The Parliament established the Bar Council of India(BCI) as a statutory body under the Advocates Act, 1961. The regulatory function is performed by prescribing standards of professional conduct and etiquette and by exercising disciplinary jurisdiction over the bar. It sets standards for legal education and grants recognition to Universities whose degree is in law, which will serve as a qualification for enrolment as an advocate.
The Bar Council of India: Guardians of Legal Standards and Integrity
Background
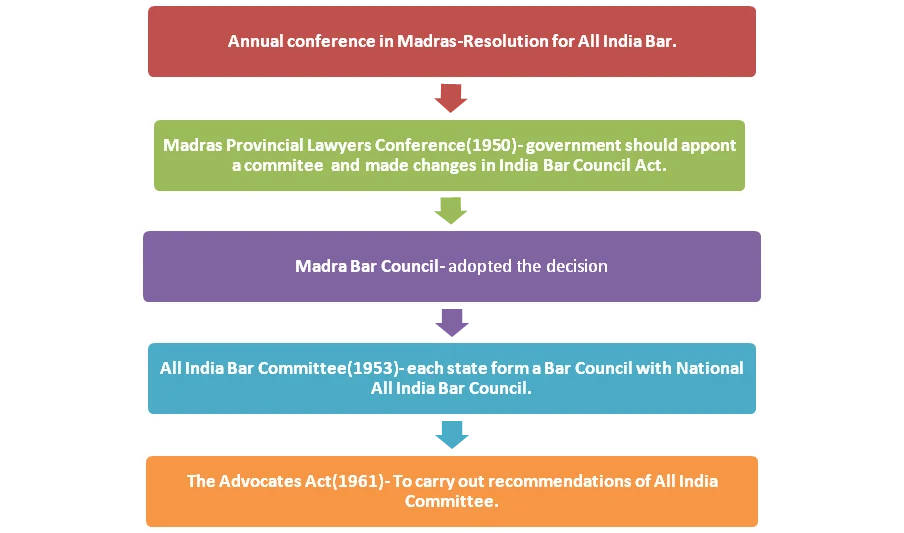
- Annual conference in Madras – The Inter-University Board issued a resolution about the necessity for an All-India Bar and to have uniform standards for legal examinations in different universities across the country.
- Madras Provincial Lawyers Conference (1950) – It was presided over by Shri S. Varadachariar, decided that the Government of India should appoint a committee to develop a strategy for an All-India Bar and made changes of earlier Indian Bar Councils Act into compliance with the new Constitution.
- Madras Bar Council- Adopted the decision during its sitting on October 1, 1950.
- All India Bar Committee(1953)-This committee issued its comprehensive report.
- It recommended that each state form a Bar Council with a national All-India Bar Council serving as the apex authority for regulating the legal profession and overseeing the quality of legal education in India.
- The Advocates Act (1961) – It was enacted to carry out the recommendations of the ‘All India Bar Committee’ and the ‘Law Commission’. At that time Chairman and Vice-chairman were M. C. Setalvad and C. K. Daphtary respectively.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Statutory Provisions
- Establishment and Purpose of the All India Bar Council: The All India Bar Council is a statutory body established by Parliament to not only regulate but also represent the Indian legal profession and it was founded in 1961 under Section 4 of the Advocates Act 1961.
- Legal Foundation and Powers of the Bar Council: Every Bar Council so constituted shall be a body corporate having perpetual succession and a common seal with power to acquire and hold property, both movable and immovable.
- Regulations: It regulates the bar by establishing norms of professional conduct and makes authority of discipline over the members.
- Concerned Ministry: The Ministry of Law and Justice is responsible for the Bar Council of India.
- Meetings of Bar Council of India: Meetings are held regularly to ensure the smooth functioning of BCI.
Composition of the Bar Council of India (BCI)
Members
- Composition: The BCI consists of 25 members which includes the elected members as well as the ex-officio members. They are as follows:
- 16 members elected by each State Bar Council from amongst its members.
- 5 members nominated by the central government.
- 4 ex-officio members, including the Attorney General of India and the Solicitor General of India.
- Leadership Structure: The BCI shall have a Chairman and a Vice-Chairman.
- They are elected by the Council from amongst its members.
- They hold office for a period of two years.
- Term of Office: The term of office of a member of the BCI, elected by a State Bar Council (SBC), shall be for the duration of their tenure as a member of that SBC.
- Eligibility: There should not be less than five elected members of each Bar Council and must have been entitled to practise in the High Court for which the Bar Council was formed for at least ten years.
Tenure of Chairperson & Members
- Tenure: The nominated and elected members of any Bar Council shall serve for three years from its first Council’s meeting.
- Absence of right to withdraw membership: No member of the Bar Council of India has the right to withdraw from membership for reasons that are not regarded genuine.
Disqualification of the Members of the BCI
An elected member of a Bar Council is disqualified:
- If he has missed three consecutive meetings of that Council without sufficient excuse,
- If his name is removed from the roll of advocates for any reason, or
- If he is otherwise disqualified under any rule made by the Bar Council of India.
Election Rules of Bar Councils
- Disputes and Notice Requirements: No election to a Bar Council member shall be called into dispute just because due notice of the date has not been given to any individual eligible to vote
- Validity of Notice Publication: If notice of the date has been published in the Official Gazette at least thirty days before that date.
Functions
-
- Establishing Standards: To lay down standards of professional conduct and etiquette for advocates.
- Procedures for Disciplinary Committees: To lay down procedure to be followed by its disciplinary committee and the disciplinary committees of each State Bar Council.
- Safeguarding Rights and Interests of Advocates: To safeguard the rights, privileges and interests of advocates.
- Promotion of Law Reform: To promote and support law reform.
- Addressing Matters Referred by State Bar Councils: To deal with and dispose of any matter which may be referred to it by a State Bar Council.
- Promotion and Regulation of Legal Education: To promote legal education and to lay down standards of legal education. This is done in consultation with the Universities in India imparting legal education and the State Bar Councils.
- Recognition of Universities for Law Degrees: To recognise Universities whose degree in law shall be a qualification for enrolment as an advocate. The Bar Council of India visits and inspects Universities, or directs the State Bar Councils to visit and inspect Universities for this purpose.
- Coduncting Seminars and Legal Publications: To conduct seminars and talks on legal topics by eminent jurists and publish journals and papers of legal interest.
- Organizing Legal Aid for the Underprivileged
- Recognition of Foreign Legal Qualifications: To recognise on a reciprocal basis, the foreign qualifications in law obtained outside India for the purpose of admission as an advocate in India.
- Management and Investment of Bar Council Funds: To manage and invest the funds of the Bar Council.
- Elections for Bar Council Membership: To provide for the election of its members who shall run the Bar Councils.
- Other functions are as:
- Giving financial assistance to organise welfare schemes for poor, disabled or other advocates,
- Giving legal aid, and
- Establishing law libraries.
Committees of BCI
- The Bar Council of India has various committees which make recommendations to the council.
- The members of these committees are elected from amongst the members of the Council.
| Executive Committee |
|
| Legal Education Committee | This committee makes recommendations to the BCI on
|
| Disciplinary Committee |
|
| Advocate Welfare Committee |
|
| Legal Aid Committee |
|
| Building Committee |
|
| Rules Committee |
|
| The Finance Committee, Special or Oversee Committee, and All India Bar Examination Committee are the other committees. |
Challenges
Despite its important role, the BCI faces several challenges, including:
- Overburdened Disciplinary System: The BCI’s disciplinary system is often overburdened with complaints, leading to delays in the resolution of cases.
- Lack of Transparency: The BCI’s decision-making process can be opaque at times, leading to concerns about accountability.
- Inadequate Resources: The BCI often lacks the resources it needs to carry out its functions effectively.
- Political Interference: The BCI has been accused of being susceptible to political interference, which can undermine its independence.
Future Directions
The BCI needs to address these challenges to ensure that it continues to play an effective role in regulating the legal profession in India. Some potential reforms include:
- Streamlining the Disciplinary Process: The BCI should streamline its disciplinary process to ensure that complaints are resolved quickly and efficiently.
- Improving Transparency: The BCI should make its decision-making process more transparent to increase public trust and confidence.
- Strengthening Resources: The BCI should be provided with the resources it needs to carry out its functions effectively.
- Ensuring Independence: The BCI should be protected from political interference to ensure that it can function independently and impartially.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
The BCI is fundamental to upholding the quality and integrity of India’s legal profession.
- By regulating conduct, advocating for legal reforms, and providing oversight, it safeguards the profession’s dignity and works towards a robust justice system.
- To remain effective, the BCI must address challenges like transparency and independence, ensuring justice and professionalism are upheld.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









