Following the Battle of Buxar, Robert Clive introduced a dual governance system in Bengal, dividing authority between the East India Company and the Nawab. This arrangement granted the Company control over revenue and law enforcement, while the Nawab retained only a symbolic role. Although intended to balance power, the system led to significant administrative and social issues, necessitating reform by 1772.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Dual Government in Bengal (1765–72)
Post the Buxar battle, the East India Company emerged as the dominant power in Bengal. Robert Clive established a two-tiered governance structure in Bengal, which saw both the Company and the Nawab holding power.
- Allocation of Diwani and Nizamat Powers to the East India Company: This meant that the Company had authority over both revenue collection (diwani) and law enforcement and judiciary (Nizamat).
- As the revenue officer (diwan), the Company wielded the diwani rights, and through its power to appoint the deputy governor, it exercised the nizamat rights.
- These functions were granted to the Company by the emperor for diwani and by Bengal’s governor for nizamat.
| eforms of Robert Clive
Civil Reforms Issues:
Clive’s Measures:
Military Reforms
Opposition:
|
- Profited Company: This governance model was hugely beneficial for the Company.
- It allowed the nominal Indian leader to seem authoritative, while actual control rested with the Company.
- Even though the Nawab was tasked with ensuring peace, he heavily relied on the Company for financial and military resources, given the Company’s hold over the treasury and armed forces.
- In terms of executing the Diwani duties, the Company designated two deputy revenue officers: Mohammad Reza Khan for Bengal and Raja Sitab Roy for Bihar. Moreover, Mohammad Reza Khan also served as the deputy governor.
However, this dual governance system resulted in administrative chaos, causing significant hardship for Bengal’s residents. Both the Company and the Nawab neglected governance and public well-being. By 1772, Warren Hastings abolished this flawed system.
Clive’s Justification of the Dual System
Clive was fully conscious of the fact that all power had passed into the hands of the Company and nothing was left to the Nawab except the name and shadow of authority. “This name”, wrote Clive to the Select Committee. “this shadow, it is indispensable we should seem to venerate”. Clive gave his reasons for the new setup:
- Preserving the Name and Shadow of Authority: Clive acknowledged that the Company had taken full control of Bengal, leaving the Nawab with only a symbolic position.
- He argued that maintaining the appearance of veneration for the Nawab was crucial. This approach served several purposes:
- Preventing Unification of Indian Princes: Clive believed that openly assuming authority would risk uniting Indian princes against the Company, potentially leading to conflict. By keeping the Nawab as a figurehead, they could avoid such opposition.
- Foreign Competitors and Imperial Grants: Clive recognized that other European powers (French, Dutch, and Danes) might not readily acknowledge the Company’s authority and pay trade duties or quit rents.
- Additionally, these powers held territories based on Imperial firmans or grants from former Nawabs, which could complicate the situation.
- Diplomatic Complications: Openly assuming political power could complicate England’s diplomatic relations with other European powers like France, Holland, Portugal, and Sweden.
- It might lead these nations to form an anti-British coalition, similar to events during the American War of Independence.
- Lack of Administrative Personnel: Clive pointed out that the Company lacked the trained personnel to effectively administer the newly acquired territories.
- Existing civil servants were insufficient in number and were unfamiliar with Indian practices, languages, and customs.
- The Company’s Commercial Interests: The Court of Directors of the British East India Company prioritized commerce and profits over territorial acquisitions.
- They opposed the acquisition of territories, fearing it might interfere with their trade and financial interests.
- Avoiding Parliamentary Interference: Clive was aware that openly assuming political power in Bengal might prompt the British Parliament to interfere in the affairs of the Company.
- To maintain autonomy and avoid such intervention, Clive believed that the Dual System was a necessary strategy.
Negative Consequences of the Dual System
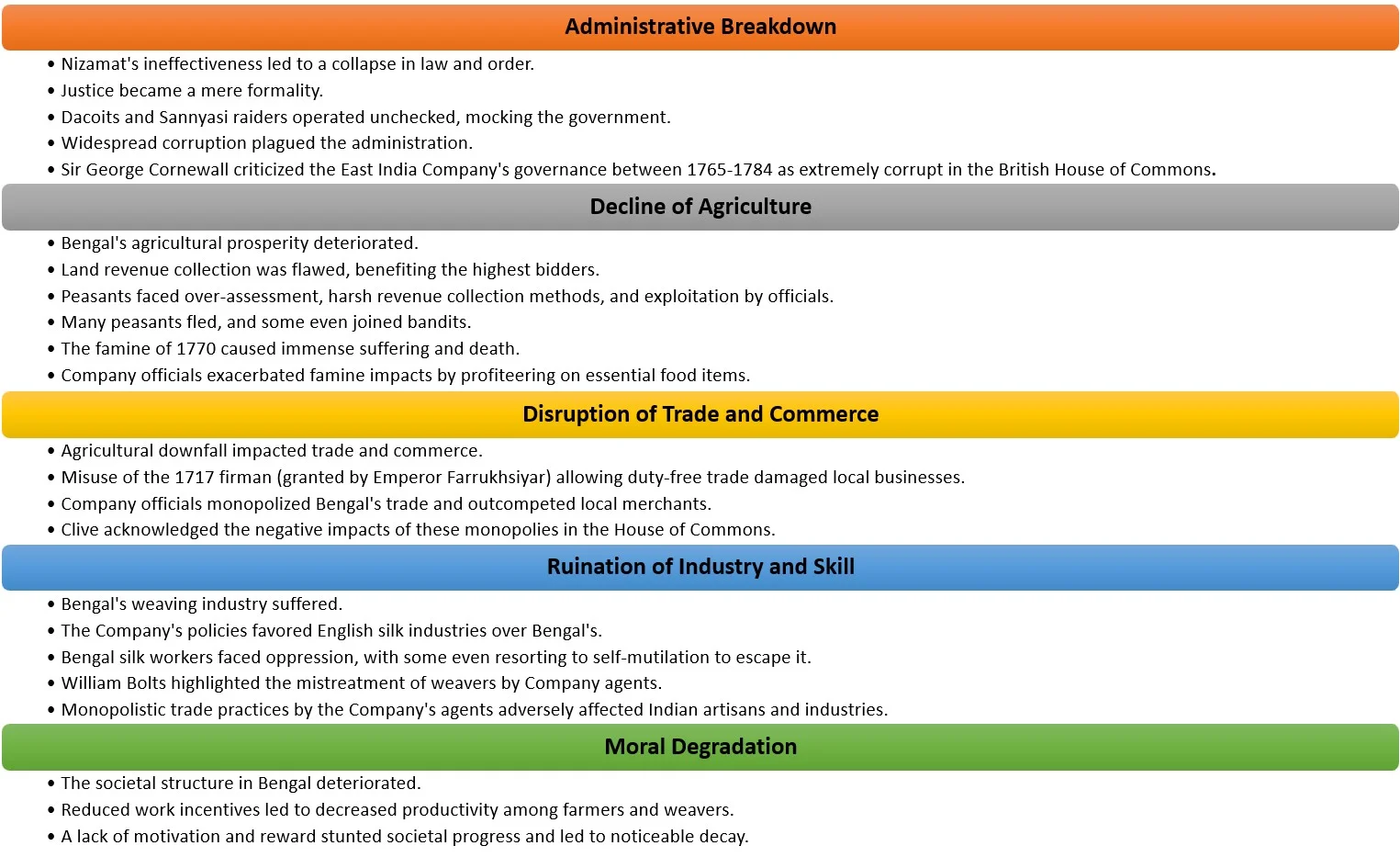
Administrative Breakdown and Lawlessness: A breakdown in administration occurred because the Nawab had no power to enforce laws and deliver justice, while the British East India Company disclaimed all responsibility. In the rural areas, bandits operated freely, and the Sannyasi raiders made a mockery of the government.
- Agricultural Decline and Peasant Hardships: Agriculture suffered a decline as peasants were burdened with excessive taxes and faced harsh treatment from government officials.
- Trade Disruptions: Trade and commerce were disrupted because the Company’s employees monopolized the internal trade of Bengal, undercutting local Indian merchants in the markets.
- The decline of industry and craftsmanship was evident.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Moral decay infiltrated Bengali society as there was little incentive to work when most profits were taken by the Company’s officials, leaving only the bare minimum for the people. The society stagnated and displayed clear signs of decay.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
The dual governance system established by Robert Clive in Bengal, while strategically beneficial for the East India Company, ultimately led to severe administrative inefficiency and social decline. The system maintained the Nawab’s nominal authority but left the real power and control in the Company’s hands, causing widespread hardship. By 1772, the system’s failure became evident, prompting Warren Hastings to abolish it. This period marked a critical juncture, highlighting the need for more effective and humane governance.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Bengal’s Dual System | European Union (EU) |
| From Trade to Territory: The East India Company’s Rise in India | The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act (AFSPA) 1958 |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program










