The concept of dual citizenship allows individuals to hold citizenship in more than one country, enjoying the benefits and responsibilities in each. India, which initially did not offer special provisions for its diaspora, introduced the Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) scheme in 2005. This program provides certain rights to individuals of Indian origin while maintaining a clear distinction from full Indian citizenship.
Understanding Dual Citizenship and Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI)
Concept of Dual Citizenship
- Dual Citizenship Overview: Citizenship can be acquired in various ways, and it is possible for someone to be recognized as a citizen of two or more countries simultaneously, a situation known as dual citizenship.
- Rights of Dual Citizens: Dual citizens typically hold two passports and enjoy the freedom to live, work, and travel in both their home country and the country they’ve become a citizen of.
- Example: South Korea and the United States allow their citizenships to coexist.
- Initial Indian Policy on Diaspora: Initially, India also did not grant any special rights to people of Indian origin living in other countries.
- High-Level Committee on Indian Diaspora: However, the government established a High-Level committee on Indian Diaspora, led by L.M. Singhvi, to conduct a comprehensive study of the global Indian Diaspora and suggest ways to foster a positive relationship with them.
- Introduction of New Citizenship Statuses: Based on these recommendations, the Indian Parliament amended the Citizenship Act in 2002 and introduced two distinct statuses:
- Person of Indian Origin Card (PIO) Scheme: This scheme is for individuals who, or their ancestors, were Indian nationals and currently hold the citizenship or nationality of another country, meaning they possess a foreign passport.
- Overseas Citizenship of India: This status is designed for those PIOs who have moved from India, acquired foreign citizenship (except from Pakistan and Bangladesh), and are eligible for specific benefits, “as long as their home countries allow dual citizenship in some form according to their local laws.”
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder
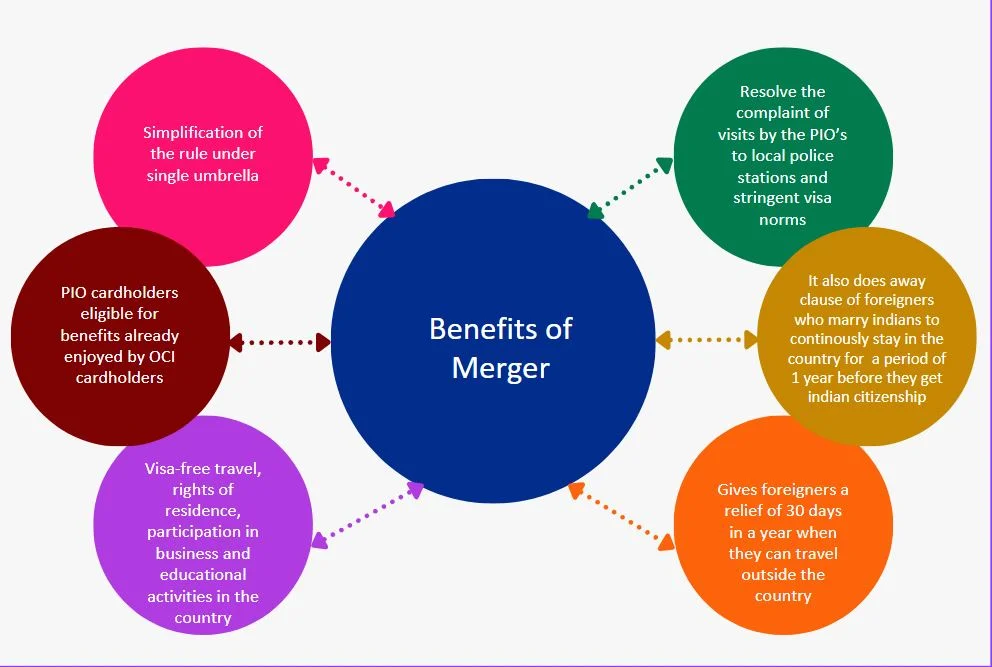
Introduction of Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder: The Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2015, brought about significant changes to the provisions related to the Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) status as outlined in the Principal Act.
- This act introduced a new category known as the “Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder,” consolidating both the Persons of Indian Origin (PIO) card scheme and the OCI card scheme.
- Consolidation of PIO and OCI Schemes: The PIO card scheme was initially introduced on August 19, 2002, followed by the introduction of the OCI card scheme on December 2, 2005.
- These two schemes were in operation concurrently, even though the OCI card scheme had gained more popularity. This situation led to confusion among applicants.
- To address these issues and provide improved services to applicants, the Government of India decided to create a single scheme that merged the positive aspects of both the PIO and OCI schemes.
- To achieve this goal, the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2015, was enacted.
- Transition from PIO to OCI Status: As part of this act, the PIO scheme was rescinded effective January 9, 2015, and it was also declared that all existing PIO card holders would be considered OCI cardholders from the same date.
- Changes in Terminology and Provisions: Moreover, the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2015, replaced the terminology “Overseas Citizen of India” with “Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder” and introduced various provisions within the Principal Act to accommodate these changes.
Registration of Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder
Eligibility: The Central Government has the authority to grant status of Overseas Citizen of India Card to any person of full age and capacity who falls under one of the following categories upon application:

- A citizen of another country who was a citizen of India at the time of, or at any time after, the commencement of the Constitution.
- A citizen of another country who was eligible to become a citizen of India at the time of the commencement of the Constitution.
- A citizen of another country who belonged to a territory that became part of India after August 15, 1947.
- A child, grandchild, or great-grandchild of such an individual or
- Any person who is a minor child of a person mentioned in clause.
- Any person who is a minor child and has both parents as citizens of India, or at least one parent who is a citizen of India.
- The foreign-origin spouse of a citizen of India or the foreign-origin spouse of an Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder, provided that their marriage has been registered and has lasted for a continuous period of not less than two years immediately preceding the application.
- Exclusions from Overseas Citizen of India Card: No person, or any of their parents, grandparents, or great-grandparents, who is or has been a citizen of Pakistan, Bangladesh, or any other country specified by the Central Government, is eligible for registration as an Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder.
- Effective Date for Existing PIO Cardholders: The Central Government has the authority to determine the date from which existing Persons of Indian Origin cardholders will be considered overseas citizens of India cardholders.
- Exceptional Registration Circumstances: In exceptional circumstances, the Central Government, if satisfied, may register a person as an Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder after recording the circumstances in writing.
- Rights Given to Overseas Citizen of India cardholders: An overseas citizen of India (OCI) cardholder is entitled to certain rights specified by the Central Government. Some of these rights are listed in table below:
- Rights Not Conferred to OCI Cardholders: However, an OCI cardholder is not entitled to the following rights, which are conferred on a citizen of India as shown in below table.
| As on 31st January, 2022 40.68 lakh OCI registration cards were issued. |
| Rights Conferred to OCI Cardholders | Rights Not Conferred to OCI Cardholders |
|
|
Renunciation of Overseas Citizen of India Card
Process of Renunciation: If an Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder submits a declaration in the prescribed manner, the Central Government registers this declaration.
- Upon registration, the individual no longer holds the status of an overseas citizen of India cardholder.
- Impact on Family Members: When a person ceases to be an Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder, their spouse of foreign origin, who possesses an overseas citizen of India card, and every minor child registered as an overseas citizen of India cardholder, will also lose their overseas citizen of India cardholder status.
Cancellation of Registration as Overseas Citizen of India Cardholder
Grounds for Revocation: The registration of an individual as an overseas citizen of India cardholder can be revoked by the Central Government under certain circumstances, as follows:
- Fraudulent or Misrepresented Registration: If the registration as an overseas citizen of India cardholder was obtained through fraud, false representation, or the concealment of any material fact.
- Disaffection Towards the Constitution: If the overseas citizen of India cardholder has demonstrated disaffection towards the Constitution of India.
- Unlawful Trade or Communication: If the overseas citizen of India cardholder has, during any war in which India may be engaged, unlawfully traded or communicated with an enemy.
- Imprisonment for a Significant Term: If the overseas citizen of India cardholder has, within five years after registration, been sentenced to imprisonment for a term of not less than two years.
- National Interest and Security: If it is deemed necessary to do so in the interests of the sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of India, friendly relations of India with any foreign country, or in the interests of the general public.
- Dissolution of Marriage: If the marriage of an overseas citizen of India cardholder:
- Has been dissolved by a competent court of law or otherwise.
- Has not been dissolved, but during the subsistence of such marriage, he has solemnized marriage with any other person.
| A Non-Resident Indian (NRI) is an individual with Indian citizenship who typically resides outside of India while holding an Indian Passport. NRIs enjoy all the benefits that are available to Indian citizens, but these privileges are subject to notifications issued by the Government as per the current regulations. One notable advantage for NRIs is that they do not require a visa to visit India and can engage in various activities within the country. |
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
The OCI scheme offers a range of benefits, including lifelong visas and parity with Non-Resident Indians in various sectors. However, it does not grant full Indian citizenship rights or privileges.
- The scheme aims to strengthen ties with the global Indian community while ensuring that the unique status of Indian citizenship remains distinct.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Electronically-Transmitted Postal Ballots for Non-Resident Indians | CAA 2024 Rules: Citizenship Amendment Rules |
| Features of Indian Constitution | CITIZENSHIP |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









