|
Ecosystem Dynamics: Characteristic, Types Of Food Webs & Species Interactions |
With this article, we are, Discovering how animals help, hurt, or live side by side in nature’s neighbourhood, how food webs are connecting all living things in the great web of life.
Food Web: Species Interactions and Energy Flow
The concept of a food web serves as a valuable tool for visualizing the feeding connections among species in a community. It helps uncover species interactions and community organization while shedding light on how energy flows within an ecosystem.
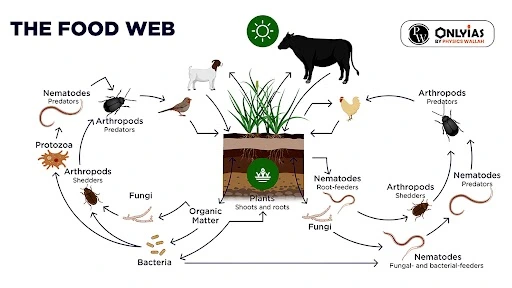
Food Webs: How Animals Eat and Share Energy
The word ‘web’ means network. A food web encompasses all the interconnected food chains within a single ecosystem.
- Multiple Routes: Every organism within the ecosystem plays a role in multiple food chains, and each food chain represents a potential route for the flow of energy and nutrients through the ecosystem.
- Interlinkages: The intricate network of overlapping and interrelated food chains collectively forms the ecosystem’s food web.
Characteristics Of Food Web: Key Traits And Survival Strategies
- Resource Overlap:
- The same food resource may be a part of more than one chain when the resource is at the lower trophic level.
- Thus all the food chains in one ecosystem are combined to form a food web.
- Interconnectedness:
- The subsequent links in the chain will be significantly impacted if any of the intermediate food chains are destroyed.
- Alternatives:
-
- The food web provides more than one alternative for food to most of the organisms in an ecosystem and thus increases their chance of survival.
Food Web: Interaction Among Biotic Factors
- An ecosystem’s biological community is an intricate web of interconnections.
-
- Interspecific interaction is the word used to describe interactions among members of various species within a community.
- While intraspecific interaction refers to interactions among members of the same species.
- Symbols: (+) benefitted; (-) harmed; (0) neither benefited or harmed.
- Ecological Interactions: It refers to the ways in which organisms in an ecosystem interact with each other. There are several types of ecological interactions include:
| Types of interactions | Species 1 | Species 2 |
| Positive Interactions | ||
| Commensalism | + | 0 |
| Mutualism | + | + |
| Proto-cooperation | + | + |
| Negative Interactions | ||
| Competition | _ | _ |
| Amensalism | _ | 0 |
| Predation | + | _ |
| Parasitism | _ | + |
| Neutralitic Interaction | ||
| Neutralism | 0 | 0 |
Promoting Harmony: Positive Species Interactions in Ecosystems
- Commensalism: Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction in which individuals from one species profit while individuals from the other species suffer neither advantages nor damage.
- Example: The sucker fish attached with sharks, The relationship between trees and epiphytic plants.
- Mutualism: Interaction favorable to both and obligatory.
- Example: Coral and zooxanthellae, Sea anemones attach to hermit crabs.
- Proto-cooperation: Interaction favorable to both but not obligatory.
- Example: Soil bacteria or fungi and plants.
Survival Struggles: Negative Species Interactions in Nature
- Competition: Direct inhibition of each species by the other.
- Competition is the battle between two organisms for the same resources within an ecosystem.
- Adversely affects both species.
- Example: Plants in a garden may compete with each other for soil nutrients, water, and light.
- Amensalism: Amensalism refers to an ecological interaction between two different species, occurring when one species’ organisms are destroyed or inhibited while the other is unaffected.
- Example: The fungi Penicillium produces penicillin, an antibiotic substance that hinders the growth of a variety of bacteria.
- A large tree provides shade for a little plant, slowing its growth.
- The small plant has no effect on the large tree.
- Predation: Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey.
- Predators help in maintaining species diversity in a community, by reducing the intensity of competition among competing prey species.
- Example: To chase and kill their prey, predators like tigers, cheetahs, and leopards employ speed, teeth, and claws.
- Parasitism: A symbiotic connection between species is parasitism, in which one creature, the parasite, lives on another, the host, harming it in some manner and becoming structurally adapted to this mode of life.
- Many parasites have evolved to be host-specific, meaning they can only parasitize one kind of host.
- As a result, the host and the parasite typically co-evolve.
- Example: Tapeworm, roundworm, malarial parasite, many bacteria, fungi, and viruses are common parasites of humans.
- Even though the female mosquito requires our blood for reproduction, she is not regarded as a parasite because it doesn’t live on the host.
Harmonious Coexistence: Neutral Species Interactions in Nature’s Neighborhood
Two species which do interact but do not affect each other.
- True neutralism is extremely unlikely and impossible to prove.
- When dealing with the complex networks of interactions presented by ecosystems, one cannot assert positively that there is absolutely no competition between or benefit to either species.
- Given the rarity or absence of true neutralism, its usage is often extended to situations where interactions are only minimal or negligible.
- Example: Rabbits and deers live together.
The Significance of Food Webs: Conclusion
- Food webs underscore the delicate balance that exists in nature, where every species, no matter how small or inconspicuous, plays a vital role.
- Food webs emerge as the threads that bind all living organisms together.
|
Previous Year Question (Prelims) Q. Which of the following have species that can establish a symbiotic relationship with other organisms? (2021)
Select the correct answer using the code given below
Answer (D) Q. Due to some reasons, if there is a huge fall in the population of species of butterflies, what could be its likely consequences/consequences? (2017)
Select the correct using the code given below:
Answer (C) |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program