The Parliament enacted the Legal Services Authorities Act in 1987, which came into force on 9th November 1995. Its aim is to establish a nationwide uniform network to provide free and competent legal services to the weaker sections of society based on equal opportunity.
The National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) was constituted under the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987. NALSA helps monitor and evaluate the implementation of legal aid programs and lays down policies and principles for making legal services available under the Act.
Objectives of NALSA
Provide free legal aid and advice: Legal aid is available to eligible individuals who cannot afford legal services.
- Spread legal awareness: NALSA conducts awareness campaigns to educate the public about their legal rights and duties.
- Organize Lok Adalats: Lok Adalats are organized for the amicable settlement of disputes.
- Promote Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) mechanisms: These include arbitration, conciliation, mediation, and judicial settlements, including those through Lok Adalats.
- Provide compensation to victims of crime: Victims of crimes, especially vulnerable groups, are provided compensation.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Constitutional Provisions
Article 39A: Mandates free legal aid for the poor and weaker sections of society to ensure equal justice for all.
- Articles 14 and 22(1): Obligate the State to ensure equality before the law and establish a legal system that promotes justice based on equal opportunities.
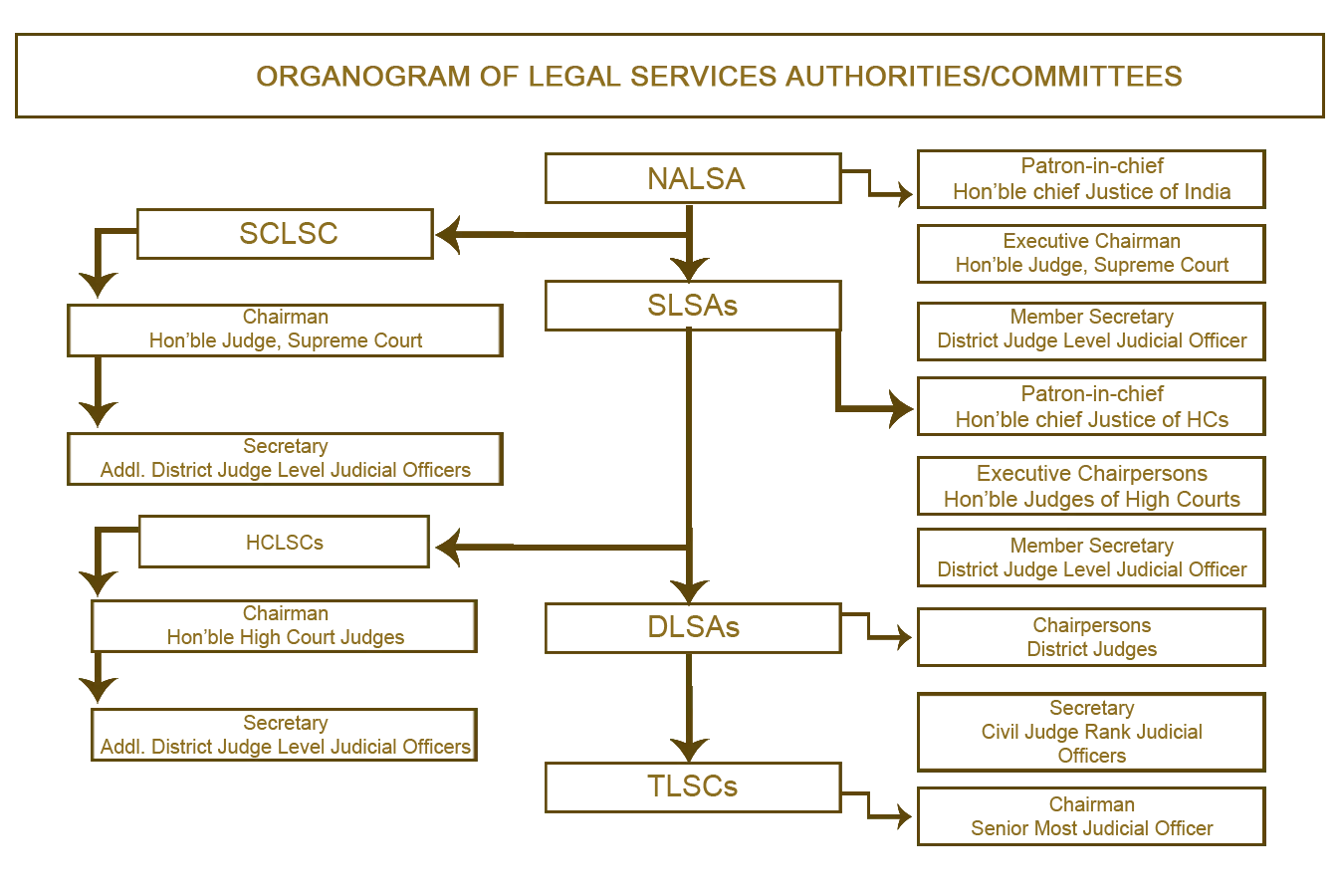
Legal Service Institutions at Various Levels
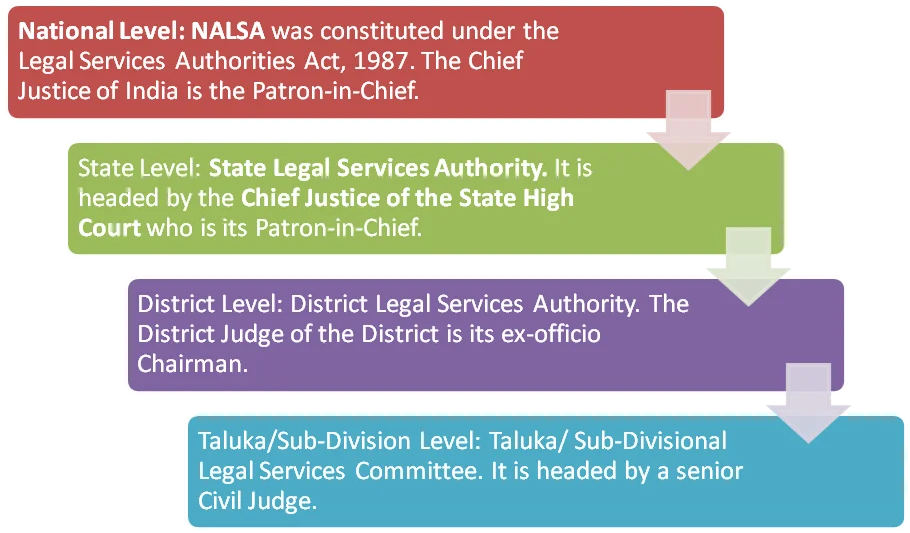
NALSA operates at multiple levels
- National, State, District, and Taluka levels: Legal services are provided at all levels to ensure easy access to justice across the country.
- Supreme Court Legal Services Committee: Administers legal services related to cases before the Supreme Court of India.
- State Legal Services Authorities (SLSA): NALSA frames policies and guidelines for SLSAs to implement legal services across states. They perform functions such as:
- Providing free and competent legal services to eligible persons.
- Organizing Lok Adalats for amicable dispute resolution.
- Conducting legal awareness camps, especially in rural areas.
Eligibility for Free Legal Services
Individuals eligible for free legal services include
- Women and children
- Members of SC/ST communities
- Victims of mass disaster, violence, floods, or droughts
- Disabled persons
- Industrial workmen
- Persons in custody
- Victims of human trafficking or beggars
- Persons with an annual income below ₹1 lakh (For the Supreme Court Legal Services Committee, this limit is ₹1.25 lakh).
Services Under Free Legal Aid
NALSA provides services such as
- Legal representation in court: For eligible persons who cannot afford a lawyer.
- Counseling and legal advice: Individuals can seek advice regarding their legal problems.
- Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR): Helping parties resolve disputes through mediation, conciliation, and Lok Adalats.

Initiatives for Legal Services
- Legal Service Mobile App: Launched by NALSA to enable equitable access to justice. The app helps citizens seek legal aid easily and provides access to legal information.
- DISHA (Designing Innovative Solutions for Holistic Access to Justice Scheme): Launched by the Department of Justice for a comprehensive and systemic solution for access to justice. This scheme (2021–2026) includes:
- Tele-law: Connects legal aid seekers with lawyers via video conferencing or telephone.
- Nyaya Bandhu: Pro bono legal services by advocates.
- Nyaya Mitra: Volunteers assist individuals in navigating the legal process.
Various NALSA Schemes |
|
Campaigns and Programs |
|
Roles and Functions of NALSA |
|
Challenges Faced by NALSA
- Lack of training: Legal aid professionals are not consistently well-trained, impacting the quality of services.
- Low beneficiary engagement: According to the India Justice Report 2019, the number of actual beneficiaries is low compared to the potential.
- Uneven organizational practices: This has led to variations in the effectiveness of legal services across the country.
- Gender parity: The lack of gender representation among legal aid providers affects assistance to women victims.
- Inadequate monitoring: There is no effective mechanism to monitor customer satisfaction, financial management, or performance of legal services.
- Awareness: There remains a lack of awareness among the general public about their right to free legal services, which hampers the full potential of NALSA’s reach.
Way Forward
- Improved training: Enhancing the training of legal aid lawyers and para-legal volunteers is essential to improve service delivery.
- Awareness programs: Increasing awareness about free legal aid services through campaigns, especially in rural areas, is crucial to improve reach and participation.
- Gender inclusivity: Ensuring gender parity in legal aid services to address the unique challenges faced by women victims.
- Better monitoring systems: Developing mechanisms to monitor the satisfaction of legal aid beneficiaries and ensuring optimal resource management.
- Collaboration with civil society: Strengthening partnerships with NGOs and other organizations can broaden the scope and impact of legal aid services.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Must Read | |
| Current Affairs | Editorial Analysis |
| Upsc Notes | Upsc Blogs |
| NCERT Notes | Free Main Answer Writing |
Conclusion
Assistance of legal services is not a charity but a civic duty and a right enshrined in the Constitution of India. NALSA has played a vital role in providing free legal aid, organizing Lok Adalats, conducting legal awareness programs, and launching various schemes. However, challenges such as low beneficiary outreach, training deficiencies, and gender disparity need to be addressed to strengthen NALSA’s effectiveness in delivering justice to all sections of society.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| Lok Adalats | Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR)Sustainability |
| NALSA | Supreme Court of India |

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program










