| Carbon Cycle: Exploration Of Processes, Forms, & Environmental Impacts |
Carbon Cycle: An interconnected process, ensuring sustainable use of resources
The carbon cycle is a complex and interconnected process that influences Earth’s climate, sustains life, and has implications for the well-being of ecosystems and human societies. In the composition of living organisms, carbon constitutes 49 per cent of dry weight of organisms and is next only to water. Thus, understanding and managing the carbon cycle is central to addressing climate change and ensuring the sustainable use of Earth’s resources.
About Carbon Cycle : Journey Through Earth’s Elemental Pulse and processes in carbon cycle
- The carbon cycle is an important biogeochemical cycle that involves the continuous movement and exchange of carbon in various forms among the atmosphere, terrestrial ecosystems, ocean and Earth’s geosphere (rock and soil).
- The carbon cycle involves the circulation of carbon in various forms, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane(CH4).
- Processes in the Carbon Cycle: The carbon cycle depicts the natural flow of the element carbon through the six main processes in the carbon cycle:
-
- Photosynthesis.
- Respiration
- Exchange
- Sedimentation
- Extraction
- Combustion.
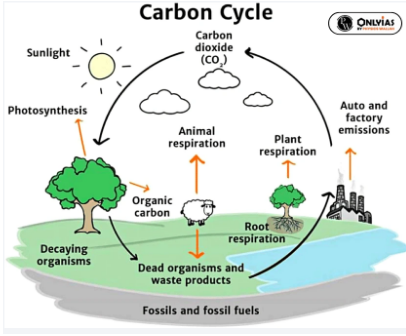
1. Photosynthesis: Carbon enters in the form of carbon dioxide into the living world by the process of photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis is the process through which solar energy is captured and utilized by primary producers like plants on Earth.
- During photosynthesis, the carbon gets converted into organic compounds i.e., glucose, which is stored within these organisms.
2. Respiration: Respiration plays a crucial role in the carbon cycle by facilitating the exchange of carbon between living organisms and the atmosphere.
- During respiration, both plants and animals release carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere as a byproduct of metabolic processes.
- This carbon dioxide is the result of breaking down organic compounds, such as glucose, to produce energy for the organism’s growth, maintenance, and reproduction.
3. Exchange: It tells us about the interaction between the water and the carbon cycle.
- CO2 and water are constantly moving through the environment and interacting with each other.
- CO2 can dissolve into oceanic water and overtime making the ocean slightly more acidic.
- This is particularly important with increasing CO2 concentrations in the air which in turn makes marine water more acidic and affects marine life negatively.
4. Sedimentation: When animals or plants die, they undergo decomposition, and their remnants transform into sediment, capturing the carbon they once contained.
- A portion of this sediment may develop into fossil fuels like coal, oil, or natural gas.
- The length of time of sedimentation determines the quality of fossil fuel.
5. Extraction: Anthropogenic activities involve the extraction of fossil fuels from the ground and burn them for energy.
The burning of fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
6. Combustion: Combustion occurs when any organic material is burned in the presence of oxygen to give off the products of carbon dioxide like heat, light etc.
- The converts fossil fuels or plant matter into CO2 and ash by combustion releases carbon back into the atmosphere.
Carbon Cycle: Major Forms of Carbon
Different forms of carbon interact with the environment and contribute to climate change and ecosystem health. These different forms are-
| Forms | Description |
| Blue carbon |
|
| Black carbon |
|
| Brown carbon |
|
| Green carbon |
|
Importance of Carbon Cycle: Nurturing Earth’s Vital Equilibrium for Climate, Life, and Sustainability
- Climate Mitigation: The carbon cycle helps regulate the Earth’s climate by controlling the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere.
- Strategies like reforestation, afforestation, and carbon sequestration aim to enhance carbon sinks and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Essential for life: Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere during photosynthesis to produce glucose which essentially become fodder for the food chain.
- This process not only reduces atmospheric CO2 but also produces oxygen which is essential for life on Earth.
- Carbon Storage: The carbon cycle encompasses long-term carbon storage in various forms, such as fossil fuels, peat, and organic matter in soils.
- Soil Health: Organic matter in soils serves as a carbon sink, storing carbon and enhancing soil fertility.
- A healthy carbon cycle supports productive agriculture and sustainable land management.
- Carbon Sink: The world’s oceans act as a significant carbon sink, absorbing and storing vast amounts of CO2.
- This helps mitigate the rise in atmospheric CO2 levels and ocean acidification.
- Energy Source: Fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) are the result of ancient carbon-rich organic material undergoing geological processes.
- These fuels have been a primary source of energy for human societies, highlighting the economic and technological significance of the carbon cycle.
- Ecosystem Services: Ecosystems rely on stable carbon cycling to support plant growth, provide habitat and food for animals, and regulate local and regional climates.
- Sustainability: Understanding and effectively managing the carbon cycle is fundamental to sustainable development.
- It ensures that we can meet our energy and resource needs without compromising the health of the planet and future generations.
Carbon Cycle: Conclusion
- The carbon cycle is a vital natural process that influences our climate, sustains ecosystems, supports life, and has direct implications for human well-being.
- Recognizing its importance is critical for making informed decisions related to environmental conservation, climate change mitigation, and the sustainable use of resources.
|
Previous Year Question (Prelims) Q. Which of the following adds/adds carbon dioxide to the carbon cycle on the planet Earth? (2014)
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Answer (c) |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









