Introduction: The Extraordinary Journey from the Big Bang to Our Universe
The origin of the universe is a remarkable mystery that scientists and astronomers have been exploring for many years. It all started with a colossal explosion called the Big Bang, which created everything we see today, including galaxies, stars, and planets.
This explosion happened around 13.8 billion years ago and set the stage for the incredible universe we know today. Understanding this cosmic birth event is a central goal of cosmology and helps us unravel the story of our existence.
The Vast Universe: Exploring Space, Time, and Cosmic Theories
The universe comprises the entirety of space, time, and everything within them, encompassing planets, stars, galaxies, and all forms of matter and energy.
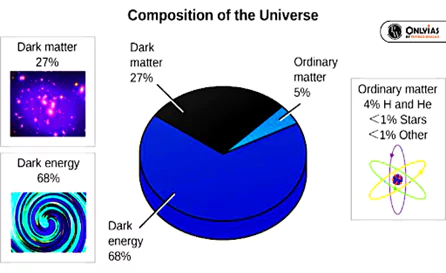
- It is commonly described as “the sum total of all that is,” encompassing all that exists, has ever existed, and will exist in the future.
- Size and Scale: The universe is at present, is said to possess about, 2 trillion galaxies, each hosting billions of stars.
- Three prevalent theories attempt to elucidate the origin and development of the universe:
- The Steady-State Theory
- The Big Bang Theory
- The Pulsating Theory
The Rise and Fall of the Steady-State Theory in Cosmology
- In the 1940s, Sir Fred Hoyle and others developed a mathematical model of the universe suggesting that the universe is eternal, unchanging, and maintains a constant density as it continuously creates new matter.
- Key Ideas:
- Eternal Universe: It posited that the universe had no beginning and would continue infinitely into the future, without a single moment of creation.
- Continuous Matter Creation: To maintain a constant density, the theory proposed the spontaneous creation of matter throughout the universe, filling the space left by the receding galaxies.
- Contradiction with Observations: Over time, observational evidence, such as the cosmic microwave background radiation and the discovery of the expanding universe, contradicted the Steady-State Theory.
- Decline and Rejection:
- The discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation in the 1960s provided strong evidence in favor of the Big Bang Theory, leading to the decline and eventual rejection of the Steady-State Theory.
The Big Bang Theory: Exploring the Explosive Birth and Evolution of the Universe
The Big Bang Theory, born from Edwin Hubble’s discoveries, postulates a hot, dense singularity’s explosive birth, fueling the continuous expansion of our universe, reshaping cosmology’s foundations
- Origin: This theory originated in 1929 when Edwin Hubble discovered that everything in the universe is moving away from everything else.
- It proposes that the universe began as a hot, dense, and incredibly small singularity approximately 13.8 billion years ago and has been expanding ever since.
- The Singular Atom: At the universe’s inception, all matter was concentrated into an unimaginably small and dense “singular atom,” occupying an infinitesimal volume with infinite temperature and density.
- The Big Bang’s Explosive Genesis: Approximately 13.7 billion years ago, the universe’s explosive birth, known as the Big Bang theory, initiated a colossal expansion, propelling matter and energy into existence.
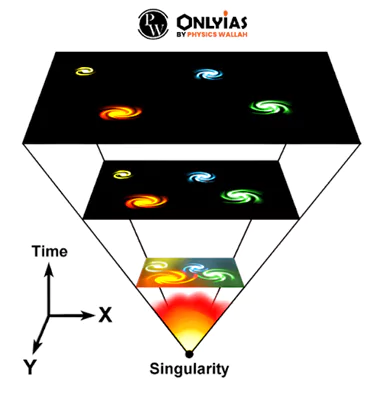
- Continuous Cosmic Expansion: The expansion, which commenced at the Big Bang, persists to this day. Initially, energy transformed into matter, with a rapid expansion phase shortly after the event.
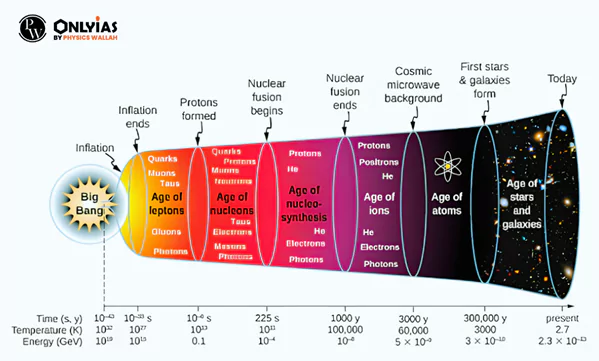
- Formation of the First Atom: Within the first three minutes after the Big Bang, the universe witnessed the birth of the first atoms, marking a crucial phase in its evolution.
- From Scorching Heat to Atomic Matter: Within 300,000 years following the Big Bang, temperatures cooled to 4,500 Kelvin, allowing the emergence of atomic matter and rendering the universe transparent.
Supporting Evidence:
- Redshift of Galaxies: Observations show that galaxies are moving away from us, with more distant galaxies exhibiting greater redshifts in their light spectra.
- Abundance of Light Elements: The theory accurately predicts the abundances of light elements like hydrogen and helium in the universe.
- Large-Scale Structure: The distribution of galaxies and the cosmic microwave background match the predictions of the Big Bang Theory.
Impact:
- The Big Bang Theory has become the cornerstone of modern cosmology and has revolutionized our understanding of the universe’s history, structure, and evolution.
- It addresses the cosmic microwave background, cosmic inflation, dark matter, and dark energy, among other key cosmological concepts.
Continual Study:
- Ongoing observations and research continue to refine our understanding of the universe’s early moments, expansion rate, and ultimate fate, ensuring that the Big Bang Theory remains a dynamic and evolving field of study.
Exploring Galaxies: Diverse Cosmic Realms in the Universe
| Galaxies are immense systems comprising stars, planets, gas, dust, and dark matter bound together by gravity. These cosmic islands come in various shapes and sizes, each hosting its stellar inhabitants.
Diversity of Galaxies:
|
The Pulsating Universe: Exploring the Hypothesis of Cosmic Oscillation
- This theory is a hypothesis suggesting that the universe undergoes a cycle of expansion and contraction, with periods of expansion followed by periods of contraction, akin to cosmic “breathing.”
- Oscillating Universe: In this model, the universe experiences repetitive cycles of expansion, reaching a maximum size, and then contracting back to a tiny, dense state.
- Infinite Existence: The Pulsating Theory implies that the universe has no definitive beginning or end but rather exists infinitely, with cycles repeating over eternity.
- Cosmic Compression: During the contraction phase, all matter and energy in the universe are compressed into a singularity, similar to the conditions before a new expansion.
- Scientific Reception:
- While the Pulsating Theory offers an alternative to the standard Big Bang model.
- It lacks substantial empirical evidence and faces challenges related to entropy and observational data.
- Contemporary Exploration: Ongoing research explores the possibility of an oscillating universe and the implications it may have for understanding the ultimate fate and nature of our cosmic domain.
The Cosmic Journey: Tracing the Evolution of the Universe Through Time
| Cosmic Event | Description |
| Primordial State |
|
| The Big Bang Theory |
|
| Cosmic Expansion |
|
| Formation of Fundamental Forces |
|
| Formation of First Atoms |
|
| Birth of Stars and Galaxies |
|
| Life’s Emergence on Earth |
|
| Continued Cosmic Exploration |
|
The Big Crunch: Exploring the Hypothetical Fate of the Contracting Universe
The Big Crunch is a theoretical scenario that suggests a potential fate for the universe, wherein the ongoing cosmic expansion eventually reverses, leading to the collapse and ultimate contraction of the entire universe.
Key Concepts: From the Big Crunch to Heat Death
- Reversal of Cosmic Expansion: In the Big Crunch hypothesis, the expansion of the universe, initiated by the Big Bang theory, slows down and eventually halts.
- Gravitational forces then take over, causing the universe to contract.
- Contraction to a Singularity: As the universe contracts, all matter and energy are compressed into an extremely hot and dense state, similar to the initial singularity of the Big Bang theory.
- Current Understanding:While the Big Crunch was once considered a possible fate for the universe, recent observations of the accelerating cosmic expansion have led to the development of the “Big Freeze” or “Heat Death” scenario as a more likely outcome.
- Heat Death vs. Big Crunch: The Heat Death hypothesis suggests that the universe will continue to expand indefinitely, gradually cooling down until it reaches a state of maximum entropy and minimal energy, resulting in a “cold” and uniform cosmos.
- Continual Study: Ongoing research and observations in cosmology aim to refine our understanding of the universe’s fate, whether it leads to a Big Crunch, Heat Death, or another scenario, as well as the role of dark energy in shaping its destiny.

 GS Foundation
GS Foundation Optional Course
Optional Course Combo Courses
Combo Courses Degree Program
Degree Program










