993-94 for augmenting resources and financial assistance in prescribed funding patterns to the State Governments in district as well as subordinate courts.
- Coverage: It covers the construction of court buildings and residential accommodations for judicial officers of district and subordinate judiciary and this scheme is also extended further from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
Current Status
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Judicial Infrastructure Development Scheme
- Objective: Improve physical infrastructure and housing for Judicial Officers in District and Subordinate Courts to enhance justice delivery.
Key Points: (As per data available from the Department of Justice)
- Responsibility:
-
-
- State Governments: Primary responsibility for infrastructure development.
- Central Government: Provides financial assistance to augment State resources.
-
- Coverage:
-
-
- Included: All States and Union Territories.
- Excluded: High Court buildings.
-
- Allowed Activities:
-
-
- New construction.
- Upgradation or renovation of existing court buildings.
- Housing needs for Judicial Officers.
- Not Allowed: Routine maintenance or upkeep.
-
- Funding:
-
-
- Initial Funding (1993): Central and State Governments shared funding on a 50:50 basis.
-
- Revised Funding:
-
-
-
- 2011-12: Changed to 75:25 (Centre: State) and 90:10 for North Eastern States.
- 2015-16: Changed to 60:40 (Centre: State) and maintained 90:10 for North Eastern and Himalayan States.
- Union Territories: 100% Central funding.
-
-
- Extension and Current Status:
-
- Extended from 01.04.2017 to 31.03.2020 with an outlay of Rs. 3,320 crores.
- Interim extension granted till 31.03.2021 pending Fifteenth Finance Commission recommendations.
- Consideration for continuation from 01.04.2021 to 31.03.2026 is ongoing.
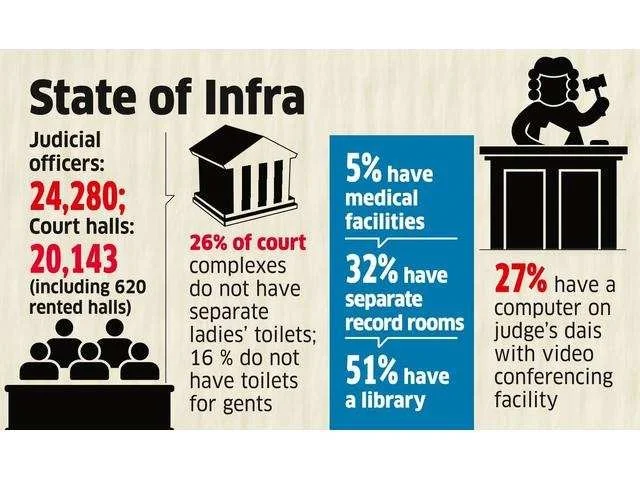
Infrastructure Statistics (as of 31.03.2021)
| Sanctioned Strength of Judicial Officers | 24,291 |
| Court Halls Available: | 20,115 |
| Court Halls Under Construction: | 2,423 |
| Residential Units Available: | 17,705 |
| Residential Units Under Construction | 1,857 |
Planning and Monitoring
- Chief Justices’ Conference (April 2016) Resolutions:
-
- Develop five-year and annual action plans.
- Complete under-construction projects pending for three or more years.
- Ensure timely completion of court complexes and residential accommodations.
- Form committees for monitoring and coordination:
- High Court Level: Three Judges, Chief Secretary, Secretaries of Finance, Public Works, and Law Departments.
- District Level: District Judges and Portfolio Judges.
- Monthly reporting and monitoring of fund utilization.
- Online progress updates by all High Courts.
Challenges for Judicial Infrastructure
- Staff Crunch: 30% of sanctioned jailed executive staff posts still lie vacant.
- Digital Literacy: Internet rural penetration is 32.34% whereas urban penetration rate is 99.12%.
- Shortage of judicial infrastructure: 32% courtrooms have separate record rooms.73% have no video-conferencing facility.
- Judicial Vacancies: According to the Supreme Court’s 2018-19 report, UP state has the highest vacancy (28%) followed by Bihar(13%).
Need for Reforms in Judicial Infrastructure
- Infrastructure and Productivity in Justice Delivery: It is a prerequisite where judicial officers shall efficiently perform their responsibilities while dispensing justice because present backlog cases are around 3.3 crore cases.
- Improve Digitisation Program of Government: Due to COVID 19 pandemic and shifting towards digitalization helps to ensure modernization of judicial infrastructure in the country
- Lack of Accountability: Most district judges who head trial courts don’t pursue development projects due to short-term appointments and transferable jobs among others.
- Under-utilisation of Funds: Some states transfer part of their funds for non-judicial purposes.
- Implementation Issue: It is still being carried out in an ad-hoc and unplanned manner owing to lack of a single dedicated agency for the purpose.

Measures to improve Judicial Infrastructure
- Increase Budgetary Allocation: Budgetary allocation to the judicial branch should be increased.
- Staff Recruitment: Recruitment of staff should be done to Improve shortage of staff in judiciary.
- Accessibility Improvements: Appropriate provisioning of availability of ramps, tactile pavements, braille notices etc.
- Decentralization of High Courts: High Courts should be decentralised and more branches should be established.
- Delegation of Administrative Functions: Administrative functions should be delegated to improve efficiency and allow judges to focus more on adjudication.
- Leveraging IT Tools: IT tools can be leveraged for video conferencing, streamlining procedures, and implementing case management systems like e-libraries of cases to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the judicial process.
Other steps taken by government to enhance judicial infrastructure
- eCourts Mission Mode Project: For establishment of districts & subordinate courts.
- Fast Track Special Courts (FSTC).
- Launching Of Gram Nyayalaya Online Portal.
- Data Governance Quality Index to assess the data preparedness.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Enhancing judicial infrastructure is one of the best gifts we can give to our nation, ensuring well-equipped courtrooms and residential facilities for judges.
- Improved infrastructure will not only increase efficiency but also promote digitization, making the justice system more accessible and effective for all.
- The ongoing efforts and reforms are essential to address current challenges and build a robust judicial framework for the future.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Subordinate Courts in India | Gram Nyayalayas & Family Courts in India |
| Finance Commission | STATES AND UNION TERRITORIES |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









