|
The Desert Ecosystem: Types, Adaptation, Biodiversity & Resilience |
Desert Ecosystem: Adapting Life to Arid Environments
The desert ecosystem is a fascinating ecosystem where life has evolved to thrive under the most stringent water conservation and temperature regulation mechanisms, making it a unique and resilient biome. Despite the challenging conditions, it is home to a remarkable array of specially adapted plant and animal species.
Desert ecosystem: A World of Unique Challenges and Adaptations
- Desert ecosystem is a biome or geographical region characterized by extremely arid conditions resulting in a scarcity of water resources.
- It has an extremely dry area of land with sparse vegetation.
- Characteristics of Desert Ecosystem:
- Unique Biodiversity: They are home to a variety of specially adapted plant and animal species that have evolved to thrive in these challenging conditions.
- Precipitation: It is a region of scanty rainfall.
- They are formed in regions with about less than 25 cm of annual rainfall.
- Coverage: Deserts cover about one-fifth of our planet.
- High Diurnal Range: Deserts are known for their high temperatures during the day and cold temperature at night.
- Sparse Vegetation: Desert environments are so dry that they support only extremely sparse vegetation and trees are usually absent.
Types of Deserts: Hot and Cold Desert Ecosystem around the World
- Hot Desert: The hot deserts of the world are formed due to the presence of dry air and low precipitation from subtropical high-pressure cells.
- Distribution: Western coasts of continents between 15 and 30 N and S (lie in the region of Horse latitudes).
- Found in tropical and subtropical regions, typically near the equator.
- Examples: Includes the Sahara Desert in Africa, the Arabian Desert in the Middle East, and the Sonoran Desert in North America.
- Abiotic components:
- Long diurnal range: Extreme diurnal range of temperature.
- Very low precipitation: Less than 25 cm of annual rainfall.
- Soil type: saline, sandy soil with low water holding capacity.
- Biotic components:
- Flora: Xerophytic or drought resistant scrub, date palms, acacia etc.
- Fauna: Diverse array of reptiles, marsupials, mammals (camels, hedgehog, hyenas).
- Cold/Mid-latitude/Temperate Desert: The large arid area of land that receives scanty annual precipitation, which occurs mainly in the form of snow or fog.
- Generally, found at higher altitudes of temperate regions.
- Distribution: Located interior of the continent, sheltered by the high mountains all around them.
- Examples: Gobi Desert of Mongolia, Ladakh in India, Patagonia etc.
- They are also found in the rain-shadow areas or the leeward side of mountain ranges.
- Examples: Himalayas, Andes and Rockies.
- Abiotic Components:
- Temperature: The annual range of temperature is much greater than that of the hot deserts.
- Continentality: it accounts for these extremes in temperature (Severe winter with cold wind).
- Biotic components:
- Flora: Alpine Mesophytic, Grasses, bushes, shrubs and even trees like junipers, birch.
- Fauna: Bactrian camel, Asiatic ibex, snow leopard, Tibetan wolf, Tibetan wild ass (kiang).
Desert Ecosystem Existence in India – Exploring the Thar, Kutch, and Ladakh Regions
- About: India has arid Thar Desert and salty Rann of Kutch in the west and the high-altitude deserts of Ladakh in the north.
- Thar Desert (Great Indian Desert): It is located in northwestern India, primarily in the state of Rajasthan.
- Characteristics: It is the largest desert in India, known for its vast stretches of arid land, sand dunes, and extreme temperatures.
- Vegetation: The Thar Desert supports some hardy desert flora and is known for its distinctive thorny bushes and drought-resistant plants.
- Kutch Desert ecosystem: The Rann of Kutch in the state of Gujarat in western India.
- Characteristics: The Kutch Desert includes a seasonal salt marsh, known for its salt flats, arid landscapes, and the famous “White Rann” during the dry season.
- Cold Desert ecosystem of Himachal Pradesh and Ladakh: High-altitude desert regions in the northern Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Ladakh region.
- Characteristics: These deserts are characterized by high-altitude barren landscapes, with limited vegetation due to extreme cold and arid conditions.
Adaptation Mechanism in Desert Ecosystem: Survival Strategies
- It is essential for the survival of plant and animal species in these harsh, arid conditions of the Desert Ecosystem.
- These adaptation mechanisms allow organisms to conserve water, tolerate extreme temperatures, and make the most of limited resources.
| Mechanism | Description |
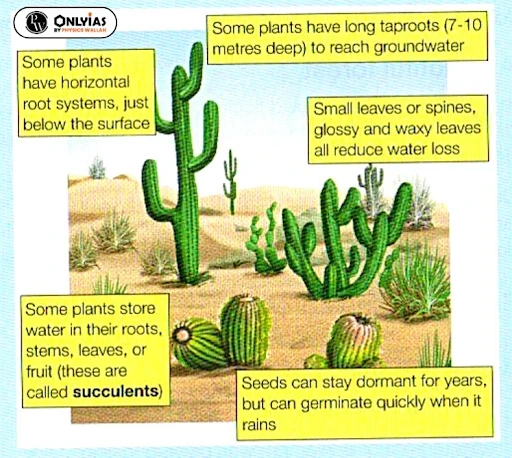
| Adaptations of Desert Vegetation |
|
| Adaptations of Desert Animals |
|
Kangaroo Rat:
About keystone species:
|
Desert Ecosystems: The Resilient World
- The desert ecosystem is a resilient biome characterized by extreme aridity and harsh environmental conditions.
- These ecosystems play a vital role in global climate regulation and contribute to our understanding of adaptation and biodiversity.
|
Previous Year Questions (Prelims) Q. Which of the following leaf modifications occur(s) in the desert areas to inhibit water loss? (2018)
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Answer (D) |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program