Heat Budget of Earth: Complex Dynamics of Our Planet’s Climate and Weather
The Earth, like a giant thermal engine, maintains a delicate equilibrium of heat and energy. This intricate interplay, known as the Earth’s “Heat Budget,” is a captivating system that governs our planet’s climate, weather patterns, and the distribution of heat across the globe. Understanding the Heat Budget is essential to understand the planet’s thermostat, unravelling the complex web of energy exchanges that determine our environmental conditions.
Balancing Earth’s Energy: Exploring the Heat Budget
Global Radiation: Understanding the Vital Role of Solar Energy in Earth’s Heat Budget and Climate Dynamics
- Definition: Global radiation, the radiant energy incident on Earth, is a critical component of the heat budget.
- It encompasses direct shortwave solar radiation from the Sun and diffuse radiation scattered by the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Energy Conversion: This solar energy, once it reaches the Earth’s surface, is transmuted into heat energy, thereby elevating the temperature of our planet and instigating the emission of longwave terrestrial radiation.
- Heat Balance: A heat balance exists between the incoming solar radiation received by the Earth’s surface and atmosphere in short wave radiation .
- The heat that escapes through outgoing terrestrial longwave radiation and atmospheric heat loss.
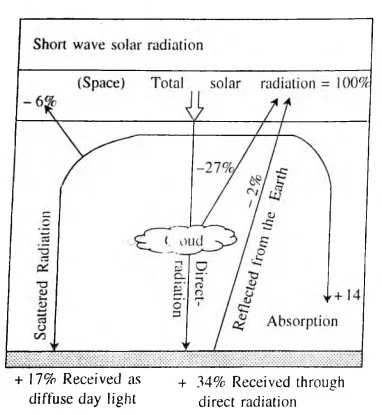
Incoming Shortwave Solar Radiation: Impact on Energy Distribution and Atmospheric Absorption
- Primary Energy Source: The Earth predominantly receives energy from the Sun, primarily in the form of shortwave solar radiation.
- This solar influx is radiated toward the Earth’s surface, where it serves as the powerhouse for a multitude of physical processes.
- Energy Distribution: Among the total incoming solar radiation penetrating the Earth’s atmosphere, 35 percent is reflected back into space through a variety of mechanisms.
- The Earth’s surface receives 51 percent of this energy, which is then distributed into direct solar radiation (34 percent) and diffused daylight (17 percent) .
- The remaining 14 percent are absorbed by the atmosphere.
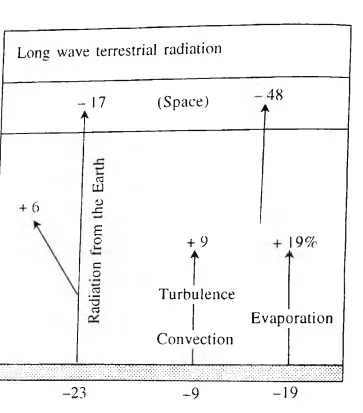
Understanding Earth’s Longwave Terrestrial Radiation: Energy Budget, Losses, and Atmospheric Dynamics
- Energy Loss: After absorbing energy from the Sun, the Earth emits heat from its surface into the atmosphere through longwave terrestrial radiation.
- Energy Path: Within the energy budget, 23 percent of the solar energy absorbed by the Earth is lost through direct longwave outgoing terrestrial radiation.
- Some of this radiation (6 percent) is absorbed by the atmosphere, while 17 percent escapes directly into space.
- Energy Utilisation: Approximately 9 percent of the terrestrial energy is allocated to processes such as convection and turbulence, while 19 percent is employed in the evaporation process, contributing latent heat of condensation to the atmosphere.
- Overall Energy Distribution: The atmosphere reradiates the total energy it receives from the Sun (14 percent) and the Earth’s surface (34 percent) back into space through various mechanisms.
The Complexity of Earth’s Energy Balance
- Counter-Radiation:
- A more comprehensive model of the Earth’s energy balance takes into account counter-radiation.
- The reradiation of terrestrial energy back to the Earth’s surface and its subsequent release into the atmosphere and space are integral components of the heat/energy budget of the Earth and the atmosphere.
- Green House Effect
-
- In this process, a portion of the heat radiated from the Earth is redirected back to the Earth’s surface by water vapour and atmospheric carbon dioxide.
- This mechanism, known as the greenhouse effect, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the relatively warmer temperatures of the lower atmosphere and the Earth’s surface.
- The reradiation of terrestrial energy back to the Earth’s surface and its subsequent release into the atmosphere and space are integral components of the heat/energy budget of the Earth and the atmosphere.
Heat Budget: Significance in Earth’s Energy Budget
- Comprehensive Understanding: The Earth’s heat budget provides invaluable insights into the Earth’s climate and the underlying processes that govern it.
- This understanding is vital for comprehending weather patterns, climate change, and the regulation of global temperatures.
- Energy Redistribution: The heat budget illustrates the way in which energy is distributed across the planet, influencing weather patterns, ocean currents, and climate zones.
- It also underscores the importance of maintaining a delicate balance to ensure the stability of our environment.
- Renewable Energy: The insights gained from the heat budget also have practical applications in the field of renewable energy.
- Solar panels, for instance, are designed to capture and convert incoming solar radiation into electricity, harnessing the very energy that drives our planet.
- Climate Science: The heat budget is at the core of climate science, helping researchers model and predict climate changes, assess the impact of greenhouse gases on global temperatures, and develop strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Complex Systems: Recognizing the complexity of the Earth’s heat budget is vital for addressing global challenges such as climate change.
- As we strive to preserve the delicate balance of energy within our planet, understanding these complex systems becomes paramount for the future of our environment and our species.
The Earth’s heat budget is an intricate and dynamic system, encapsulating the energy exchanges between the Earth’s surface, the atmosphere, and the vast expanse of space. It underscores the pivotal roles played by solar radiation and longwave terrestrial radiation in shaping the Earth’s climate, and the inclusion of counter-radiation in the model adds layers of complexity to this already intricate system.
Conclusion
The Earth’s heat budget guides our understanding of climate, influences weather, aids renewable energy, and is crucial for climate science. Preserving this balance is key to addressing climate change and ensuring a sustainable future.

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program