| Grassland Ecosystems: Biodiversity, Conservation, And Economic Significance |
In this article, we are Exploring the world of Grassland Ecosystems and will be Learning about their rich biodiversity, conservation efforts, and economic significance and Uncovering the vital role these ecosystems play in our environment and economy.
Grassland Ecosystem: Nature’s Open Fields
A grassland ecosystem is a biome characterized by vast expanses of grasses, herbs, and occasionally some scattered trees or shrubs. Grasslands are found on every continent except Antarctica and can vary significantly in terms of climate, geography, and species composition.
What is Grass?
- Grass refers to a wide variety of green, ground-covering non woody plants that are short in stature.
- These plants belong to the plant family known as Poaceae.
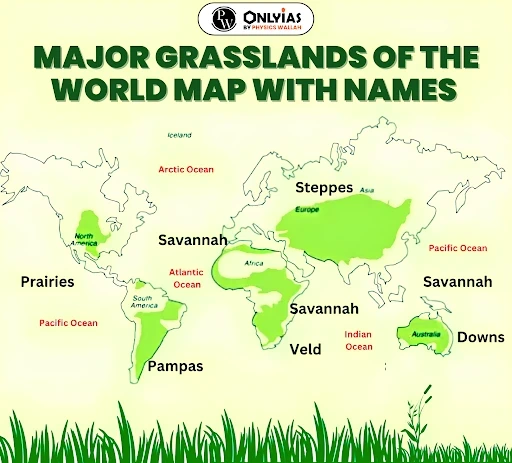
Grassland Ecosystem: Revealing the Grasslands and their characteristics and types
- These are lands which generally have open and continuous and fairly flat areas of grasses.
- They are often located between temperate forests at high latitudes and deserts at subtropical latitudes.
Grassland Ecosystem: Characteristics and Types
- The wide area that is predominantly covered with grasses or non-woody plants is known as a grassland ecosystem.
- Characteristics of the Grassland Ecosystem:
- Short stature: The height of grass is closely linked to the precipitation it receives.
- Precipitation: The grasslands grow when annual rainfall ranges from 25 to 75 cm, which is more than a true desert but not enough to maintain a forest.
- Space cover: It makes about 20 to 40% of the world’s land surface.
- Types of Grassland Ecosystem: There are primarily two categories of grasslands: tropical and temperate
- Tropical grasslands (Savanna): Tropical grassland is a type of terrestrial biome characterized by a combination of grasses and scattered trees or shrubs.
- These Grassland ecosystems are found in tropical regions with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- Temperate grasslands (Steppes): Temperate grasslands are terrestrial ecosystems characterized by vast expanses of grasses with minimal tree cover.
- These grassland ecosystems are typically found in regions with temperate climates that experience distinct seasons, including hot summers and cold winters, present.
- Tropical grasslands (Savanna): Tropical grassland is a type of terrestrial biome characterized by a combination of grasses and scattered trees or shrubs.
Grassland Ecosystem: Comparison Between Tropical (Savannas) and Temperate (steppes)
| Grassland | Description |
| Savanna/ Tropical Grassland: “Big Game Country” |
|
| Steppe/ Temperate Grassland: “Granaries of The World” |
|
India’s Diverse Grassland Ecosystem : Exploring Nature’s wealth
- Deccan Plateau Grasslands: Found in central and southern India, primarily covering parts of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- Characteristics: These grasslands are often referred to as the “Mysore Plateau” or “Deccan Plateau” grasslands.
- They have a mix of short and tall grasses and support diverse flora and fauna.
- Biodiversity: These grasslands are home to various species, including the Indian wolf, Indian fox, and a variety of bird species.
- Western Ghats Grasslands (Shola Grasslands): Found in the Western Ghats mountain range in states like Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Characteristics: These grasslands are interspersed within the shola forests and are known for their unique high-altitude ecosystems.
- Biodiversity: They host a wide range of endemic plant species and provide habitat for species like the Nilgiri tahr, an endangered mountain goat.
- Punjab Plains (Northwestern Plains) Grasslands: Includes parts of Punjab, Haryana, and western Uttar Pradesh.
- Characteristics: These grasslands are part of the Indo-Gangetic plain and are often used for agricultural purposes, primarily for wheat and rice cultivation.
- Agricultural Importance: The fertile soils of this region make it one of the most important agricultural areas in India.
- Eastern Himalayan Grasslands: Primarily in the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, and Bhutan.
- Characteristics: These grasslands are found at high altitudes and are crucial for local biodiversity and the livelihoods of indigenous communities.
- Biodiversity: They provide habitat for several endangered species, including the red panda and the snow leopard.
- Banni Grasslands: In the Kutch district of Gujarat, in the Rann of Kutch region.
- Characteristics: These grasslands are seasonally flooded and provide grazing grounds for livestock. They are also known for their distinct landscape and wildlife.
- Biodiversity: The Banni grasslands support a range of bird species, including migratory birds.
Grassland Ecosystem Resilience: Factors and Dynamics
- Three factors that contribute to the preservation of grassland ecosystems are limited rainfall, natural wildfires, and grazing by animals.
-
- Limited Precipitation: The relatively low levels of precipitation are sufficient to support the growth of grasses but insufficient to sustain a full-fledged forest of trees.
- Wildfires: Frequent wildfires are also instrumental in maintaining the integrity of grassland ecosystems.
- When circumstances are moist, fire favors grass over trees.
- When conditions are dry, fire is sometimes required to protect grasslands against the invasion of desert shrubs.
- Grasses have evolved to recover and regrow quickly after a fire.
- Additionally, animals inhabiting grasslands have adapted to deal with fires by either escaping or seeking refuge underground until the flames subside.
- Animals Grazing: The quality of grasslands rapidly degrades under severe grazing pressure.
- Soil’s mulch cover shrinks,
- Microclimate gets drier.
- Xerophytic plants and burrowing animals enter the area.
- Larger animals, such as African elephants, can also help prevent tree growth by trampling the ground.
Grassland Ecosystem: Economic and Ecological Significance
- Agricultural Productivity: Grasslands are used for growing crops such as wheat, barley, oats, and forage crops.
- Livestock Grazing: Grasslands support cattle ranching, sheep farming, and dairy operations, thus providing dairy products, and other livestock-related products.
- Trade: Grasslands play a vital role in food production and the livestock industry, contributing to domestic consumption and international trade.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Maintaining grasslands preserves native plant and animal species, and their ecological services.
- Wildlife Tourism: Grasslands attract tourists interested in safaris, birdwatching, and other wildlife-oriented experiences, generating revenue for local economies.
- Carbon Sequestration and Climate Mitigation: Grasslands sequester carbon dioxide, making them important in carbon offset markets and climate change mitigation.
- Soil Fertility and Nutrient Cycling: Grasslands help maintain soil structure and fertility, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and supporting sustainable agriculture.
- Biomass Production: Grasslands offer potential for biomass crops, contributing to biofuel production. Grasslands can host wind and solar energy projects thus supporting the renewable energy sector.
- Research and Development: Grasslands are valuable subjects of ecological and environmental research, advancing scientific knowledge.
Grassland Ecosystem: Essential for Environment, Economy, and Society
- Grassland ecosystems are incredibly valuable with a wide-ranging impact on our planet’s environment, economy, and society.
- From supporting agriculture and livestock industries to conserving biodiversity, grasslands are essential to our well-being.
|
Previous Year Questions (Prelims) Q. The vegetation of savannah consists of grassland with scattered small trees, but extensive areas have no trees. The forest development in such areas is generally kept in check by one or more or a combination of some conditions. Which of the following are such conditions? (2021)
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
Answer (c) |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program