The governance of Union Territories (UTs) in India presents unique constitutional and legal challenges due to their special status. Issues such as the composition of legislatures, the role of nominated members, and the power of administrators create complexities. These challenges impact democratic representation and federal cooperation, especially in places like Puducherry and Delhi.
Issues Related to Union Territories
Challenges in the Governance of Union Territories: The governance structure of Union Territories (UTs) in India presents several constitutional and legal challenges that highlight their inherent fragility within the Indian Federation:
- Legislature Composition: The 14th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1962 included Article 239A, which gives Parliament the authority to create legislatures for UTs.
- But this has led to a situation where a simple amendment to The Government of Union Territories Act, 1963 can create a legislature that is largely made up of members who have been nominated—more than half of the total.
- Issue of Nomination: According to the Government of Union Territories Act, Puducherry will have a 33-member House, of which the Central government will nominate three members.
- Legal Challenge: A legal challenge arose when the Union authority nominated representatives to the Assembly without first contacting the local authority.
- K. Lakshminarayanan v. Union of India: The Supreme Court of India decided in 2019 that nominated members had the same voting rights as elected members and that the State government’s consultation was not necessary for nominations.
- This problem draws attention to a possible lack of accountability and openness in the nomination process.
- Arbitrariness in Nomination: Article 239A and the Government of Union Territories Act do not specify any criteria for the Puducherry Assembly, in contrast to the Rajya Sabha, where such requirements are mandated.
- The democratic ideals of representation and knowledge may be compromised by this omission, which encourages arbitrary selection of UT legislative members
- Administrator’s Power: Union Territories lack the independence and democratic system required for self-governance. Significant power is vested in the administrator (Lieutenant Governor), who frequently clashes with the legislators of UTs that are elected to government.
- The administrator may disagree and send issues to the President, who makes decisions in accordance with the advice of the Union government.
- This structure essentially gives the Union government the authority to decide on contentious matters.
- Federal cooperation has been impacted by such tensions, which have been noted in areas such as Puducherry and the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
- Overlapping Jurisdictions: A Legislative Assembly for Puducherry is established by the Government of Union Territories Act, 1963, along with a Council of Ministers.
- The council’s recommendations do not, however, bind the administrator.
- Conflicts and overlapping responsibilities arise between the Union government and the Union Territory’s elected government as a result.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Ignite your Mind:
We often hear the advantages of having smaller states; administrative convenience being the prominent one. What do you think of the notion that smaller states’ performance is better as compared to bigger states. Based on your analysis, prepare a list of factors that should be considered to look at the demand of new states. |
Delhi Statehood Issue
- Background: The Delhi State Legislative Assembly having a Chief Minister came into being in 1952 under the Government of Part-C States Act, 1951. (Chief Commissioners Province) .
- The States Reorganisation Act, 1957, conferred UT status on Delhi, to be administered by an Administrator appointed by the President.
- Limited representative government was provided by the Delhi Administration Act, of 1966. 69th Amendment added Article 239AA & Article 239AB which gave constitutional status and the National Capital Territory of Delhi (GNCT) Act, 1991 was enacted based on recommendations of the Balakrishnan Committee Report.
- The Election Commission under Article 324 conducts elections to the Legislative Assembly of Delhi.
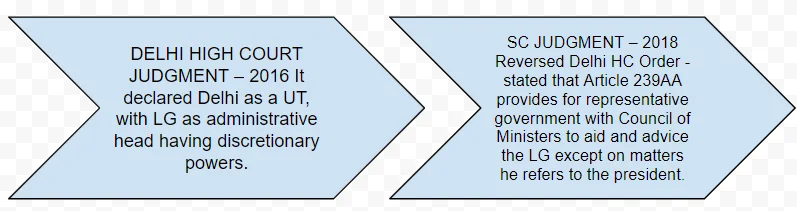
The Government NCT of Delhi Amendment Act (2021)
- Definition of “Government” Under the Act: Under this act, the term “Government” referred to in any law made by the Legislative Assembly will imply Lieutenant Governor of Delhi.
- Consistency with Lok Sabha Procedures: Rules regulating procedure and conduct of business in Delhi Assembly to be consistent with Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha.
- Prohibition on Assembly Rules: The Act Prohibits Delhi Assembly from making any rule to enable itself or its committees to:
- Consider matters of the day-to-day administration of NCT of Delhi
- Conduct any inquiry in relation to administrative decisions.
- Requirement for Lieutenant Governor’s Opinion: The Amendment adds that on certain matters, as specified by the Lieutenant Governor, his opinion must be obtained before taking any executive action on the decisions of the Minister/ Council of Ministers
Future Direction

- Acknowledging the Rationale for Legislatures in UTs: It is imperative for the Union government to acknowledge the fundamental rationale behind providing legislatures and Councils of Ministers to select UTs, primarily to honor the democratic aspirations of their residents.

- Upholding Distinct Identities of UTs: While UTs operate under central administration, they maintain their distinct identities, as underscored by the Supreme Court.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
-
- Respecting this principle is crucial to uphold the democratic values and rights of the people in these territories.
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Addressing the governance issues of UTs requires a balance between central control and local representation.
- Ensuring accountability and clarity in the nomination process, as well as respecting the democratic aspirations of UT residents, is crucial.
- This approach will help uphold democratic values while managing the unique needs of Union Territories.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Membership in State Legislatures | Major Constitutional Amendments: Evolution of India’s Constitution |
| Union Territories | Leader of Opposition in Lok Sabha |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









