Judicial activism refers to the proactive role of the judiciary in protecting citizens’ rights and ensuring justice. It emerged in the United States in 1947 and was later adopted in India by influential judges in the 1970s. This concept empowers judges to interpret laws flexibly, often stepping in when the legislative or executive branches fail to uphold their duties. Judicial activism aims to address societal issues and safeguard constitutional values.
Judicial Activism in India
Meaning of Judicial Activism
- Origin of Judicial Activism: The concept of judicial activism was first coined by Arthur Schlesinger Jr. in 1947, originating in the USA.
- In India, the doctrine of judicial activism was introduced in the mid-1970s by Justices V.R. Krishna Iyer, P.N. Bhagwati, O. Chinnappa Reddy, and D.A. Desai.
- Definition of Judicial Activism: The active role of the judiciary in upholding the rights of citizens and preserving the constitutional and legal system of the country is known as judicial activism.
- Proactive Role of the Judiciary: It denotes the proactive role played by the judiciary for the protection of the rights of citizens and promotion of justice in the society.
- Judicial Obligation: It implies that the role of the judiciary is to force the other two organs of the government i.e. legislature and executive to do its constitutional obligation.
- Judicial Dynamism: It is also known as “judicial dynamism”.
- Comparison with Judicial Restraint: It works oppositely compared to “judicial restraint”, which means that the self-control is exercised by the judiciary.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Significance of Judicial Activism
- Exercise of Judicial Power: It is a way of exercising judicial power which motivates judges to depart from normally practised strict adherence to judicial precedent in favour of progressive and new social policies
- Protection and Expansion of Individual Rights: It is the practice to protect or expand individual rights through decisions that move away from established precedent to have constitutional or legislative intent.
- Active Interpretation for Social Betterment: It denotes an active interpretation of earlier legislation made by a judge to enhance the utility of that law for social betterment.
- Philosophy of Judicial Decision-Making: It is a philosophy of judicial decision-making where judges are allowed for their personal views about public policy for guidance to others.
- Evolution of Legal Principles: It helps to evolve new principles, concepts, maxims, formulae and relief to do justice .
- Relation to Public Interest Litigation (PIL): Judicial activism is closely related to the concept of Public Interest Litigation (PIL).
Need for Judicial Activism
- Failure of the Executive and Legislature: The failure of the executive and legislatures to deliver the desired results.
- Rampant Corruption and Human Rights Violations: Rampant corruption and violation of basic human rights through the government agencies.
- Ineffectiveness of the System: It occurs because the entire system has been plagued by ineffectiveness and inactiveness.
- Degradation of Democratic Principles: Due to the misuse and abuse of some of the provisions of the Constitution. The principles of democracy were continuously degrading.
- Judiciary’s Role in Preventing Democracy’s Compromise: In such a scenario, the judiciary was forced to play an active role.
- It was possible only through an institution like judiciary which is vested with powers to correct the various wrongs in society.
- In order to prevent the compromise of democracy, the Supreme Court and High Courts took the responsibility of solving these problems.
Manifestation of Judicial Activism
- Through Judicial Review
- Through Public Interest Litigation
- Through Constitutional Interpretation
- Through Access to international statutes for ensuring constitutional rights
Cases Associated with Judicial Activism
- A.K. Gopalan v. State of Madras (1950)
- I. C. Golaknath & Ors vs State Of Punjab & Anrs. (1967)
- Kesavananda Bharati case (1973)
- Hussainara Khatoon (I) v. State of Bihar (1979)
- Sheela Barse v. State of Maharashtra (1983)
Judicial Review and Judicial Activism

- Differences Between Judicial Review and Judicial Activism: The concept of judicial review and judicial activism seems closely related to each other, but there are certain differences between them which we can see from the following table.
| Basis | Judicial Review | Judicial Activism |
| Definition |
|
|
| Goals |
|
|
| Intent |
|
|
| Power |
|
|
| Example |
|
|
Justification of Judicial Activism
- Reasons for Judicial Activism According to Dr. B.L. Wadehra: As per Dr. B.L. Wadehra, judicial activism happens due to the following reasons:
- Due to the collapse of the responsible government
- The citizens expect protection of their rights and freedoms from the judiciary
- The judges encourages the Public Interest Litigation and relaxing the principles of ‘Locus Standi’ to participate in the social reforms
- Instances of Judicial Overreach According to Subhash Kashyap: Similarly, Subhash Kashyap finds out certain events which happens when the judiciary overstep from its normal jurisdiction and intervene in areas which falls under the domain of the legislature and the executive
- Legislature fails to discharge its responsibilities.
- In the event of a ‘hung’ legislature when the government is unable to take decisions on certain crucial matters due to political considerations.
- Political unwillingness to take honest and hard decisions.
- When legislature and executive fails to protect the basic rights of citizens, like the right to live a decent life
- When the court of law is misused by a strong authoritarian parliamentary party government
- Also when the courts become victims of weaknesses of craze for populism and publicity.
- Judicial Activism According to Dr. Vandana: According to Dr. Vandana, judicial activism can be seen from the following aspects,
- Enhancement of the right to be heard in the administrative procedure.
- No limitation for Excessive delegation
- Judicial control over discretionary powers.
- Judicial review over the administration.
- Encouragement of Open government
- Excessive use of power of Contempt.
- Exercise of jurisdiction when non-exist.
- Excessive interpretation of rules in its search to achieve economic, social and educational objectives.
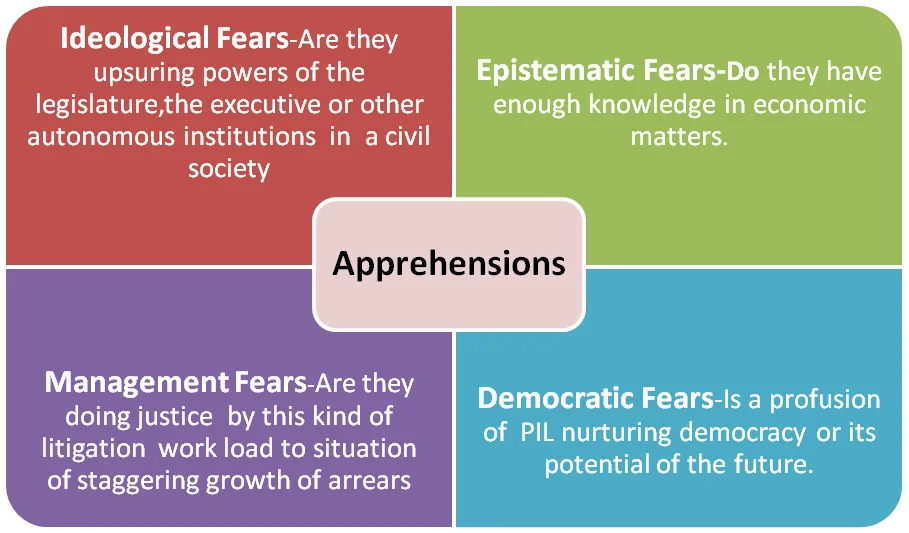
Apprehension of Judicial Activism
JUDICIAL ACTIVISM VS JUDICIAL RESTRAINT

| Judicial Activism | Judicial Restraint |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Judicial Overreach
- Definition of Judicial Overreach: Judicial overreach refers to instances where the judiciary, beyond its constitutional mandate, becomes excessively active in policymaking or infringes upon the domain of the executive and legislative branches.
- Thin Line Between Judicial Activism and Judicial Overreach: There is a thin line dividing judicial activism and judicial overreach.
- When Judicial Activism goes overboard, and becomes Judicial Adventurism, it is referred to as Judicial Overreach.
- Causes of Judicial Overreach: The direct effect of legislative and executive negligence or inability is “judicial overreach”.
Impact of Judicial Overreach
- Threat to the Doctrine of Separation of Powers: It threatens the doctrine of separation of powers which undermines the spirit of the constitution.
- Lack of Harmony Between Legislature and Judiciary: There is a lack of harmony between legislature and judiciary and an impression on the public of inaction by the legislature.
- Need for Expertise in Certain Cases: In certain cases like that of environmental, ethical, political, expert knowledge is required which the judiciary might not possess.
- Risks of Judgements Without Expertise: If it renders judgement while having no experience in these domains, then it not only undermines expert knowledge but also can prove harmful to the country.
Examples of Judicial overreach
- Censorship of the Film Jolly LLB II: The film portrayed the legal profession as a joke, making it an act of contempt and provocation
- The Supreme Court Banned the Sale of Liquor: On a PIL about road safety, the Supreme Court banned the Sale of Liquor, at retail shops, restaurants, bars within 500m of any national or state highway.
Supreme Court’s Call for Judicial Restraint
- Reminder for Judicial Restraint: The Supreme Court has itself reminded other courts, in 2007, to practise Judicial restraint.
- Importance of Modesty and Humility: It stated “Judges must know their limits and must try not to run the government. They must have modesty and humility, and not behave like emperors.”
- Caution Against Judicial Overreach: Further, it said, “In the name of judicial activism, judges cannot cross their limits and try to take over states which belong to another organ of the state”.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Judicial activism plays a vital role in promoting justice and protecting individual rights in India.
- While it empowers the judiciary to intervene when other branches of government fail, it also raises concerns about judicial overreach.
- Striking a balance between activism and restraint is essential to maintain the integrity of the judicial system and uphold the principles of democracy.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| PIL Full Form- Public Interest Litigation | High Courts in India |
| Judicial Activism: Empowering Rights & Impact on Democracy | Supreme Court |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program









