Warren Hastings |
Warren Hastings: Bengal’s Governor-General and Architect of Change
Warren Hastings was chosen by the Company to serve as Governor of Fort William in 1772. By virtue of the Regulating Act of 1773, he was elevated to the position of Governor of Bengal and the first Governor General of Bengal. Warren Hasting studied numerous languages, including Bengali and Persian, and has an Orientalist perspective. The Rohilla War, the First Anglo-Maratha War, and the Second Anglo-Mysore War all took place under his rule. In 1758, Warren was accepted as a British Resident in the city of Murshidabad. He was given the duties of a representative in Bengal. However, the East India Company at the time was in charge of Bengal. They were therefore charged with distributing the new Nawab regulations. He sent orders on behalf of Robert Clive.
Warren Hastings: Catalyst for India’s Independence Reforms
Warren Hastings oversaw a number of major reforms that later helped India become an independent nation. Some of the significant reforms that took place at this time include the following:
Warren Hastings: Architect of Administrative Overhaul in India
The Dual System, which Sir Robert Clive had instituted, was abolished in large part because of Warren Hastings. The following reforms were undertaken:
- In 1772, the Dual system was abolished. Warren Hasting also stopped the 26 lakhs payment made to the Mughal Emperor each year.
- Warren Hasting founded the first Supreme Court of India in Calcutta based upon English law.
- During his reign, the Regulating Act of 1773 was passed. The Regulating Act of 1781, split the Supreme Court’s authority in Calcutta between the Government and that institution.
- Together with Sir William Jones, Warren Hasting founded the Asiatic Society of Bengal in 1784.
- With the passage of Pitt’s India Act of 1784, the Governor General’s Executive Council’s size was increased from three to four.
- The Board of Control was also established in England.
- In 1772, Calcutta was designated as Bengal’s capital.
Warren Hastings: Revolutionizing Revenue Systems in Bengal
A Board of Revenue was established in Calcutta to collect the taxes. In the year 1772, Calcutta officially took over as the capital of Bengal. Additionally, the treasury was moved to the new capital from Murshidabad. The following reforms were undertaken:
- Each district was assigned an English Collector.
- The Accountant General was appointed.
- Board of Revenue:
- Instead of selling the lands at auction for just one year, it did it for five years to determine their true worth. Priority was granted to zamindars in the auction.
- It is also referred to as the Quinquennial System, the Five-Year Settlement, or Pachashala Bandobast. The system was still ineffective.
- After the five-year settlement period expired, Hastings switched back to the annual settlement system (Salana Bandobast).
Warren Hastings’ Judicial Overhaul: Reforms and Reorganization
When Warren Hastings was in charge, there were numerous judicial reforms. The first step was the abolition of the zamindars’ judicial authority. The following reforms were undertaken:
- The court system was reorganised by Warren Hastings.
- Sadar Diwani Adalat: The highest civil court of appeals and it was presided over by the governor-general and two judges chosen from his council.
- Sadar Nizamat Adalat: The highest criminal appeals court was presided over by an Indian judge who had been chosen by the Governor General in Council.
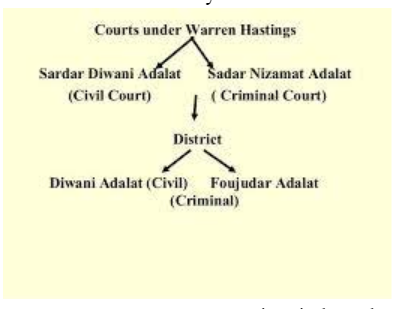
- To assist the judges, experts in Hindu and Muslim law were hired.
Warren Hastings: Leading Battles and Controversies
| Wars | About |
| First Anglo Maratha War (1775-1782) |
|
| Second Anglo Mysore War (1780-1784) |
|
| Rohilla War (1774) |
|
|
#PW-OnlyIAS Edge |
|
Conclusion
Between 1787 and 1795, attempts were made to remove Warren Hastings from office due to his misdeeds while serving as the governor of Kolkata (then Calcutta). He was accused of being personally corrupt and of poor management. The British Parliament’s attempt to remove Warren Hastings from office in 1788 proved unsuccessful. Hastings was issued a ticket for misconduct while he was a resident of Calcutta. It was related to bad management and personal vice. The probe truly happened, and it turned up a wide range of conversations about the East India Company’s role and growing the Indian empire. The trial for Warren Hastings was continued for seven years. Hastings received a resoundingly unanimous verdict of not guilty.
Warren Hastings Faqs
Q1. What was Warren Hastings’s activity in India?
Ans. The first Governor-General of Bengal from 1774 until his resignation in 1785 was Warren Hastings (1732–1818), who also served as the Presidency of Fort William’s first Governor in Bengal in 1772.
Q2. What made Warren Hastings significant?
Ans. Warren Hastings, a statesman, served as the first governor-general of British India from 1732 to 1818. He established the civil administration system that was the foundation for the security and prosperity of Anglo-India.
Q3. Which policy did Warren Hastings abolish?
Ans. In 1772, Warren Hastings abolished the Dual system of government.
Q4. Why was Hastings removed from office?
Ans. Hastings was accused of misbehaviour while he was living in Calcutta, particularly in regard to poor management and personal corruption.
Q5. Who was India’s greatest viceroy?
Ans. Lord Ripon served as a viceroy in India under British rule from 1880 and 1884. He is recognised as the most liberal viceroy and is also referred to as the “Good Viceroy of India.”
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program










